Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 What are Interactive Flood Maps?
- 3.2 Benefits of Using Interactive Flood Maps
- 3.3 Key Features of Interactive Flood Maps
- 3.4 Applications of Interactive Flood Maps
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Using Interactive Flood Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
In an era marked by increasing climate change impacts, the threat of flooding has become a pressing concern for communities worldwide. This heightened risk necessitates advanced tools and resources to understand, prepare for, and mitigate potential flood events. Enter the realm of interactive flood maps, powerful digital platforms that provide valuable insights into flood risk and preparedness. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of interactive flood maps, exploring their capabilities, benefits, and practical applications.
What are Interactive Flood Maps?
Interactive flood maps are digital representations of geographic areas, overlaid with data that depicts flood risk and potential inundation zones. These maps utilize advanced technologies like Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and hydrological modeling to visualize flood scenarios.
Unlike static maps, interactive flood maps offer users the ability to:
- Zoom and pan: Explore specific areas in detail, focusing on neighborhoods, streets, or individual properties.
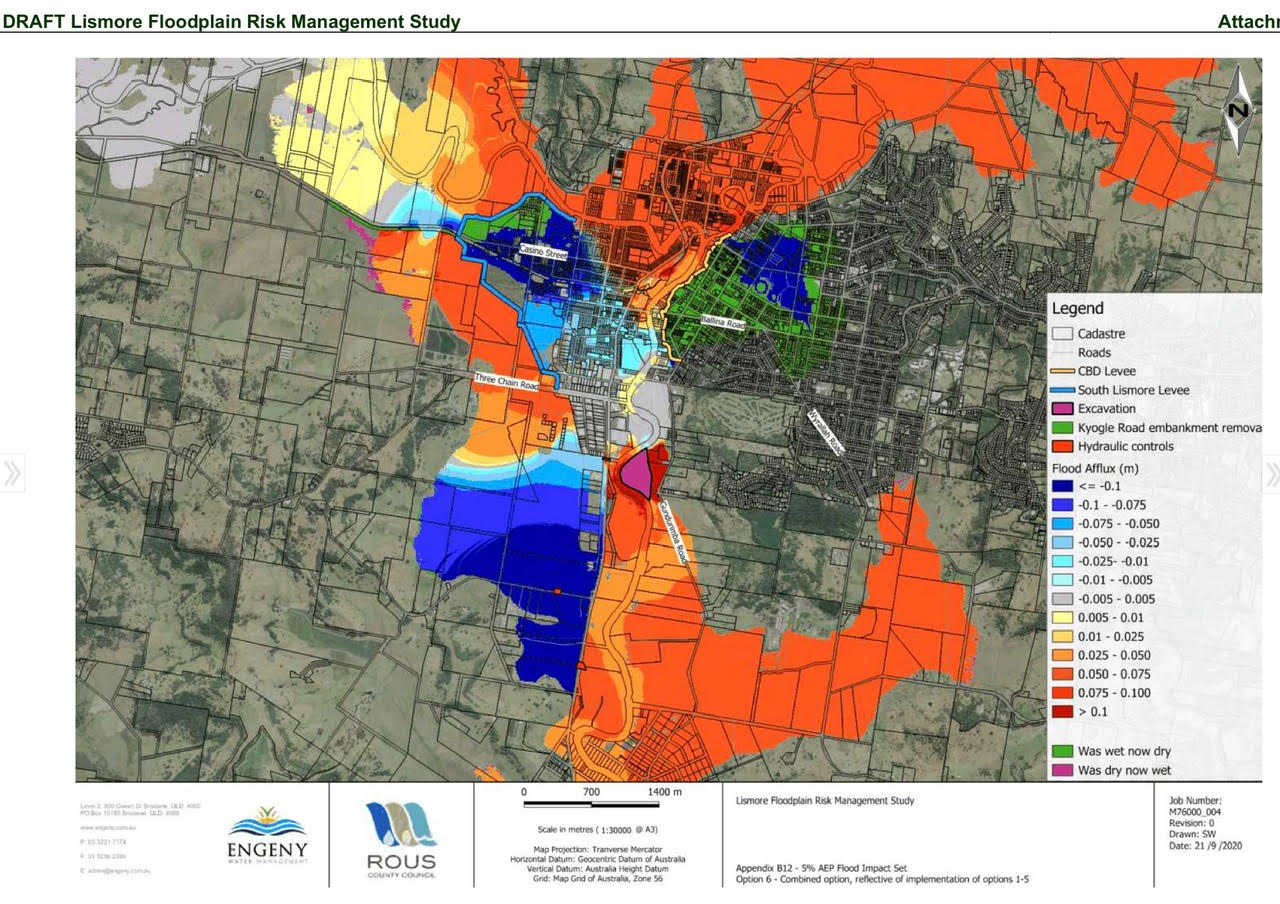
- Layer information: Access various data layers, such as elevation, rainfall intensity, and historical flood events, to gain a multi-dimensional understanding of flood risk.
