Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities
- 3.1 The Evolution of the Byzantine Urban Landscape
- 3.2 Understanding the Importance of Byzantine Cities
- 3.3 Deciphering the Map: Key Features and Insights
- 3.4 FAQs: Understanding the Byzantine Urban Landscape
- 3.5 Tips for Exploring the Byzantine Urban Landscape
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Byzantine Cities
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities
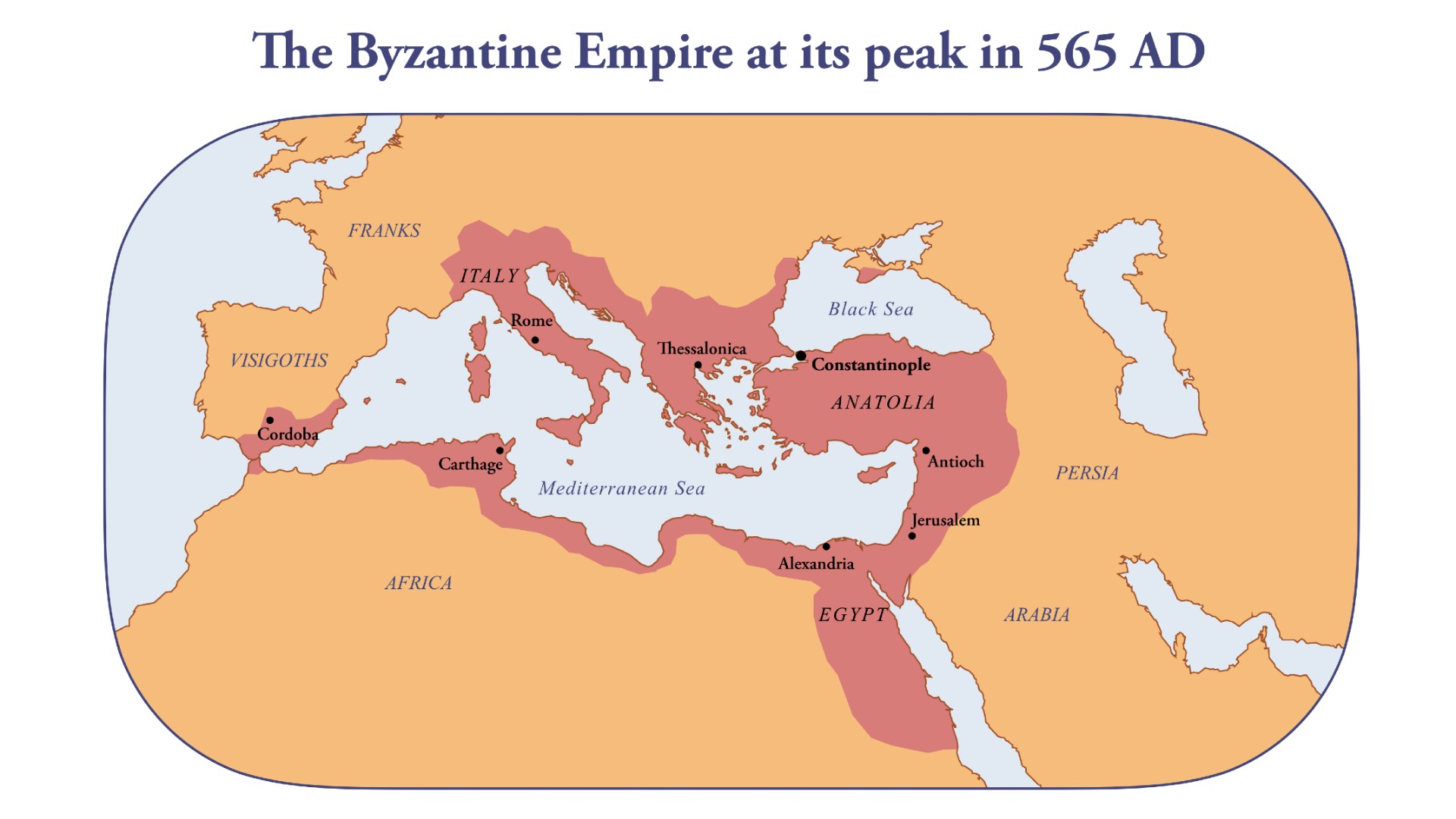
The Byzantine Empire, a vibrant and enduring civilization that spanned over a millennium, left an indelible mark on history and culture. Its vast geographical expanse, encompassing territories that stretched from the Balkans to North Africa and the Middle East, housed a multitude of bustling cities, each contributing to the empire’s unique character and influence.
