Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Anatomy of a Process Map
- 3.2 The Diverse Landscape of Process Map Samples
- 3.3 The Value Proposition of Process Map Samples
- 3.4 Exploring Process Map Samples: A Practical Guide
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide
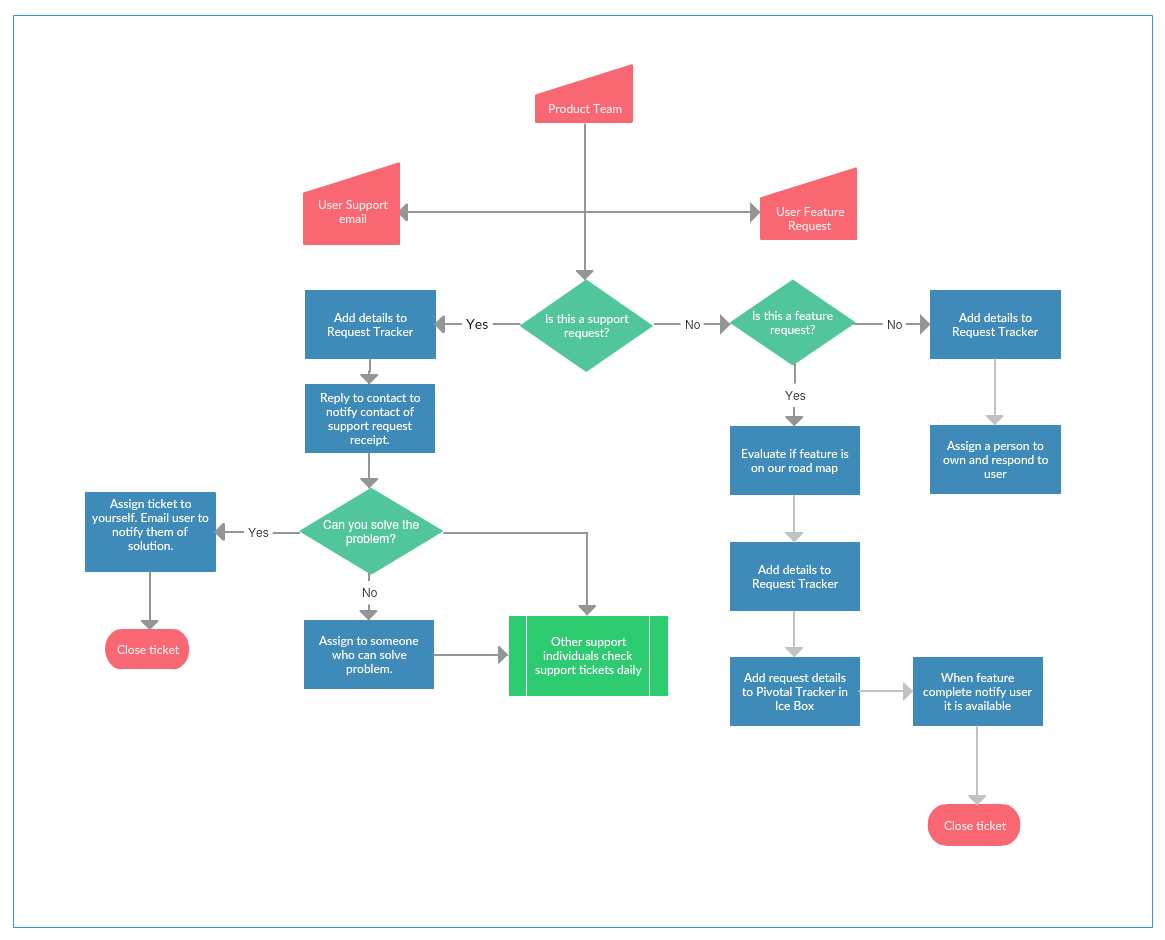
Process mapping is a visual representation of a sequence of events or activities that constitute a process. It is a powerful tool for analyzing, understanding, and improving the efficiency and effectiveness of any process, whether it’s a business operation, a software development cycle, or a customer service workflow. Process map samples serve as valuable blueprints, offering insights into how different processes are structured and executed, facilitating learning, and inspiring innovation.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Process Map
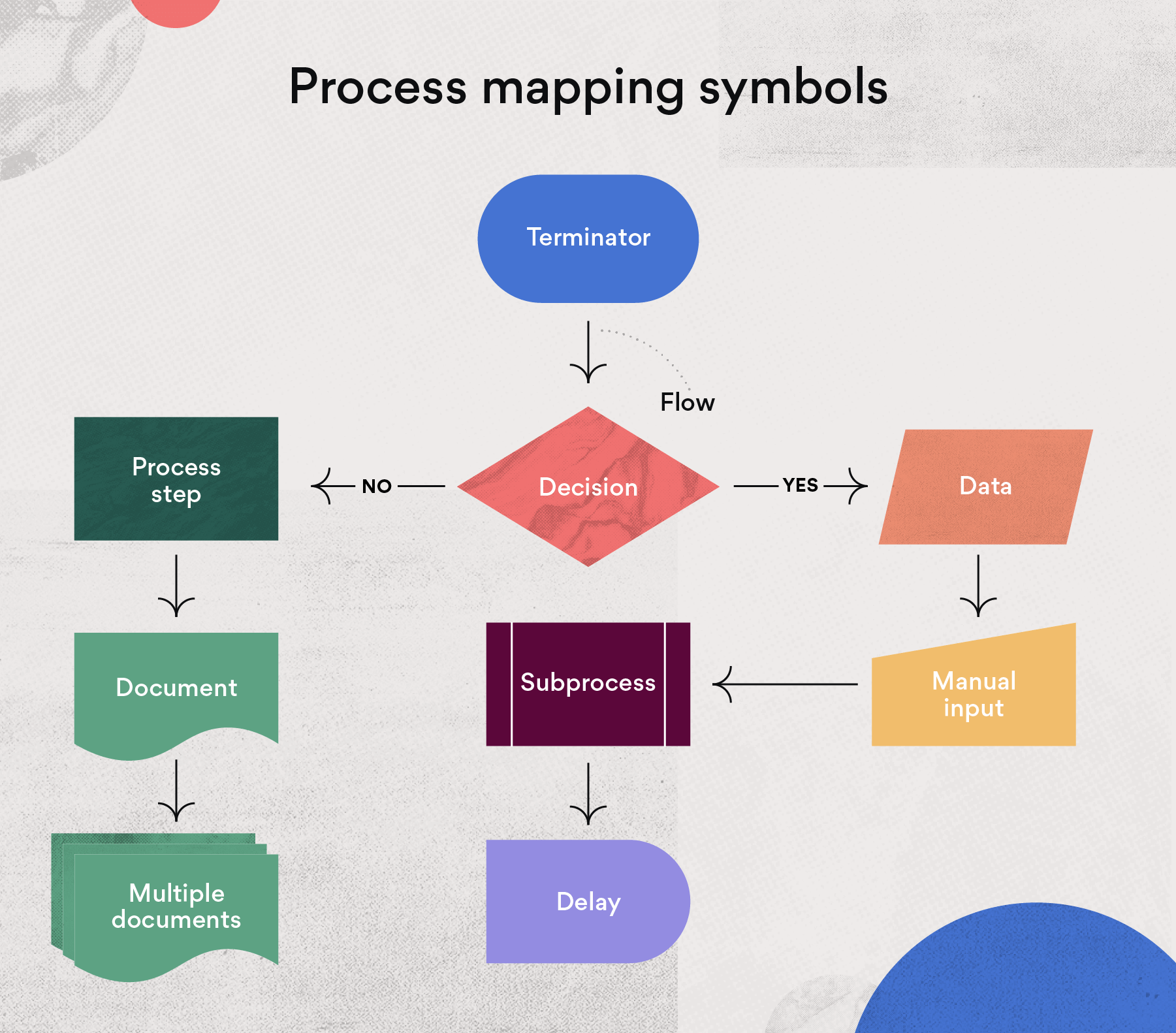
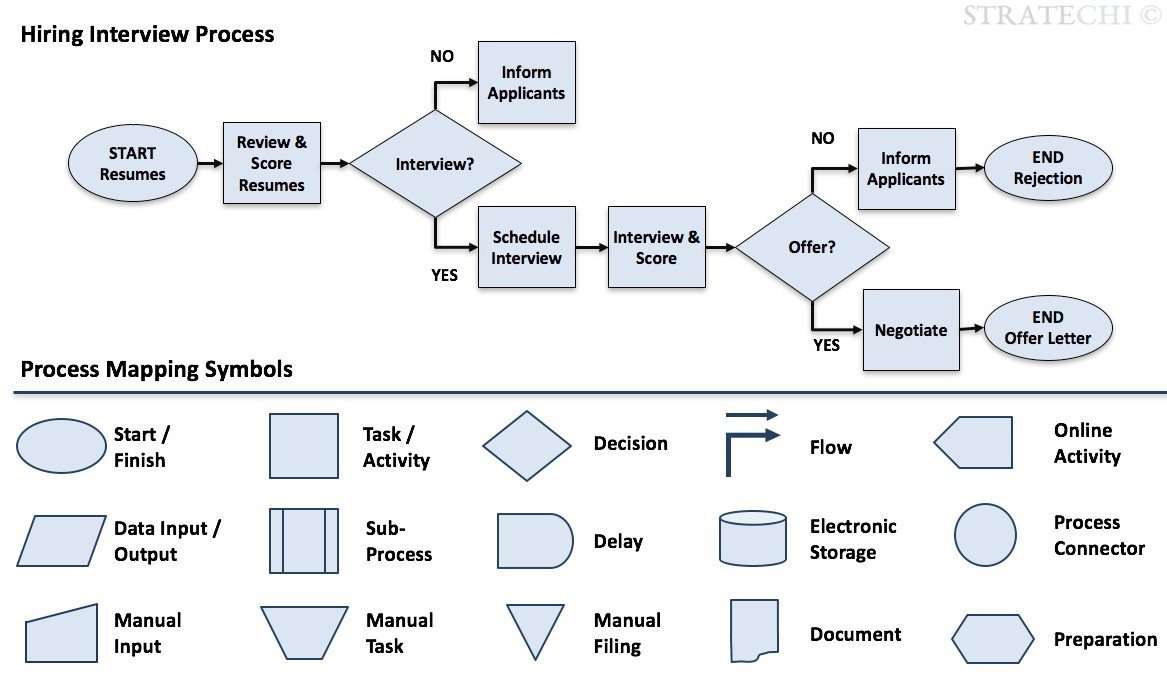
Process maps, also known as flowcharts, typically employ a standardized set of symbols and notations to depict the flow of activities, decision points, and resources involved in a process. Common elements include:
- Start/End: Represents the beginning and end of the process.
- Process Step: Depicts an individual activity or task within the process.
- Decision Point: Indicates a choice or branching point in the process.
- Flow Lines: Connect different elements of the map, showing the sequence of activities.
