Understanding the Present-Day Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Present-Day Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Present-Day Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Present-Day Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide

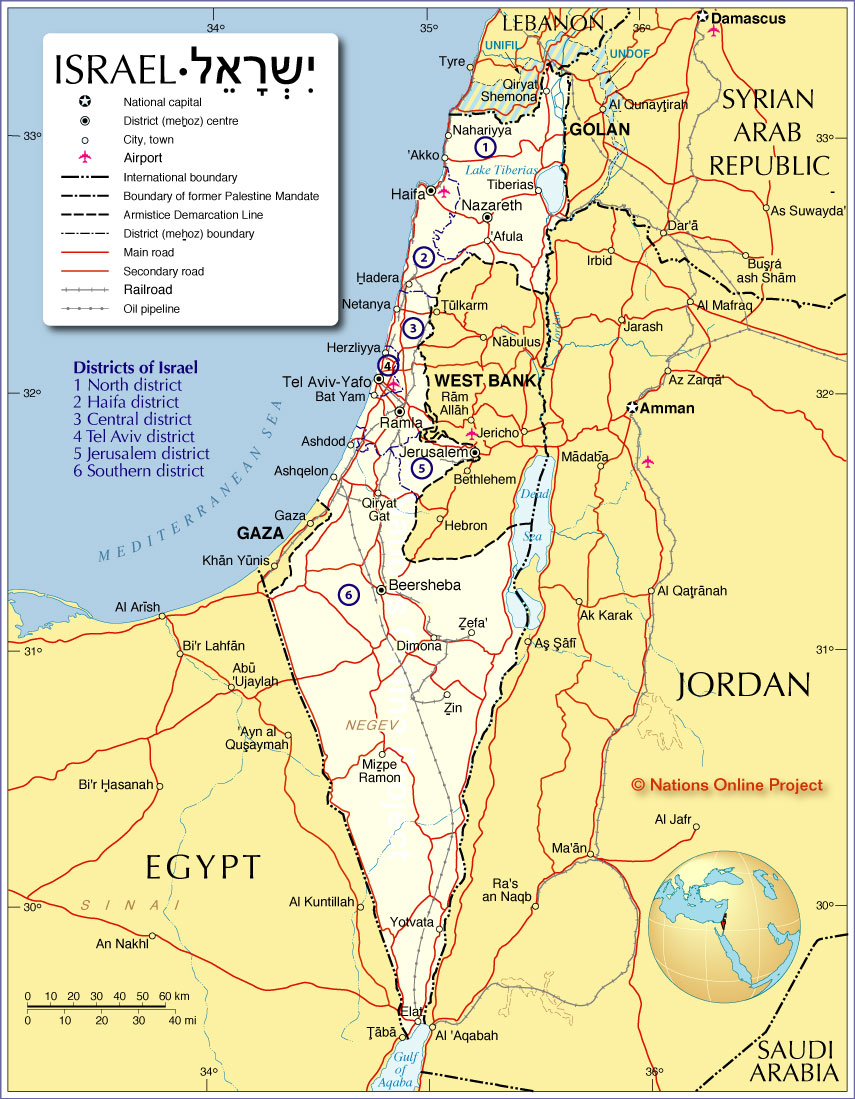
The present-day map of Israel, a nation situated in the Middle East, is a complex and dynamic landscape shaped by historical events, political negotiations, and ongoing conflicts. Understanding its geography, political divisions, and historical context is essential for comprehending the region’s current affairs and future prospects.
