Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map
Related Articles: Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map
- 3.1 A Land of Contrasts: Russia’s Agricultural Geography
- 3.2 The Influence of Climate: A Major Factor
- 3.3 Resource Distribution: Uneven and Varied
- 3.4 Key Agricultural Commodities: A Diverse Portfolio
- 3.5 Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Landscape
- 3.6 FAQs about Russia’s Agricultural Map
- 3.7 Tips for Understanding Russia’s Agricultural Map
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map
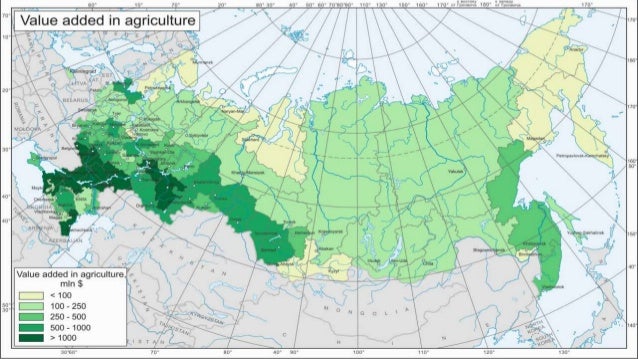
Russia, a vast landmass spanning eleven time zones, holds immense agricultural potential. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its agricultural landscape requires delving into the nuances of its diverse geography, climate, and resource distribution. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Russia’s agricultural map, highlighting its key features, challenges, and opportunities.
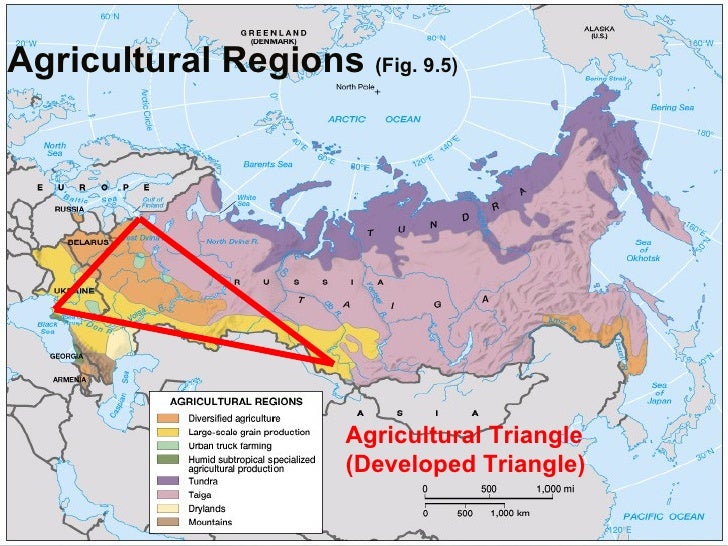
A Land of Contrasts: Russia’s Agricultural Geography
Russia’s agricultural landscape is characterized by stark contrasts. The European part of the country, with its fertile black earth soils and moderate climate, is the heart of Russian agriculture. This region, known as the "Black Earth Belt," boasts high agricultural productivity, contributing significantly to the country’s grain production.
However, moving eastwards, the landscape transforms dramatically. Siberia and the Far East face harsher climates, with long winters, permafrost, and limited arable land. These regions primarily focus on animal husbandry, particularly reindeer herding in the north and cattle raising in the south.
The Ural Mountains, a natural barrier separating Europe and Asia, further divide Russia’s agricultural potential. The western slopes experience more favorable conditions, while the eastern side faces colder temperatures and shorter growing seasons.
The Influence of Climate: A Major Factor
Climate plays a crucial role in shaping Russia’s agricultural map. The country experiences a wide range of climatic conditions, from the humid continental climate of the European part to the subarctic and arctic climates of the north.
The Black Earth Belt enjoys warm summers and moderate rainfall, ideal for growing a variety of crops, including wheat, barley, sunflowers, and potatoes. However, the region is also susceptible to droughts, which can significantly impact yields.
Further east, the climate becomes increasingly challenging. Siberia and the Far East face long, cold winters, limiting the growing season and forcing farmers to adapt their practices. The permafrost, a layer of permanently frozen ground, poses additional challenges for agriculture in these regions.