A map of Byzantine cities, therefore, serves as a crucial tool for understanding the empire’s political, economic, and social fabric. It provides a visual representation of the interconnectedness of these urban centers, revealing the intricate network of trade routes, administrative structures, and cultural exchanges that shaped the Byzantine world.
The Evolution of the Byzantine Urban Landscape
The Byzantine Empire inherited a legacy of urban development from its Roman predecessor. Cities like Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, and Ephesus, already thriving centers of commerce and administration, continued to flourish under Byzantine rule. However, the empire also saw the emergence of new cities, strategically located to secure its borders and facilitate economic growth.
The map of Byzantine cities reflects this dynamic evolution. It reveals the emergence of new urban centers in the Balkans, such as Thessalonica, Serdica (Sofia), and Durazzo, which served as important military outposts and administrative hubs. In the eastern provinces, cities like Caesarea Maritima, Edessa, and Amida (Diyarbakır) played a vital role in trade and cultural exchange with the East.
Understanding the Importance of Byzantine Cities
Beyond their geographical locations, Byzantine cities were much more than mere points on a map. They were vibrant centers of life, pulsating with economic activity, religious fervor, and intellectual pursuits. Each city had its unique character, shaped by its history, culture, and role within the empire.
- Political and Administrative Hubs: Constantinople, the empire’s capital, served as the seat of power, housing the imperial court, the Senate, and various government offices. Other major cities, like Thessalonica and Antioch, functioned as regional administrative centers, overseeing the administration of their respective provinces.
- Economic Powerhouses: Byzantine cities were crucial nodes in the empire’s extensive trade network. Constantinople, with its strategic location on the Bosporus Strait, emerged as a major center for international trade, connecting the East and West. Other cities, like Alexandria and Antioch, thrived as major ports, facilitating the flow of goods across the Mediterranean and beyond.
- Centers of Religion and Culture: The Byzantine Empire was deeply religious, with Christianity playing a central role in its society. Cities like Constantinople, Jerusalem, and Antioch housed magnificent churches and monasteries, attracting pilgrims and scholars from across the empire. These cities were also centers of artistic and intellectual activity, fostering the development of Byzantine art, architecture, and literature.
Deciphering the Map: Key Features and Insights
A detailed map of Byzantine cities offers a wealth of insights into the empire’s history and civilization. By analyzing its features, we can glean valuable information about:
- Urban Planning and Architecture: The map reveals the layout and design of Byzantine cities, showcasing their distinctive architectural features, such as the use of marble, mosaics, and elaborate domes. It allows us to trace the evolution of urban planning from the Roman era to the Byzantine period, highlighting the influence of Roman traditions and the development of new architectural styles.
- Trade Routes and Networks: The map highlights the key trade routes that crisscrossed the Byzantine Empire, connecting its cities and facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. It reveals the importance of sea routes, such as the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea, and overland routes, such as the Silk Road, in the empire’s economic prosperity.
- Military Fortifications and Defenses: The map illustrates the strategic locations of Byzantine cities, highlighting their role in defending the empire’s borders. It reveals the presence of fortifications, such as walls and towers, which were designed to protect cities from invaders and maintain security.
- Cultural Exchange and Influence: By examining the distribution of cities across the empire, we can understand how Byzantine culture and influence spread. The map reveals the presence of cities with strong cultural connections to the East, such as Antioch and Alexandria, and cities with a more pronounced Greek influence, like Constantinople and Thessalonica.
FAQs: Understanding the Byzantine Urban Landscape
1. What were the largest cities in the Byzantine Empire?
The largest cities in the Byzantine Empire included Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, Thessalonica, Ephesus, and Jerusalem. These cities were major centers of population, commerce, and culture, playing crucial roles in the empire’s political, economic, and social life.
2. How did the Byzantine Empire’s cities differ from Roman cities?
While inheriting many features from their Roman predecessors, Byzantine cities developed their own unique characteristics. Byzantine cities often featured more elaborate churches and monasteries, reflecting the importance of Christianity in the empire. They also developed new architectural styles, incorporating features like domes and mosaics.
3. What was the role of Constantinople in the Byzantine Empire?
Constantinople, the empire’s capital, served as the seat of power, housing the imperial court, the Senate, and various government offices. It was also a major center of trade, culture, and religious life, attracting people from across the empire and beyond.
4. How did the Byzantine Empire’s cities contribute to its economic prosperity?
Byzantine cities were vital to the empire’s economic prosperity, serving as centers of trade and production. They facilitated the exchange of goods across the Mediterranean and beyond, connecting the empire to major trade routes like the Silk Road.
