Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Mapping the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats
- 3.2 FAQs about Sea Turtle Habitats:
- 3.3 Tips for Protecting Sea Turtle Habitats:
- 3.4 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide

Sea turtles, ancient mariners that have traversed the oceans for millions of years, are captivating creatures with a fascinating life cycle intimately linked to specific geographic locations. Understanding where these majestic reptiles reside and migrate is crucial for their conservation and the health of the marine ecosystem. This comprehensive guide delves into the global distribution of sea turtle habitats, exploring the factors that influence their presence, the threats they face, and the importance of their ecological role.
Mapping the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats
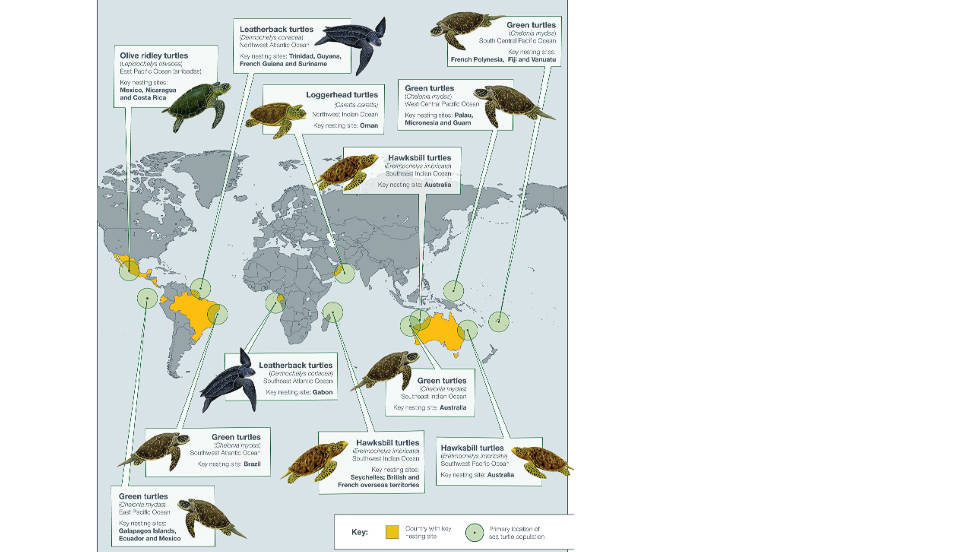
Sea turtles are found in all major oceans, with their distribution influenced by factors like water temperature, food availability, and nesting sites. The world map reveals a fascinating mosaic of sea turtle habitats, each with unique characteristics and challenges.
1. The Pacific Ocean:
The Pacific Ocean boasts a diverse range of sea turtle species, including the critically endangered leatherback, the green sea turtle, and the hawksbill. The warm waters of the central Pacific, particularly the Hawaiian Islands and the Coral Triangle, offer ideal conditions for these reptiles. The eastern Pacific, encompassing the coasts of Mexico, Central America, and South America, is another significant habitat, particularly for the olive ridley sea turtle.
2. The Atlantic Ocean:
The Atlantic Ocean is home to all seven species of sea turtles, with specific areas holding particular significance. The Caribbean Sea, with its abundant coral reefs and warm waters, is a critical habitat for the loggerhead, green, and hawksbill turtles. The western Atlantic, from Florida to Brazil, is a key nesting ground for the leatherback, while the eastern Atlantic, particularly the Mediterranean Sea, supports populations of loggerhead and green turtles.
3. The Indian Ocean:
The Indian Ocean, with its warm waters and diverse ecosystems, provides a suitable habitat for green, hawksbill, loggerhead, and olive ridley turtles. The northern Indian Ocean, encompassing the coasts of India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, is particularly important for nesting. The western Indian Ocean, including Madagascar and the Seychelles, is a crucial foraging ground for several species.
4. The Mediterranean Sea:
While the Mediterranean Sea is a relatively small body of water, it plays a vital role in the life cycle of loggerhead and green turtles. The warm waters and abundant food sources provide ideal conditions for these reptiles, making it a critical habitat for their survival.
5. The Black Sea:
The Black Sea, though smaller than other major oceans, is home to a small population of loggerhead turtles, primarily found in the northern part of the sea. This unique habitat underscores the importance of understanding the distribution of sea turtles even in seemingly smaller water bodies.
Understanding the Dynamics of Sea Turtle Habitats
The distribution of sea turtles is not static. These reptiles undertake extensive migrations, traveling thousands of kilometers between their nesting beaches and foraging grounds. This dynamic movement highlights the need for a comprehensive approach to conservation, encompassing not just their breeding sites but also their feeding areas and migratory routes.
Threats to Sea Turtle Habitats
Sea turtles face numerous threats, many stemming from human activities that impact their habitats.
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: Coastal development, pollution, and climate change are significantly altering sea turtle habitats. The destruction of nesting beaches, the degradation of coral reefs, and the increasing ocean acidification pose serious threats to their survival.