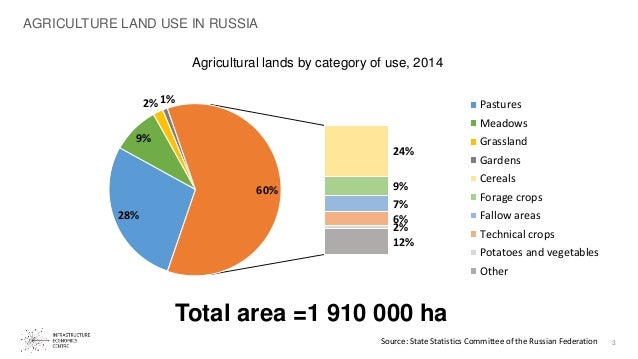
Resource Distribution: Uneven and Varied
The distribution of agricultural resources across Russia is far from uniform. The European part boasts the most fertile soils, with the "Black Earth Belt" standing out as a region of exceptional agricultural potential. However, the availability of water resources varies significantly.
The southern regions, including the Volga River basin, enjoy relatively abundant water supply, while the drier regions of the south-east face water scarcity. The northern regions, with their permafrost and limited precipitation, are particularly challenged in terms of water availability.
Key Agricultural Commodities: A Diverse Portfolio
Russia is a major producer of a wide range of agricultural commodities, reflecting the diversity of its agricultural landscape. Wheat, barley, sunflower seeds, potatoes, and sugar beets are among its most significant crops. The country is also a significant producer of livestock products, including beef, pork, poultry, and dairy.
While the European part accounts for the majority of agricultural production, other regions play a crucial role in specific commodities. Siberia, for example, is known for its reindeer herding and timber production, while the Far East contributes significantly to the country’s fish and seafood exports.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Landscape
Despite its vast potential, Russia’s agricultural sector faces a number of challenges. These include:
- Climate change: Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, are becoming more frequent, posing significant risks to agricultural production.
- Aging infrastructure: The country’s agricultural infrastructure, including irrigation systems and storage facilities, requires modernization to improve efficiency and reduce losses.
- Lack of investment: The agricultural sector has historically received limited investment, hindering its growth and competitiveness.
- Technological gap: Russia lags behind other developed nations in terms of agricultural technology adoption, limiting productivity and efficiency.
- Land fragmentation: The fragmentation of agricultural land, often inherited from the Soviet era, poses challenges for large-scale farming operations.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth and development.
- Modernization: Investing in modern agricultural technologies, such as precision farming and automation, can significantly improve productivity and efficiency.
- Sustainable practices: Adopting sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming and water conservation, can enhance environmental protection and long-term sustainability.
- Market access: Expanding market access for Russian agricultural products, particularly in international markets, can boost export earnings and create new economic opportunities.
- Innovation: Fostering innovation in the agricultural sector, through research and development, can lead to the development of new crop varieties, livestock breeds, and agricultural technologies.
FAQs about Russia’s Agricultural Map
1. What are the major agricultural regions in Russia?
The European part of Russia, particularly the "Black Earth Belt," is the most important agricultural region. Other significant regions include the Volga River basin, the North Caucasus, and the southern part of Siberia.
2. What are the main agricultural commodities produced in Russia?
Russia is a major producer of wheat, barley, sunflower seeds, potatoes, sugar beets, beef, pork, poultry, and dairy products.
3. What are the major challenges facing Russia’s agricultural sector?
Climate change, aging infrastructure, lack of investment, technological gap, and land fragmentation are some of the major challenges.
4. What are the opportunities for growth in Russia’s agricultural sector?
Modernization, sustainable practices, market access, and innovation are key opportunities for growth.
5. How is the government supporting the development of Russia’s agricultural sector?
The Russian government has implemented a number of programs to support the agricultural sector, including subsidies, loans, and infrastructure development initiatives.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Agricultural Map
- Focus on regional variations: Russia’s agricultural landscape is highly diverse, with significant regional variations in climate, soil types, and agricultural practices.
- Consider the impact of climate change: Climate change is a major factor influencing agricultural production in Russia, leading to more frequent extreme weather events.
- Pay attention to infrastructure: The availability and quality of agricultural infrastructure, such as irrigation systems and storage facilities, play a crucial role in productivity and efficiency.
- Explore technological advancements: Russia is making strides in adopting modern agricultural technologies, which can significantly enhance productivity and sustainability.
- Understand the role of government policy: Government policies, such as subsidies and investment programs, have a significant impact on the development of Russia’s agricultural sector.
Conclusion
Russia’s agricultural map is a complex and dynamic landscape, shaped by a combination of geographic, climatic, and resource factors. While the country faces challenges, it also holds immense potential for growth and development. By leveraging its vast resources, embracing modern technologies, and fostering innovation, Russia can unlock the full potential of its agricultural sector, contributing to its economic prosperity and food security.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Agricultural Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