- Data Input/Output: Represents the information or data entering or leaving a process step.
- Resources: Depicts the people, equipment, or materials involved in the process.
The Diverse Landscape of Process Map Samples
Process map samples are available in various forms, catering to different industries, purposes, and levels of detail. Some common types include:
1. Basic Process Maps: These maps provide a high-level overview of a process, focusing on the major steps and decision points without delving into intricate details. They are ideal for understanding the overall flow of a process or for communicating it to a wider audience.
2. Detailed Process Maps: These maps offer a more in-depth representation of a process, capturing specific activities, sub-processes, and decision criteria. They are useful for analyzing and improving individual steps within a process, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing resource allocation.
3. Swimlane Process Maps: These maps divide a process into different lanes, each representing a specific role or department involved in the process. This visualization helps to clarify responsibilities, identify potential handoffs, and streamline communication.
4. Cross-Functional Process Maps: These maps illustrate the interactions and dependencies between different departments or teams involved in a process. They are particularly useful for understanding how processes span across organizational boundaries and for identifying opportunities for collaboration and efficiency gains.
5. Value Stream Maps: These maps focus on the flow of value from the customer’s perspective, highlighting activities that add value and those that are non-value-adding. They are helpful for identifying areas of waste and for implementing lean process improvements.
The Value Proposition of Process Map Samples
Process map samples offer a multitude of benefits, making them indispensable tools for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and enhance their performance.
1. Improved Understanding and Communication: Process maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of a process, facilitating understanding among stakeholders, regardless of their technical expertise. They enable effective communication and knowledge sharing, reducing ambiguity and fostering collaboration.
2. Enhanced Process Analysis and Improvement: By visualizing the flow of activities, process maps enable a thorough analysis of the process, identifying potential inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. They provide a framework for implementing process changes, optimizing resource allocation, and streamlining operations.
3. Increased Efficiency and Productivity: By eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing rework, and streamlining workflows, process maps contribute to improved efficiency and productivity. They help to minimize waste, optimize resource utilization, and accelerate cycle times.
