Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps
- 3.1 The Language of Symbols: Decoding the Visual Landscape
- 3.2 The Key to Understanding: The Map Legend
- 3.3 Beyond Basic Representation: The Importance of Symbol Variation
- 3.4 The Power of Effective Symbol Design
- 3.5 Navigating Complexity: The Role of Symbols and Keys in Specialized Maps
- 3.6 FAQs: Demystifying the World of Symbols and Keys
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Symbols and Keys
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps

Maps, in their essence, are visual representations of the world, whether it be a vast continent, a bustling city, or a quaint neighborhood. Their ability to condense intricate spatial information into a comprehensible format relies heavily on the use of symbols and keys. These seemingly simple elements are the cornerstone of map comprehension, transforming abstract geographical data into readily interpretable information.
The Language of Symbols: Decoding the Visual Landscape
Symbols, the visual language of maps, are iconic representations of real-world features. They range from simple geometric shapes to intricate illustrations, each carefully designed to convey specific information.
Common Map Symbols:
- Points: Dots, stars, and crosses mark locations of interest, such as cities, landmarks, or points of historical significance.
- Lines: Straight or curved lines depict roads, rivers, boundaries, or other linear features.
- Areas: Colors, patterns, or textures define specific regions, indicating land use, elevation, or other spatial characteristics.
Symbol Types:
- Pictograms: These are highly stylized illustrations that resemble the object they represent, like a tree for a forest or a house for a residential area.
- Geometric Symbols: Simple shapes like circles, squares, or triangles are used to represent various features, often accompanied by text labels for clarity.
- Abstract Symbols: These are abstract designs that hold specific meaning within the context of the map, often assigned to represent specific types of infrastructure or land use.
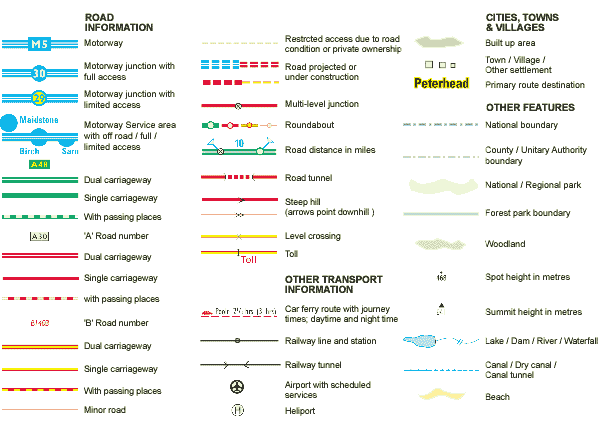
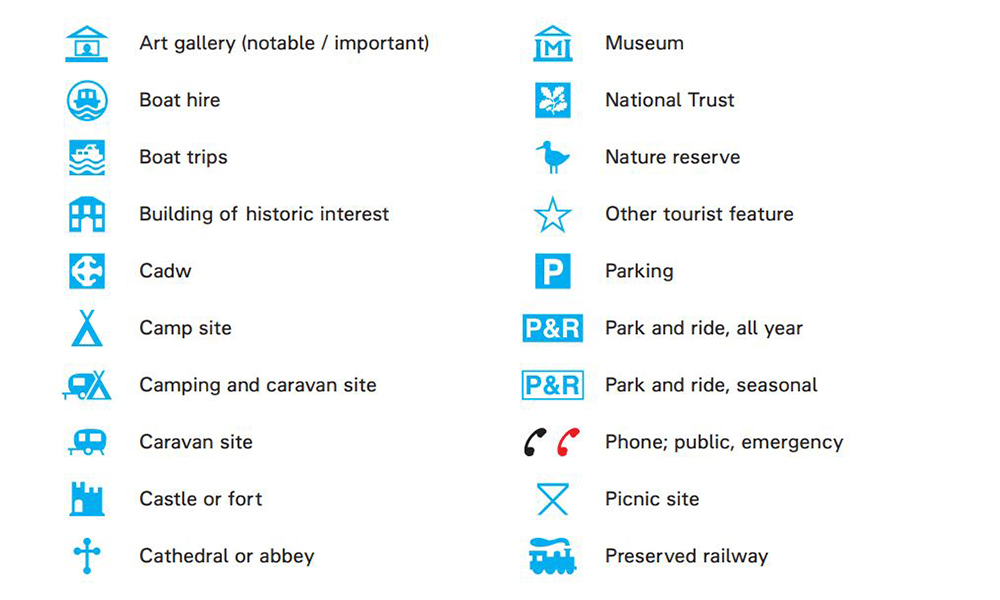
The Key to Understanding: The Map Legend
The map key, also known as the legend, acts as a dictionary for the map’s symbols. It provides a visual glossary, linking each symbol to its corresponding real-world feature. This crucial element ensures that users can accurately interpret the map’s information, regardless of their prior knowledge.