- Overfishing and Bycatch: Sea turtles are often caught unintentionally in fishing gear, leading to injuries and mortality. This bycatch poses a significant threat to their populations, particularly in areas with intensive fishing activities.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures and altered ocean currents can disrupt nesting cycles and food availability. The increased frequency and intensity of storms can also damage nesting beaches and threaten hatchlings.
- Pollution: Plastic debris, oil spills, and chemical pollutants contaminate sea turtle habitats, leading to ingestion, entanglement, and other forms of harm.
The Importance of Sea Turtle Habitats
Sea turtles play a crucial role in the marine ecosystem, contributing to its balance and health.
- Maintaining Biodiversity: Sea turtles are apex predators that help regulate the populations of various marine organisms, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the oceans.
- Nutrient Cycling: Sea turtles contribute to nutrient cycling by feeding on seagrass and algae, releasing nutrients that support other marine life.
- Coral Reef Health: Sea turtles play a role in maintaining the health of coral reefs by grazing on algae that can overgrow and suffocate corals.
- Indicator Species: Sea turtles are considered indicator species, meaning their presence and health reflect the overall health of the marine environment.
Conservation Efforts and the Future of Sea Turtle Habitats
Protecting sea turtle habitats is paramount for their survival.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration among nations is essential to address transboundary threats and ensure the conservation of sea turtles across their migratory routes.
- Protected Areas: Establishing marine protected areas, particularly around nesting beaches and foraging grounds, is crucial to safeguarding these critical habitats.
- Sustainable Fisheries: Implementing sustainable fishing practices, including the use of turtle-friendly gear and fishing quotas, can reduce bycatch and minimize the impact on sea turtle populations.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of sea turtles and the threats they face is crucial for fostering a sense of responsibility and promoting conservation efforts.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change are essential for preserving sea turtle habitats and ensuring their long-term survival.
FAQs about Sea Turtle Habitats:
1. What are the key factors that determine where sea turtles live?
Sea turtle distribution is influenced by several factors, including:
- Water Temperature: Sea turtles are cold-blooded reptiles and require warm water for optimal body temperature regulation.
- Food Availability: Sea turtles have specific dietary needs, and their distribution is often linked to the presence of their preferred prey, such as seagrass, algae, jellyfish, and crustaceans.
- Nesting Sites: Sea turtles require sandy beaches with suitable conditions for nesting, including accessibility, sand quality, and limited human disturbance.
2. How do sea turtles migrate, and why is it important?
Sea turtles undertake extensive migrations, traveling thousands of kilometers between their nesting beaches and foraging grounds. These migrations are crucial for their life cycle, allowing them to access food resources and suitable nesting sites.
3. What are the biggest threats to sea turtle populations?
Sea turtles face numerous threats, including:
- Habitat Loss and Degradation: Coastal development, pollution, and climate change are altering their habitats, impacting their survival.
- Overfishing and Bycatch: Sea turtles are often caught unintentionally in fishing gear, leading to injuries and mortality.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures and altered ocean currents can disrupt their nesting cycles and food availability.
- Pollution: Plastic debris, oil spills, and chemical pollutants contaminate their habitats, leading to ingestion, entanglement, and other forms of harm.
4. How can we protect sea turtle habitats?
Protecting sea turtle habitats requires a multi-faceted approach, including:
- International Cooperation: Collaboration among nations to address transboundary threats.
- Protected Areas: Establishing marine protected areas to safeguard critical habitats.
- Sustainable Fisheries: Implementing sustainable fishing practices to minimize bycatch.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of sea turtles and the threats they face.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of climate change.
5. Why are sea turtles important to the marine ecosystem?
Sea turtles play a crucial role in the marine ecosystem by:
- Maintaining Biodiversity: Regulating populations of various marine organisms, contributing to biodiversity.
- Nutrient Cycling: Feeding on seagrass and algae, releasing nutrients that support other marine life.
- Coral Reef Health: Grazing on algae that can overgrow and suffocate corals.
- Indicator Species: Reflecting the overall health of the marine environment.
Tips for Protecting Sea Turtle Habitats:
- Reduce Your Plastic Footprint: Use reusable bags, water bottles, and containers to minimize plastic waste that can end up in the ocean and harm sea turtles.
- Support Sustainable Seafood: Choose seafood from sustainable sources that minimize bycatch and promote responsible fishing practices.
- Volunteer for Sea Turtle Conservation: Join organizations that conduct sea turtle research, monitoring, and conservation efforts.
- Educate Others: Spread awareness about the importance of sea turtles and the threats they face to encourage responsible actions.
- Be a Responsible Tourist: Avoid disturbing nesting beaches, dispose of trash properly, and support eco-friendly tourism operators.
Conclusion:
The distribution of sea turtle habitats across the globe is a testament to their resilience and adaptability. However, the threats they face are significant and require concerted global efforts to ensure their survival. By understanding the factors that influence their distribution, the threats they face, and their ecological importance, we can work towards a future where these ancient mariners continue to grace our oceans for generations to come.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-502266246-f238799593734bb3a9dc5230389bd2b0.jpg)






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Network of Sea Turtle Habitats: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