A Historical Overview:
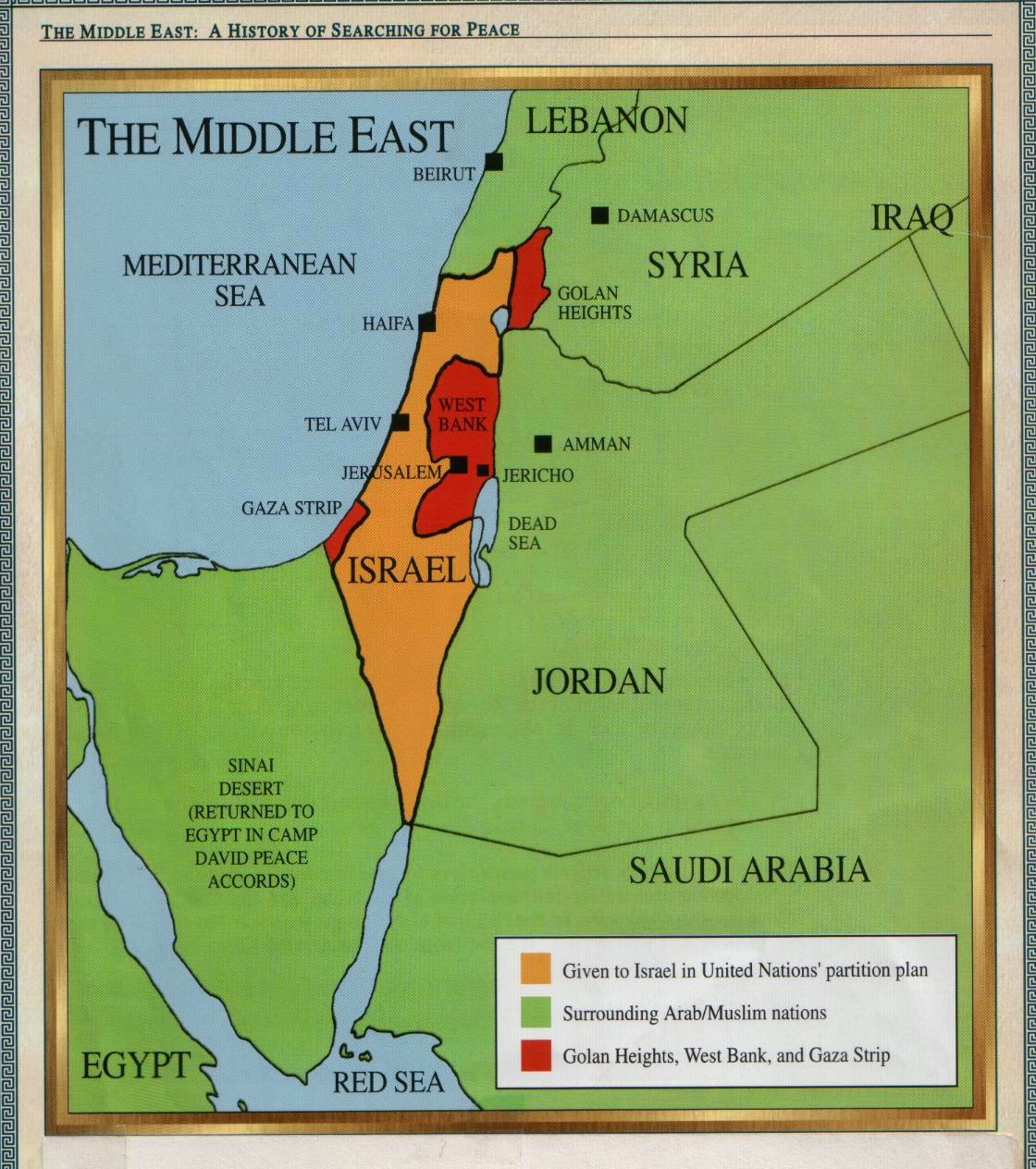
The land encompassing present-day Israel holds profound historical and religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. For centuries, it has been a focal point of conflict and contested claims. The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, following the British Mandate for Palestine, triggered the first Arab-Israeli War and subsequent conflicts that continue to impact the region.
