Unveiling the Complexities of Coronary Artery Disease: A Visual Guide to Understanding
Related Articles: Unveiling the Complexities of Coronary Artery Disease: A Visual Guide to Understanding
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Complexities of Coronary Artery Disease: A Visual Guide to Understanding. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Complexities of Coronary Artery Disease: A Visual Guide to Understanding

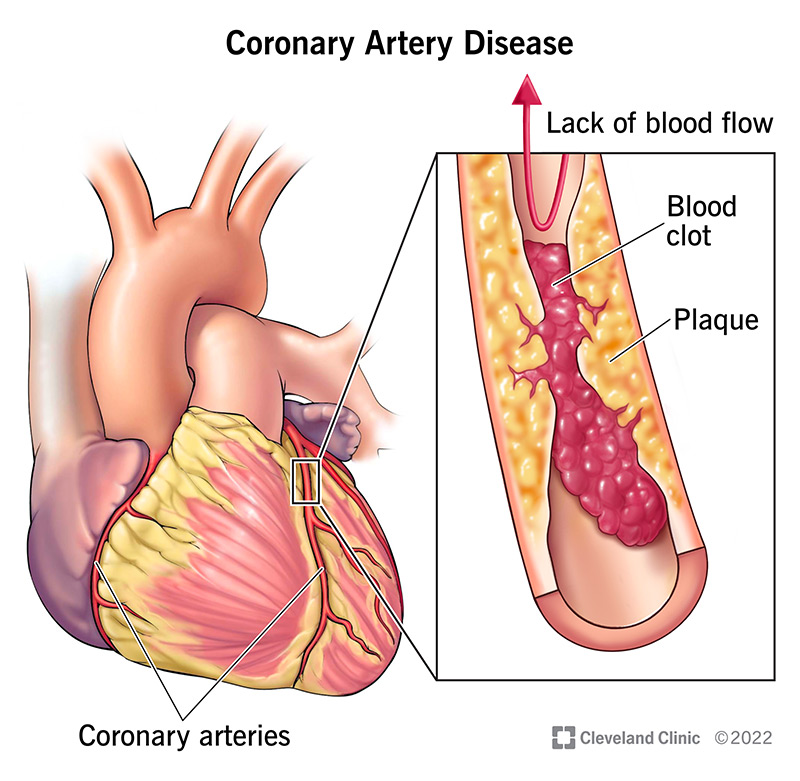
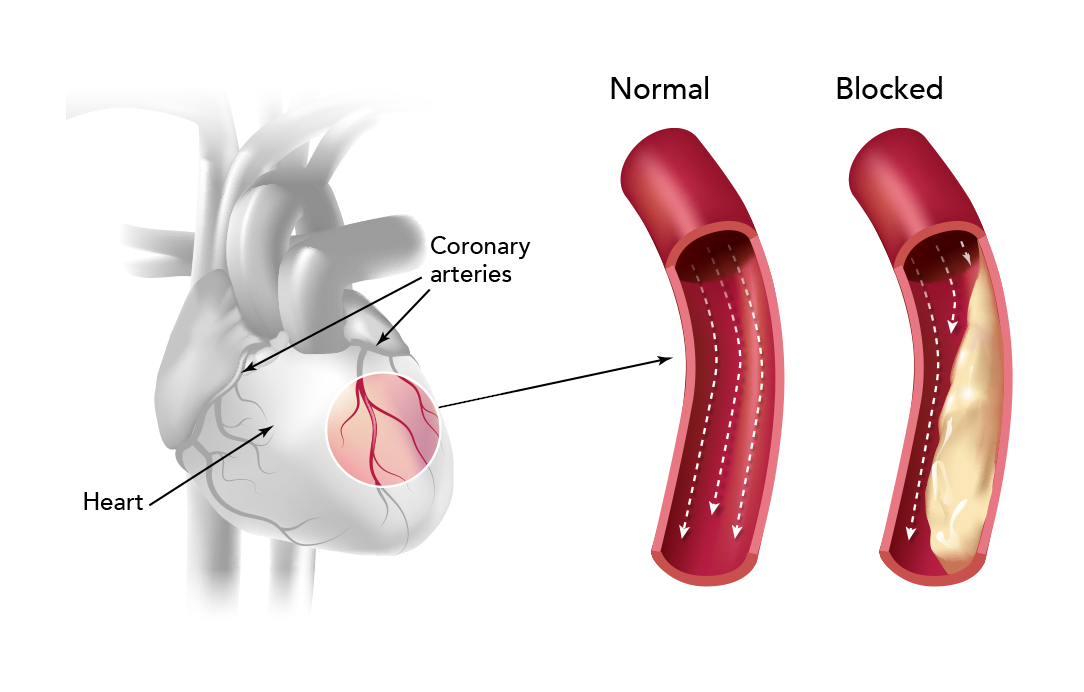
Coronary artery disease (CAD), a leading cause of death globally, affects millions worldwide. This complex condition involves the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. Understanding the intricate interplay of factors contributing to CAD is crucial for effective prevention, diagnosis, and management. This article delves into the essence of coronary artery disease, exploring its key components through a comprehensive concept map.