Components of a Map Key:
- Symbol: The visual representation used on the map.
- Label: A brief description of the feature represented by the symbol.
- Color, Pattern, or Texture: If applicable, the key specifies the color, pattern, or texture used to represent the feature on the map.
Beyond Basic Representation: The Importance of Symbol Variation
Maps often utilize variations in symbol size, color, or shape to convey additional information. For example, a larger city on a map might be represented by a larger point symbol, while a road’s width might be indicated by the thickness of the line representing it. This variation adds a layer of complexity and detail, enhancing the map’s ability to communicate nuanced information.
The Power of Effective Symbol Design
The effectiveness of map symbols lies in their clarity and memorability. A well-designed symbol should be easily recognizable, visually distinct from other symbols, and intuitively associated with the feature it represents.
Principles of Effective Symbol Design:
- Simplicity: Symbols should be visually simple and easily recognizable.
- Distinctiveness: Each symbol should be unique and easily distinguishable from others on the map.
- Relevance: The symbol should be visually related to the feature it represents, fostering intuitive understanding.
- Consistency: Symbols should be consistent in their design and application across the map.
Navigating Complexity: The Role of Symbols and Keys in Specialized Maps
Symbols and keys are not limited to general-purpose maps. They play a crucial role in specialized maps used in various fields, including:
- Navigation Maps: These maps rely heavily on symbols to represent roads, landmarks, and points of interest, aiding in wayfinding and route planning.
- Topographical Maps: Symbols indicate elevation, terrain features, and land use, providing valuable information for hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts.
- Geological Maps: Symbols depict rock types, geological formations, and mineral deposits, aiding in geological research and resource exploration.
- Weather Maps: Symbols represent weather phenomena like precipitation, temperature, and wind direction, enabling meteorologists to analyze and predict weather patterns.
FAQs: Demystifying the World of Symbols and Keys
Q: Why are symbols used on maps?
A: Symbols provide a concise and visually appealing way to represent various features on a map, making it easier to understand and interpret spatial information.
Q: How do I know what a symbol means on a map?
A: The map key, or legend, provides a detailed explanation of each symbol used on the map, linking the visual representation to the real-world feature it represents.
Q: What makes a good map symbol?
A: A good map symbol is simple, distinctive, relevant, and consistent. It should be easily recognizable, visually distinct from other symbols, and intuitively associated with the feature it represents.
Q: Can symbols be used to convey more than just basic information?
A: Yes, symbols can be varied in size, color, or shape to represent additional information, such as the size of a city, the width of a road, or the elevation of a mountain.
Q: Are symbols and keys only used in traditional paper maps?
A: No, symbols and keys are also essential components of digital maps and online mapping platforms, ensuring consistency and clarity in the presentation of spatial data.
Tips for Effective Map Interpretation
- Start with the key: Before delving into the map itself, carefully review the key to understand the meaning of each symbol.
- Look for patterns: Pay attention to variations in symbol size, color, or shape, as they often convey additional information.
- Consider the context: The map’s scale and purpose can influence the choice of symbols and the level of detail provided.
- Use multiple sources: If possible, consult different maps or resources to cross-reference information and ensure accurate interpretation.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Symbols and Keys
Symbols and keys are the foundation of map comprehension, enabling us to navigate the world around us. They transform complex spatial data into accessible and interpretable information, empowering us to understand our surroundings, plan our journeys, and make informed decisions. As technology advances, the methods of map creation and presentation may evolve, but the fundamental role of symbols and keys in conveying spatial information will remain vital. They are the invisible language that unlocks the power of maps, connecting us to the world in a way that transcends words.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Symbols and Keys: A Guide to Navigating Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