- Simulate scenarios: Input different flood parameters, such as rainfall duration and intensity, to visualize potential flood extents and impacts.
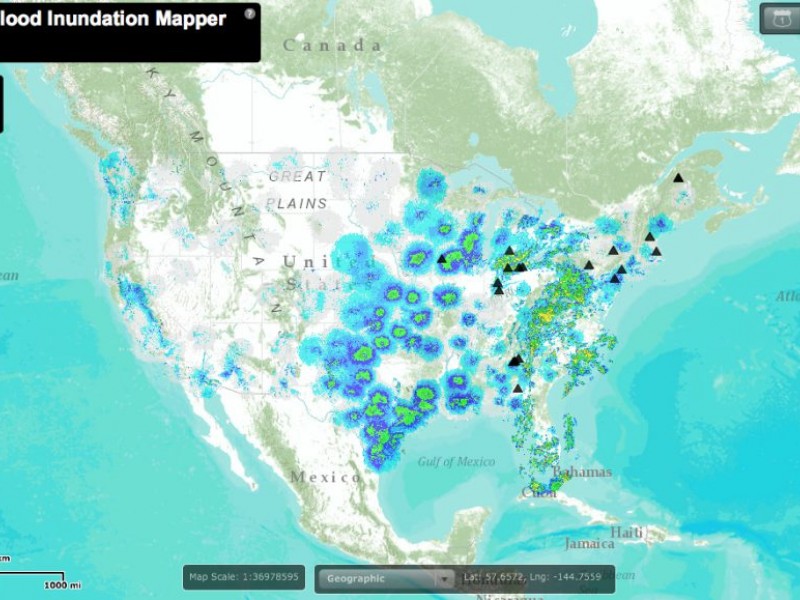
- View real-time data: Access live data feeds, including river levels, rainfall gauges, and weather forecasts, for immediate insights into current conditions.
Benefits of Using Interactive Flood Maps
Interactive flood maps offer a multitude of benefits for individuals, communities, and organizations, including:
- Enhanced Awareness: Visualizing flood risk through interactive maps promotes public awareness and understanding of potential hazards. This knowledge empowers individuals and communities to take proactive measures for flood preparedness.
- Improved Planning and Mitigation: By analyzing flood data and simulating scenarios, communities can effectively plan infrastructure development, identify vulnerable areas, and implement mitigation strategies to reduce flood impacts.
- Efficient Response and Recovery: Interactive maps provide crucial information for emergency responders during flood events, enabling them to prioritize rescue efforts, allocate resources effectively, and navigate affected areas safely.
- Informed Decision-Making: These maps support informed decision-making for various stakeholders, including property owners, insurance companies, and government agencies, by providing data-driven insights into flood risk and its potential financial and social implications.
- Community Resilience: Interactive flood maps foster community resilience by empowering residents to understand their individual risks, participate in preparedness initiatives, and contribute to a safer and more resilient community.
Key Features of Interactive Flood Maps
Interactive flood maps are equipped with various features that enhance their functionality and usefulness:
- Historical Flood Data: Maps often incorporate historical flood data, including flood extents, water depths, and flood frequencies, to provide a historical perspective on flood risk.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Integrating real-time data feeds from weather stations, river gauges, and other sensors allows users to monitor current conditions and receive timely alerts.