The Coronary Artery Disease Concept Map: A Visual Framework for Comprehension
A concept map, a visual representation of interconnected ideas, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the multifaceted nature of CAD. It presents a structured framework that outlines the major concepts, their relationships, and the underlying mechanisms involved. This map, designed to be both informative and accessible, aims to provide a clear and concise overview of CAD, encompassing its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications.
Key Elements of the Coronary Artery Disease Concept Map
1. Causes of Coronary Artery Disease:
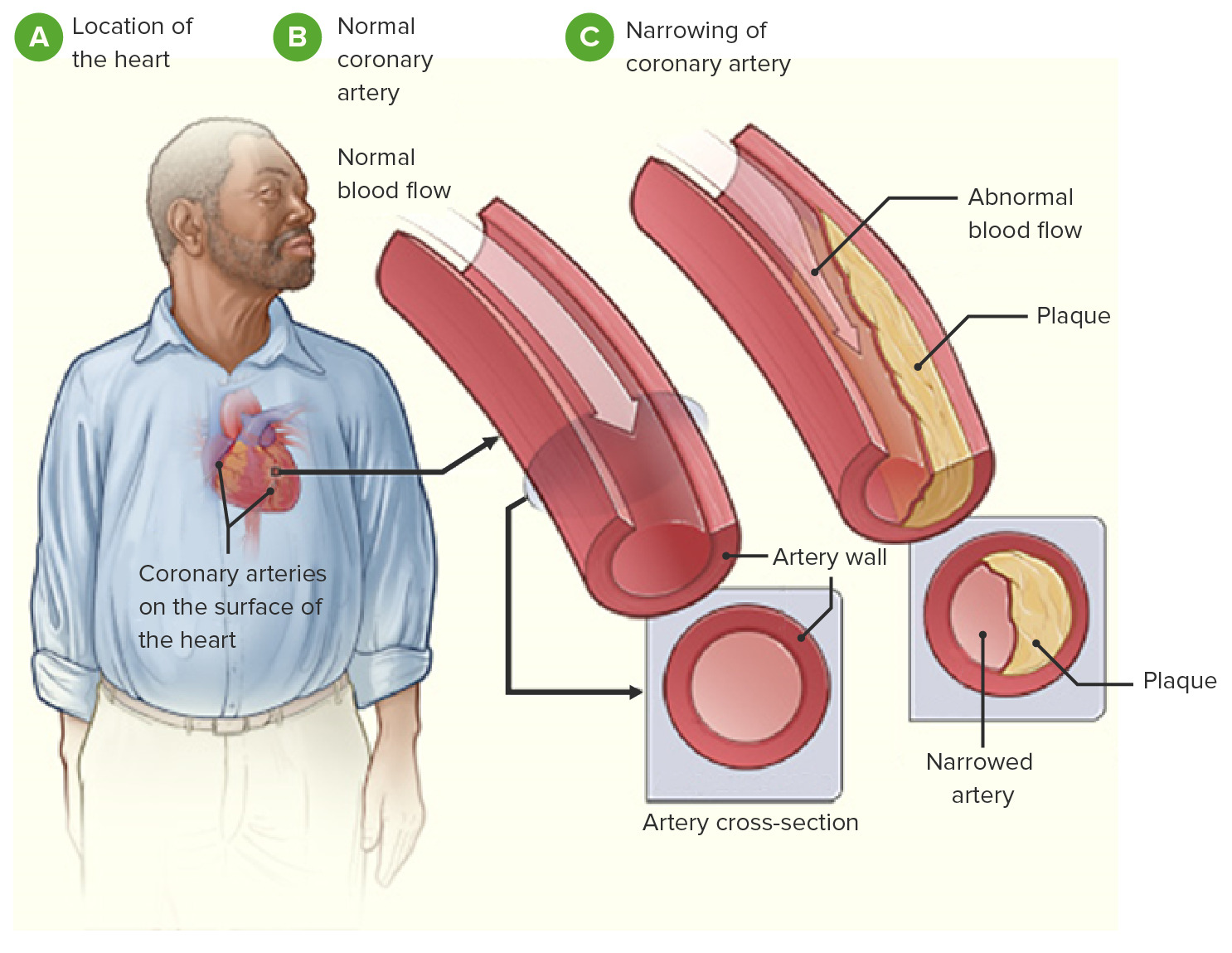
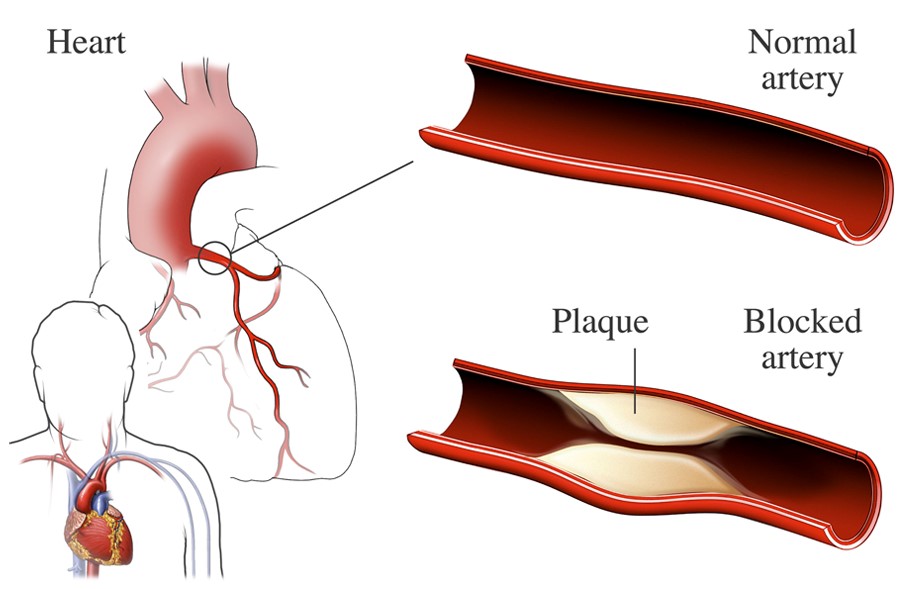
- Atherosclerosis: The primary culprit behind CAD, atherosclerosis is a gradual process involving the buildup of plaque (cholesterol, fats, and other substances) within the artery walls. This plaque narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attack.
- Genetics: Family history of heart disease can significantly increase the risk of developing CAD. Certain genetic predispositions can influence cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and other factors that contribute to atherosclerosis.
-
Lifestyle Factors:
- Diet: High intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can accelerate atherosclerosis.
- Physical Activity: Lack of regular physical activity contributes to obesity, high cholesterol, and hypertension, all risk factors for CAD.
- Smoking: Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes damage the arteries, accelerate atherosclerosis, and increase the risk of blood clots.
- Stress: Chronic stress can elevate blood pressure and contribute to unhealthy lifestyle choices.
-
Other Factors:
- Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): High blood pressure puts extra strain on the arteries, accelerating atherosclerosis.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol contribute to plaque buildup.
2. Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease:
- Chest Pain (Angina): The most common symptom, angina presents as a squeezing, pressure, tightness, or aching sensation in the chest, often triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress.
- Shortness of Breath: CAD can cause shortness of breath due to reduced oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue and weakness are common symptoms, especially with exertion.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause dizziness and lightheadedness.