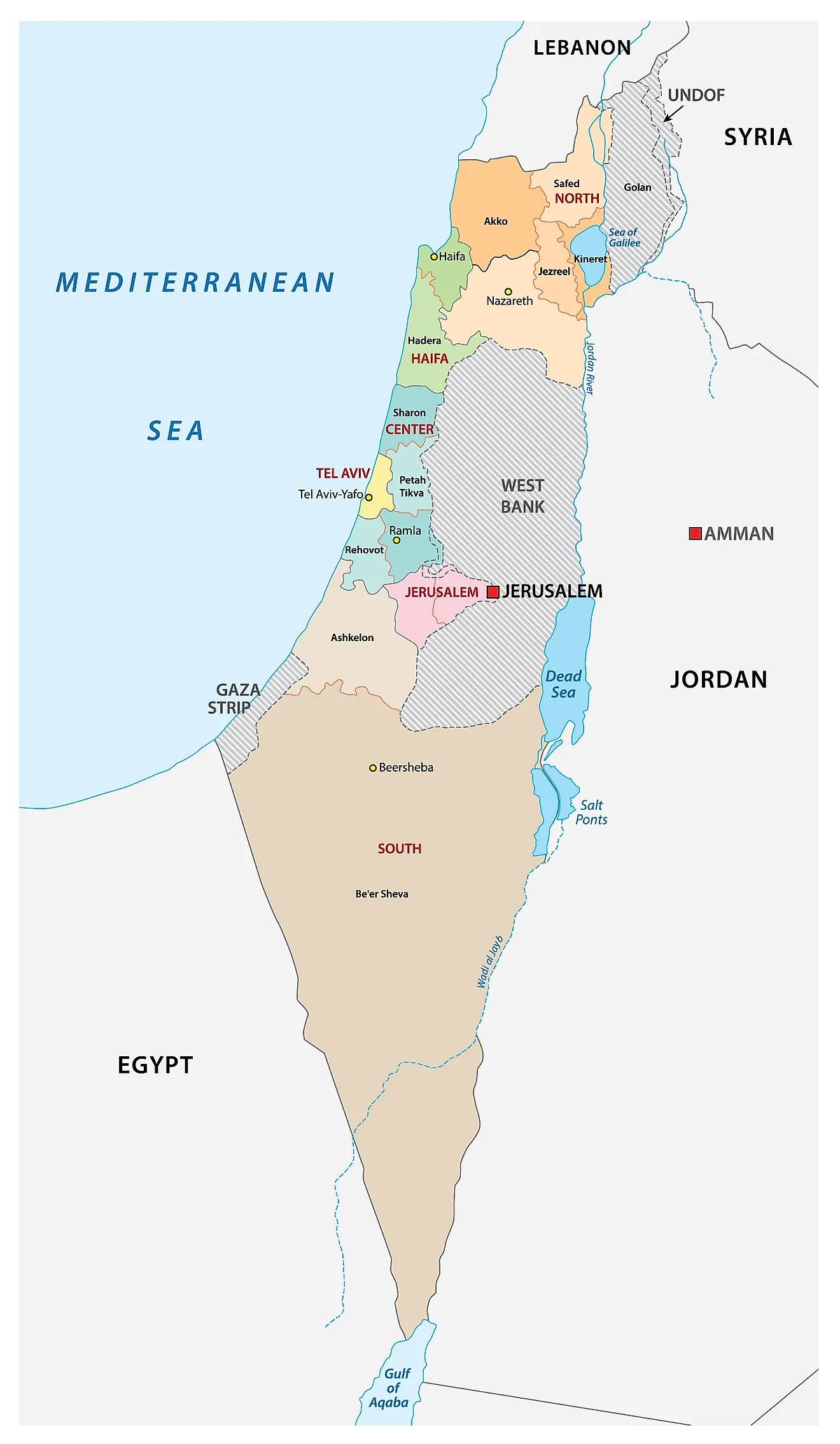
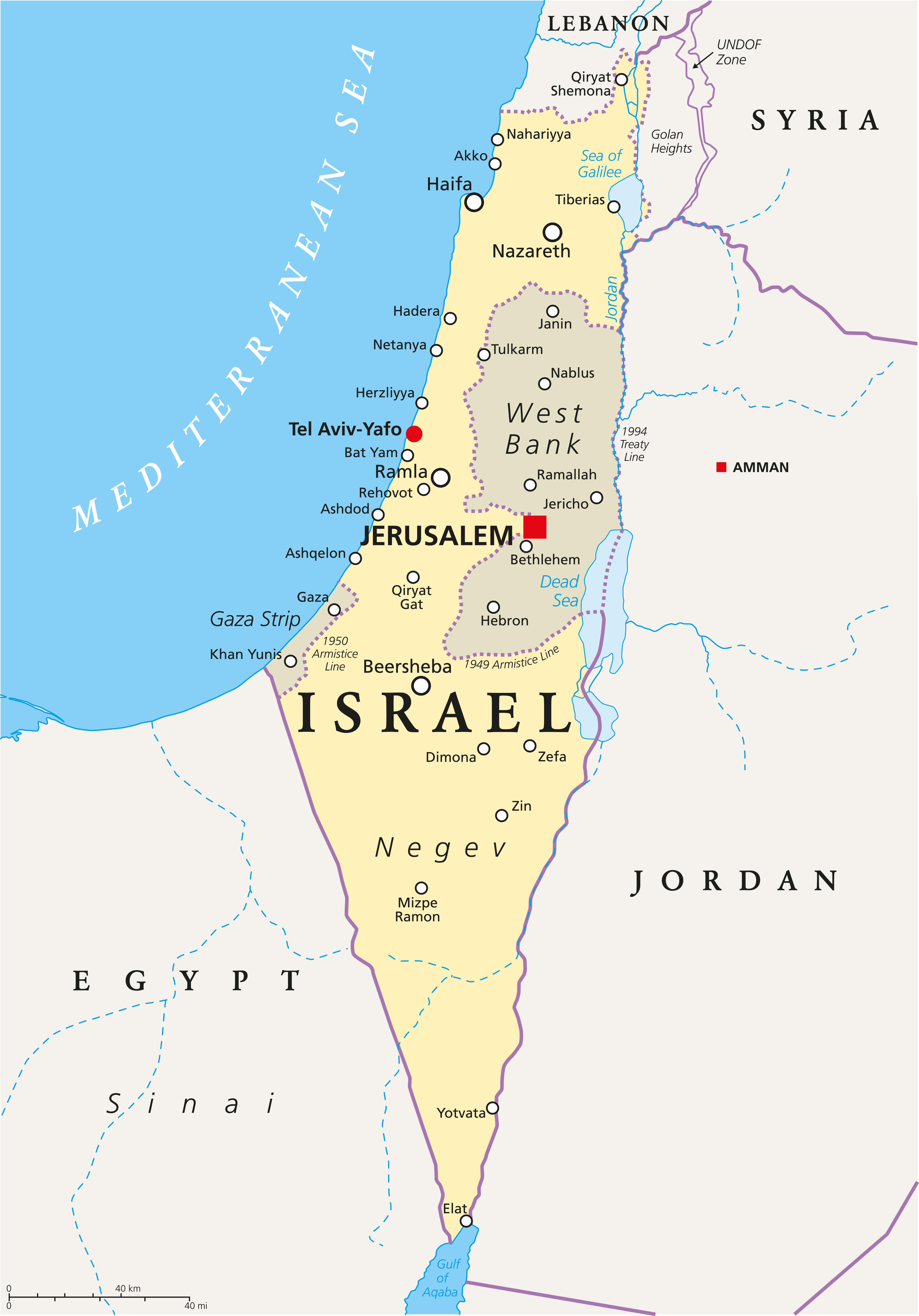
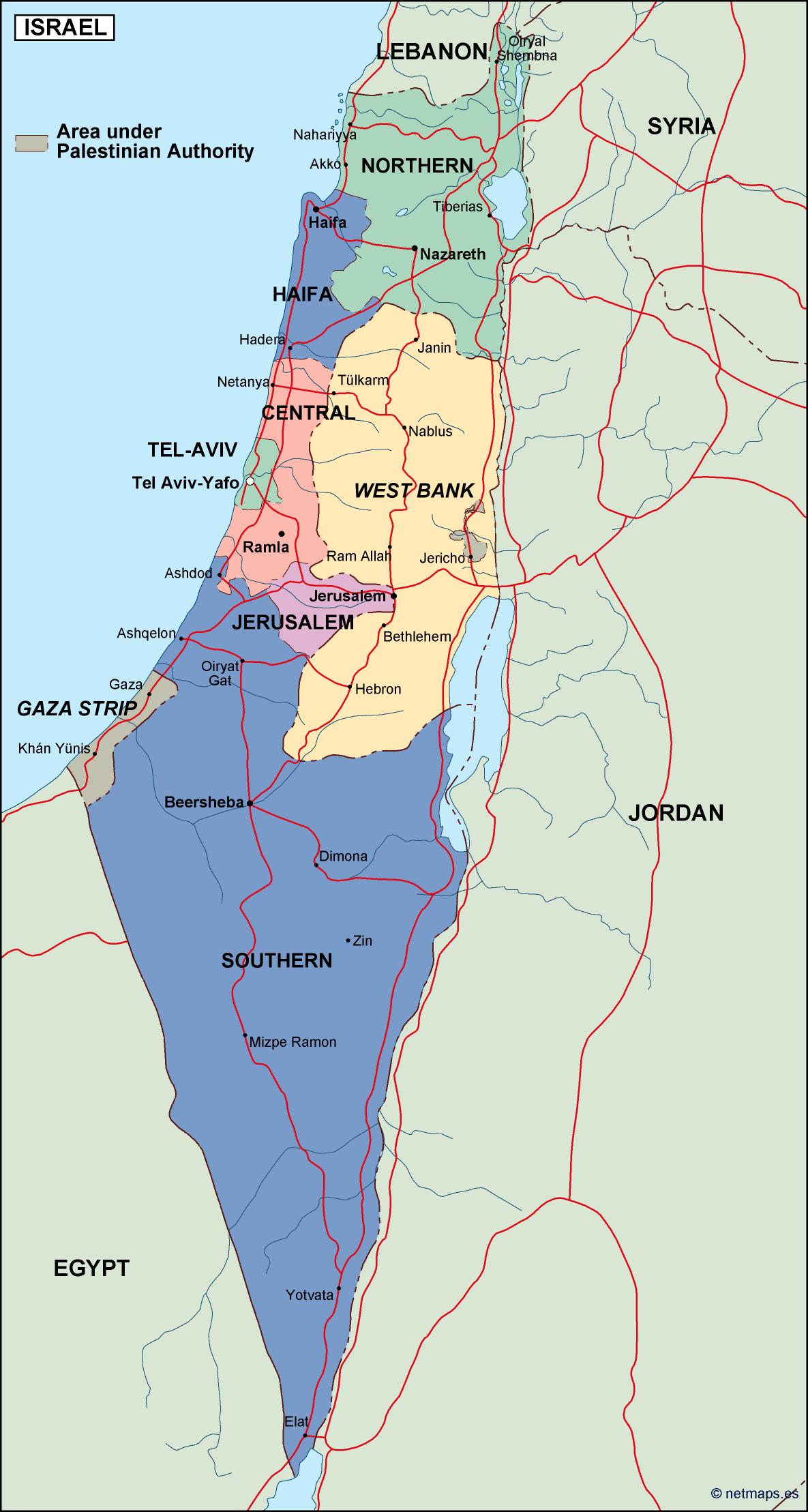
The Present-Day Map:
The current map of Israel reflects the outcome of these historical events and ongoing negotiations. It is characterized by:
- The Green Line: This internationally recognized boundary, established in 1949, separates Israel from the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. It represents the pre-1967 war armistice lines.