- Flood Modeling Capabilities: Advanced hydrological models simulate flood scenarios based on various input parameters, such as rainfall intensity, river flow, and terrain elevation.
- Customizable Views: Users can customize map views to focus on specific areas, layer different data sets, and adjust display settings to meet their individual needs.
- Interactive Tools: Features like zoom, pan, and measurement tools enable users to explore maps in detail, analyze specific areas, and measure distances and areas.
- Accessibility and User-Friendliness: Interactive flood maps are designed for accessibility and ease of use, allowing users with varying levels of technical expertise to navigate and understand the information presented.
Applications of Interactive Flood Maps
Interactive flood maps find applications across various sectors and domains:
- Emergency Management: Emergency responders use flood maps to identify affected areas, assess damage, and plan rescue and evacuation operations.
- Urban Planning: Planners use flood maps to guide development projects, identify vulnerable areas, and incorporate flood mitigation measures into infrastructure designs.
- Insurance Industry: Insurance companies use flood maps to assess risk, determine premiums, and develop flood insurance policies.
- Property Owners: Individuals can use flood maps to understand their property’s flood risk, make informed purchase decisions, and take preventative measures.
- Environmental Management: Environmental agencies use flood maps to monitor flood events, assess environmental impacts, and manage water resources.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How accurate are interactive flood maps?
A: The accuracy of interactive flood maps depends on the quality and availability of data used in their development. Maps based on high-resolution data, accurate elevation models, and validated hydrological models tend to be more accurate. However, it’s important to note that flood modeling involves inherent uncertainties, and maps should be used as a tool for risk assessment rather than a definitive prediction.
Q2: What data sources are used to create interactive flood maps?
A: Interactive flood maps utilize various data sources, including:
- Topographic Data: Elevation data from sources like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) provides accurate terrain information for flood modeling.
- Hydrological Data: River flow data, rainfall data, and other hydrological data are used to simulate flood scenarios.
- Historical Flood Data: Records of past flood events, including flood extents and water depths, provide valuable insights into flood risk.
- Land Use Data: Information on land cover, such as urban areas, forests, and agricultural land, influences flood modeling by affecting water infiltration and runoff.
Q3: Are interactive flood maps available for all areas?
A: The availability of interactive flood maps varies depending on the geographic area and the availability of data. Some areas may have comprehensive flood maps, while others may have limited or no data. It’s essential to check the availability and coverage of maps for specific areas.
Q4: Can I use interactive flood maps to predict future flood events?
A: While interactive flood maps can simulate flood scenarios based on different parameters, they cannot predict future events with absolute certainty. Flood modeling involves inherent uncertainties related to climate variability, rainfall patterns, and other factors. Maps should be used as a tool for risk assessment and preparedness, not for definitive prediction.
Q5: How can I access interactive flood maps?
A: Interactive flood maps are often available through:
- Government Agencies: Many government agencies, such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the United States, provide interactive flood maps on their websites.
- Private Companies: Several private companies specialize in flood risk assessment and provide interactive maps as part of their services.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research institutions often develop and maintain interactive flood maps for specific areas or research purposes.
Tips for Using Interactive Flood Maps Effectively
- Understand map limitations: Remember that flood maps are tools for risk assessment and not definitive predictions. They are based on available data and modeling assumptions, which may have limitations.
- Consider multiple data sources: Compare flood maps from different sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of flood risk.
- Consult with experts: Seek guidance from flood risk experts or emergency management professionals to interpret map results and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Stay informed about updates: Flood maps are constantly being updated with new data and modeling improvements. Check for updates regularly to ensure you have the most accurate information.
- Integrate maps into preparedness plans: Use flood map data to develop and refine flood preparedness plans, including evacuation routes, emergency supplies, and communication strategies.
Conclusion
Interactive flood maps are invaluable tools for understanding, preparing for, and mitigating flood risks. By providing visual representations of flood hazards, simulating scenarios, and integrating real-time data, these maps empower individuals, communities, and organizations to make informed decisions, plan effectively, and enhance resilience in the face of flood events. As climate change continues to exacerbate flood risks, the importance of interactive flood maps will only grow, serving as a vital resource for building safer and more resilient communities.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Interactive Flood Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