5. What happened to the Byzantine cities after the empire’s fall?
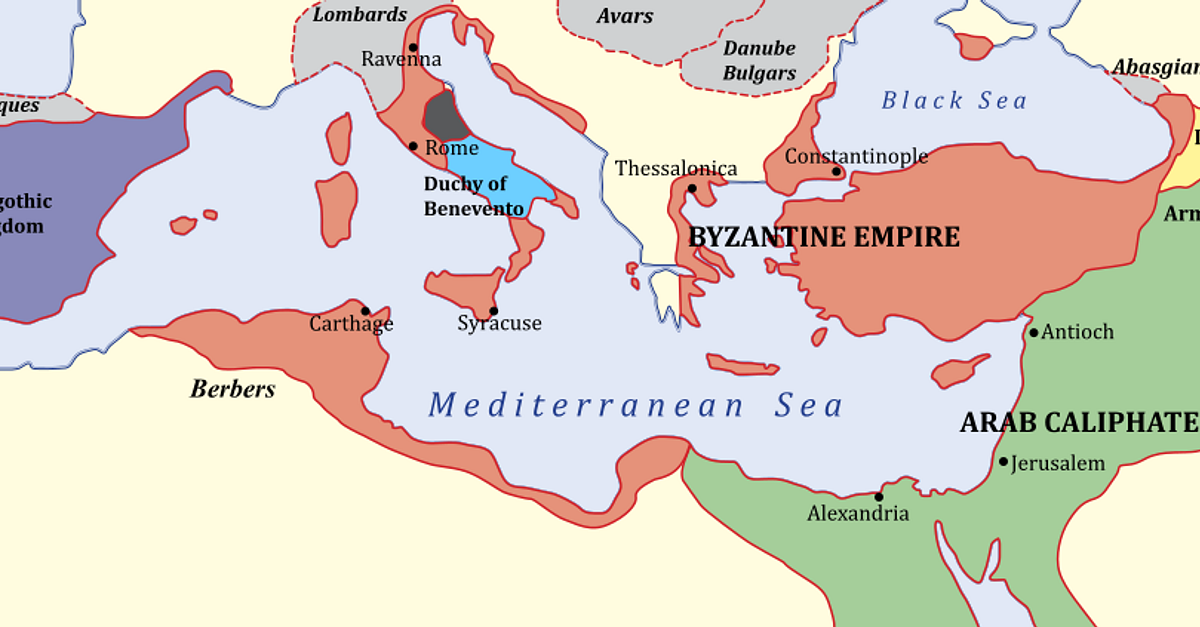
After the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, many of its cities continued to exist, but under different rulers. Some cities, like Constantinople, became major centers of the Ottoman Empire, while others experienced a decline in their importance. However, the legacy of Byzantine cities continues to shape the urban landscape of the Eastern Mediterranean region.
Tips for Exploring the Byzantine Urban Landscape
- Use a detailed map: A comprehensive map of Byzantine cities is essential for understanding the empire’s urban landscape. Look for maps that include information about the city’s location, size, population, and historical significance.
- Explore historical sources: Primary and secondary sources, such as chronicles, travelogues, and archaeological reports, provide valuable insights into the lives of people who lived in Byzantine cities.
- Visit Byzantine sites: Many Byzantine cities still stand today, offering visitors a glimpse into the empire’s rich past. Explore the ruins of Constantinople, the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, or the ancient city of Ephesus in Turkey.
- Engage with scholarly works: Numerous books and articles have been written about Byzantine cities, providing a deeper understanding of their history, culture, and significance.
- Connect with online resources: Websites, databases, and virtual tours can enhance your understanding of Byzantine cities, offering interactive maps, historical images, and scholarly articles.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Byzantine Cities
The map of Byzantine cities serves as a powerful reminder of the empire’s enduring legacy. It reveals the interconnectedness of its urban centers, highlighting the complex network of trade routes, administrative structures, and cultural exchanges that shaped the Byzantine world. By exploring these cities, we gain a deeper understanding of the empire’s history, culture, and influence, recognizing its lasting impact on the world today.
The Byzantine Empire, though long gone, continues to resonate through its cities, reminding us of the vibrant and complex civilization that once flourished across the Eastern Mediterranean. The map of Byzantine cities, a testament to its enduring legacy, invites us to embark on a journey through time, unraveling the tapestry of this fascinating and influential empire.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of the Byzantine Empire: A Journey Through its Cities. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