- The West Bank: A territory captured by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War, it is currently under Israeli military control, with Palestinian areas governed by the Palestinian Authority. The status of the West Bank remains a major point of contention in peace negotiations.
- The Gaza Strip: Another territory captured by Israel in 1967, it is currently under the control of Hamas, a Palestinian Islamist group. Israel maintains a blockade on the Gaza Strip, which has led to humanitarian concerns and ongoing tensions.
- Jerusalem: A holy city for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, it is divided between Israeli control (West Jerusalem) and Palestinian control (East Jerusalem). The status of Jerusalem is a highly sensitive issue, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming it as their capital.
- Golan Heights: A plateau captured by Israel from Syria in 1967, it is currently under Israeli control. Its status remains a point of contention with Syria.
Key Geographical Features:
Israel’s geography is diverse and plays a significant role in its economic development and security:
- The Mediterranean Coast: This coastline provides access to international trade and transportation, contributing to Israel’s economic growth.
- The Negev Desert: Covering a large portion of southern Israel, it presents challenges for agriculture but holds potential for renewable energy development.
- The Jordan Valley: A fertile region bordering Jordan, it is an important agricultural area and a source of water resources.
- The Galilee: A mountainous region in northern Israel, it is known for its scenic beauty and diverse cultural heritage.
Political and Social Landscape:
The present-day map of Israel reflects a complex political and social landscape:
- Israeli Society: Israel is a diverse society with a significant Jewish population, alongside a growing Arab minority. There are also smaller communities of Druze, Bedouin, and Circassians.
- Palestinian Society: The Palestinian population is divided between the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, facing challenges related to political instability, economic hardship, and limited self-governance.
- International Relations: Israel maintains diplomatic relations with many countries, but its relationship with neighboring Arab states remains complex and often strained.
The Importance of the Present-Day Map:
Understanding the present-day map of Israel is crucial for:
- Peace Negotiations: The map serves as a basis for negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians, outlining the territorial claims and contested areas.
- International Security: The map reflects the ongoing conflicts and tensions in the region, highlighting the need for international involvement in peace efforts.
- Economic Development: The map influences infrastructure development, resource allocation, and trade opportunities within the region.
- Cultural Heritage: The map reveals the historical and religious significance of the land, attracting tourists and scholars from around the world.
FAQs:
Q: What is the status of the West Bank?
A: The West Bank is currently under Israeli military control, with Palestinian areas governed by the Palestinian Authority. The status of the West Bank remains a major point of contention in peace negotiations.
Q: What is the significance of Jerusalem?
A: Jerusalem is a holy city for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, and its status is a highly sensitive issue. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim it as their capital.
Q: What is the role of the Green Line?
A: The Green Line represents the pre-1967 war armistice lines, separating Israel from the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. It is internationally recognized as the boundary between Israel and the occupied territories.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the Palestinian population?
A: The Palestinian population faces challenges related to political instability, economic hardship, limited self-governance, and ongoing conflicts.
Q: What is the future of the present-day map of Israel?
A: The future of the present-day map of Israel is uncertain and depends on the outcome of peace negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians.
Tips:
- Refer to reputable sources: Consult reliable maps and articles from reputable organizations such as the United Nations, the International Crisis Group, and the Middle East Institute.
- Stay informed: Keep up with current events and political developments in the region through news reports, analytical articles, and academic journals.
- Consider different perspectives: Engage with diverse viewpoints and perspectives on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, acknowledging the complexities and challenges involved.
Conclusion:
The present-day map of Israel is a complex and dynamic landscape reflecting historical events, political negotiations, and ongoing conflicts. Understanding its geography, political divisions, and historical context is essential for comprehending the region’s current affairs and future prospects. The map serves as a basis for peace negotiations, international security, economic development, and the preservation of cultural heritage. The future of the present-day map of Israel remains uncertain and depends on the outcome of ongoing efforts towards peace and reconciliation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Present-Day Map of Israel: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