4. Better Decision-Making: Process maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the process, enabling data-driven decision-making. They help to identify risks, assess potential impacts of changes, and make informed choices about process improvement initiatives.
5. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By streamlining workflows, reducing errors, and improving communication, process maps can lead to increased customer satisfaction. They help to ensure that processes are designed to meet customer needs and expectations, leading to a more positive customer experience.
6. Reduced Costs: By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving efficiency, process maps can contribute to significant cost savings. They help to minimize the cost of operations, reduce rework, and improve resource utilization.
7. Enhanced Compliance and Risk Management: Process maps can facilitate compliance with industry regulations and standards. They help to identify potential risks, document processes, and ensure that activities are conducted in accordance with established procedures.
Exploring Process Map Samples: A Practical Guide
The following section explores a series of process map samples, highlighting the diverse applications and benefits of this powerful tool.
Example 1: Sales Process Map
This sample process map depicts a typical sales process, from lead generation to order fulfillment. It showcases the key steps involved, including lead qualification, proposal creation, negotiation, order processing, and customer support. This map can be used to identify potential bottlenecks in the sales funnel, optimize the customer experience, and improve overall sales performance.
Example 2: Software Development Process Map
This sample process map illustrates a typical software development process, from requirements gathering to deployment. It highlights the key stages of the development lifecycle, including design, coding, testing, and deployment. This map can be used to track progress, identify dependencies, and ensure that the development process is efficient and effective.
Example 3: Customer Service Process Map
This sample process map depicts a typical customer service process, from initial contact to resolution. It showcases the different channels of communication, the escalation procedures, and the steps involved in resolving customer issues. This map can be used to improve customer service efficiency, reduce resolution times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Example 4: Manufacturing Process Map
This sample process map illustrates a typical manufacturing process, from raw material procurement to finished product delivery. It highlights the various stages of production, including assembly, testing, and packaging. This map can be used to optimize production flow, identify potential bottlenecks, and improve overall manufacturing efficiency.
Example 5: Human Resources Process Map
This sample process map depicts a typical human resources process, from recruitment to employee onboarding. It showcases the key steps involved, including job posting, candidate screening, interviewing, hiring, and onboarding. This map can be used to streamline the recruitment process, improve employee onboarding experience, and reduce administrative burdens.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the key benefits of using process map samples?
A: Process map samples offer numerous benefits, including improved process understanding, enhanced analysis and improvement, increased efficiency and productivity, better decision-making, enhanced customer satisfaction, reduced costs, and improved compliance and risk management.
Q: How can I choose the right process map sample for my needs?
A: Consider the specific process you want to map, the level of detail required, the purpose of the map, and the target audience. There are various types of process maps available, each catering to different needs.
Q: What software tools can I use to create process maps?
A: There are numerous software tools available for creating process maps, including Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, Draw.io, and Creately. These tools offer a range of features and templates, allowing you to create professional and visually appealing process maps.
Q: Can I create my own process map samples?
A: Yes, you can create your own process map samples using software tools or even by hand. The key is to understand the elements of a process map and to use clear and concise language.
Q: How can I ensure that my process maps are effective?
A: Ensure that your process maps are accurate, up-to-date, and easily understandable. Use clear and concise language, standardized symbols and notations, and avoid unnecessary complexity.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective process maps?
A: Start with a clear objective, identify the key stakeholders, use a standardized approach, focus on value-adding activities, and ensure that the map is easy to understand and navigate.
Q: How can I use process map samples to improve my organization’s performance?
A: Use process map samples to analyze existing processes, identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and track the impact of those changes. Regularly review and update your process maps to reflect changes in your organization and its environment.
Conclusion
Process map samples are invaluable tools for organizations seeking to enhance their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve better outcomes. By providing a clear and concise visual representation of processes, they facilitate understanding, communication, and collaboration, enabling organizations to identify and address bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and optimize performance. Whether used for analyzing existing processes, implementing process improvements, or simply communicating process information to stakeholders, process map samples play a crucial role in driving organizational success.