- Sweating: Cold sweats, especially with chest pain, are a warning sign.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some individuals experience nausea or vomiting with angina.
3. Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Doctors gather information about symptoms, risk factors, and family history.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records electrical activity in the heart, detecting abnormalities that may indicate CAD.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound scan of the heart provides images of the heart’s structure and function, revealing any damage caused by CAD.
- Stress Test: This test monitors heart function during exercise or medication-induced stress, revealing the presence of CAD.
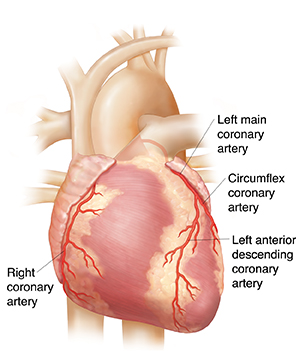
- Coronary Angiography: A minimally invasive procedure using contrast dye to visualize the coronary arteries, revealing blockages or narrowing.
4. Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease:
-
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Diet: A heart-healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise strengthens the heart muscle and improves blood flow.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking significantly reduces CAD risk.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
-
Medications:
- Statins: Reduce cholesterol levels.
- Aspirin: Prevents blood clots.
- Beta-blockers: Slow heart rate and reduce blood pressure.
- Nitrates: Dilate blood vessels, relieving chest pain.
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): A minimally invasive procedure to open blocked arteries using a catheter with a balloon or stent.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG): A surgical procedure to bypass blocked arteries using grafts from other blood vessels.
5. Complications of Coronary Artery Disease:
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): Occurs when a coronary artery becomes completely blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle.
- Heart Failure: The heart weakens and is unable to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup and shortness of breath.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats caused by damage to the heart’s electrical system.
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Occurs when the heart stops beating unexpectedly.
6. Importance of Early Detection and Prevention:
- Early Detection: Recognizing symptoms early allows for timely intervention, potentially preventing serious complications like heart attack.
- Prevention: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and smoking cessation, can significantly reduce the risk of developing CAD.
FAQs Regarding Coronary Artery Disease Concept Map
1. How does the concept map help understand coronary artery disease?
The concept map provides a structured and visual framework that connects key aspects of CAD, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications. This visual representation aids in comprehending the intricate relationships between various elements, enhancing understanding and retention.
2. Can the concept map be used for educational purposes?
Absolutely. The concept map serves as an effective educational tool for students, healthcare professionals, and patients. It simplifies complex information, promotes understanding, and facilitates knowledge sharing.
3. What are the benefits of using a concept map for coronary artery disease?
Using a concept map for CAD offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Comprehension: Visualizing the interconnectedness of concepts facilitates a deeper understanding of the disease.
- Improved Memory: The visual nature of the map aids in information retention and recall.
- Effective Communication: The map serves as a shared language for discussing CAD, promoting clear communication between healthcare professionals and patients.
- Increased Patient Engagement: Visual representations can empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions.
4. Can the concept map be customized for specific audiences?
Yes, the concept map can be customized to cater to specific audiences, such as patients, healthcare professionals, or students. The level of detail, complexity, and language can be tailored to suit the target audience’s needs and understanding.
Tips for Utilizing the Coronary Artery Disease Concept Map
- Review the map regularly: Frequent revisiting of the map helps reinforce key concepts and maintain understanding.
- Connect the concepts: Focus on the relationships between different elements within the map, understanding how they interact and contribute to CAD.
- Discuss the map with others: Sharing the map with healthcare professionals, friends, or family members can facilitate open discussion and promote knowledge sharing.
- Use the map as a reference: The map serves as a valuable resource for understanding CAD and navigating information about the disease.
Conclusion: Embracing a Comprehensive Approach to Coronary Artery Disease
The coronary artery disease concept map provides a powerful visual tool for comprehending this complex condition. By outlining the intricate network of causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications, the map empowers individuals to understand their risk, make informed decisions about their health, and engage in proactive preventative measures. The concept map, through its accessibility and clarity, serves as a valuable resource for individuals, healthcare professionals, and educators alike, fostering a comprehensive approach to managing and preventing coronary artery disease.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Complexities of Coronary Artery Disease: A Visual Guide to Understanding. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!