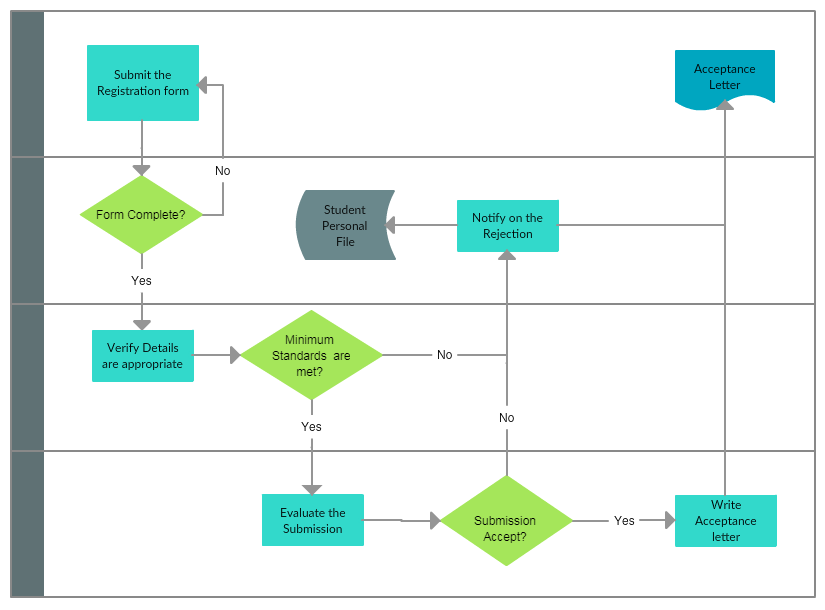

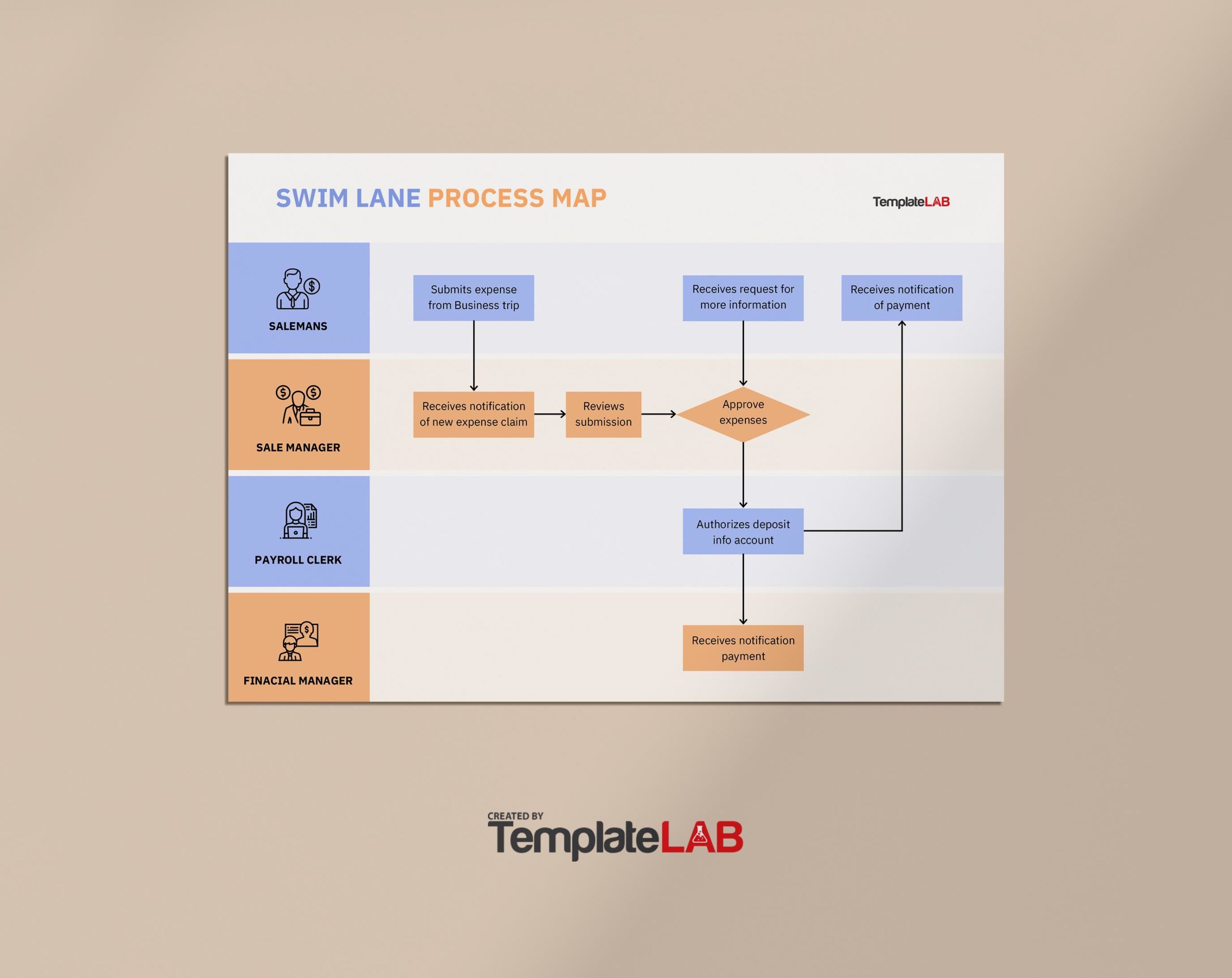
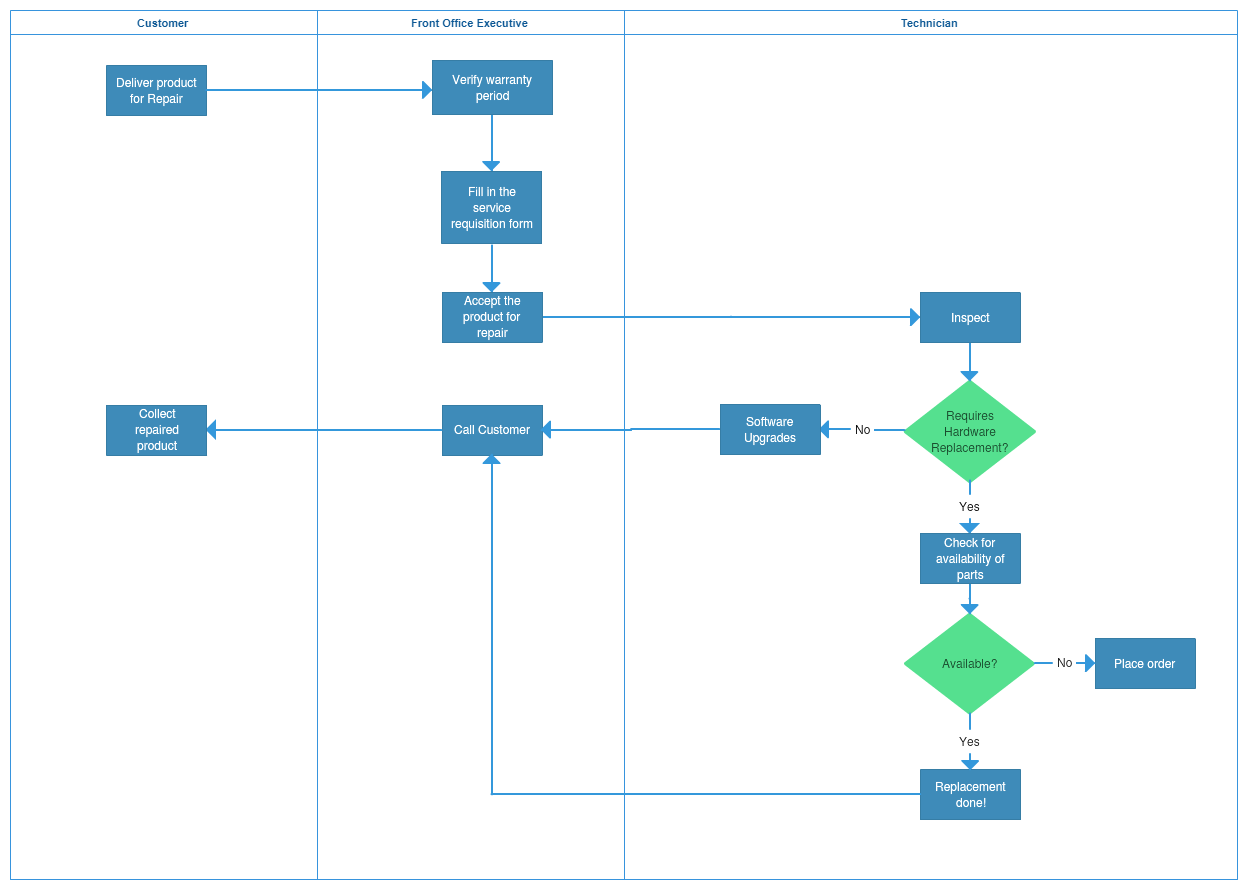

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Process Map Samples: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
