Understanding the Power of Background Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of Background Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of Background Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of Background Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of data visualization and spatial analysis, background maps serve as the foundational layer, providing context and enhancing the understanding of geographic data. These maps, often referred to as base maps, are essential tools for researchers, analysts, and decision-makers across various fields, from urban planning and environmental monitoring to market research and public health.
What is a Background Map?
A background map, or base map, is a visual representation of geographical features that provides a reference framework for overlaying and analyzing other data. It typically includes elements like:
- Landforms: Mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, and coastlines.
- Political Boundaries: Countries, states, counties, and cities.
- Transportation Networks: Roads, highways, railways, and airports.
- Hydrographic Features: Rivers, lakes, oceans, and seas.
- Urban Features: Buildings, parks, and infrastructure.
Types of Background Maps:
Background maps come in various types, each offering unique functionalities and visual styles:
- Topographic Maps: These maps emphasize elevation and terrain features, using contour lines and shading to depict landforms.
- Political Maps: Focusing on administrative boundaries, these maps showcase countries, states, and cities, often highlighting specific regions or territories.
- Road Maps: Primarily designed for navigation, these maps display road networks, highways, and major cities.
- Satellite Imagery Maps: Derived from satellite data, these maps offer high-resolution views of the Earth’s surface, capturing details like vegetation, land use, and urban development.
- Aerial Photography Maps: Similar to satellite imagery, aerial photographs provide a bird’s-eye view of the terrain, revealing detailed features and structures.
The Importance of Background Maps:
Background maps are crucial for various reasons:
- Contextualization: They provide a spatial framework, anchoring data points and visualizations to their geographical location, enabling better understanding and interpretation.
- Visualization: They enhance data visualization by offering a clear and intuitive visual representation of geographic relationships and patterns.
- Analysis: They facilitate spatial analysis, allowing researchers to explore relationships between data and geographic features, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
- Communication: They effectively communicate complex spatial information to diverse audiences, promoting understanding and collaboration.
Benefits of Using Background Maps:
- Enhanced Data Interpretation: Background maps provide a visual context that enhances data comprehension, enabling users to identify spatial patterns, anomalies, and trends.
- Improved Decision-Making: By integrating data with geographical context, background maps support informed decision-making in areas like resource management, urban planning, and disaster preparedness.
- Effective Communication: They facilitate clear and concise communication of spatial information, making complex data accessible to a broader audience.
- Increased Efficiency: Background maps streamline data analysis and visualization processes, saving time and resources.
Examples of Background Map Applications:
- Urban Planning: Background maps are used to analyze urban growth patterns, identify areas for development, and optimize infrastructure planning.
- Environmental Monitoring: They help track deforestation, monitor pollution levels, and assess the impact of climate change on ecosystems.
- Market Research: Background maps assist in analyzing consumer demographics, identifying market opportunities, and optimizing marketing campaigns.
- Public Health: They are used to track disease outbreaks, identify risk factors, and develop targeted public health interventions.
- Disaster Response: Background maps are essential tools for disaster preparedness, providing real-time information on affected areas and facilitating efficient relief efforts.
FAQs about Background Maps:
Q: What are the best sources for obtaining background maps?
A: There are numerous sources for acquiring background maps, including:
- Government Agencies: Agencies like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) offer a wide range of free and open-source maps.
- Commercial Map Providers: Companies like Esri, Google Maps, and Mapbox provide high-quality maps with advanced functionalities, often available through subscription services.
- Open-Source Data Repositories: Platforms like OpenStreetMap (OSM) offer crowdsourced map data that can be freely accessed and used.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when choosing a background map?
A: Selecting the right background map depends on your specific needs and requirements:
- Purpose: The map’s intended use will influence the type of map needed, such as topographic, political, or road maps.
- Scale: The level of detail required for your analysis will determine the appropriate map scale.
- Data Availability: Ensure the map provides the necessary data layers and information relevant to your analysis.
- Accuracy and Reliability: Choose maps from reputable sources with high accuracy and reliability.
- Compatibility: Verify that the map format and data structure are compatible with your software and analysis tools.
Q: How can I effectively use background maps in my research or analysis?
A: To leverage the full potential of background maps, consider the following tips:
- Define your Objectives: Clearly identify your research questions or analysis goals before selecting a background map.
- Choose the Appropriate Map Type: Select a map that aligns with your specific needs and data requirements.
- Overlay Data Layers: Integrate your data points or visualizations onto the background map to visualize spatial relationships.
- Utilize Map Tools: Explore the various tools and functionalities offered by map software to enhance analysis and visualization.
- Communicate Effectively: Present your findings clearly and concisely, using maps to illustrate key insights and support your conclusions.
Conclusion:
Background maps are indispensable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and communicating geographic data. They provide a crucial foundation for understanding spatial relationships, identifying trends, and making informed decisions across various fields. By understanding the different types of background maps, their benefits, and effective usage strategies, researchers, analysts, and decision-makers can unlock the power of spatial information to address complex challenges and drive innovation.

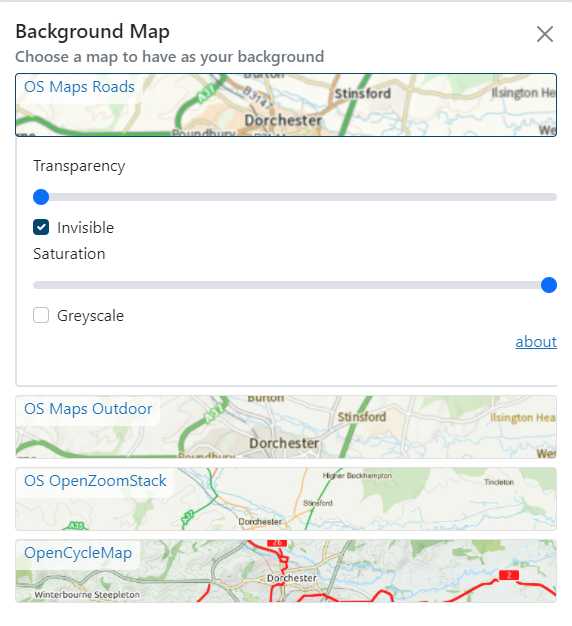




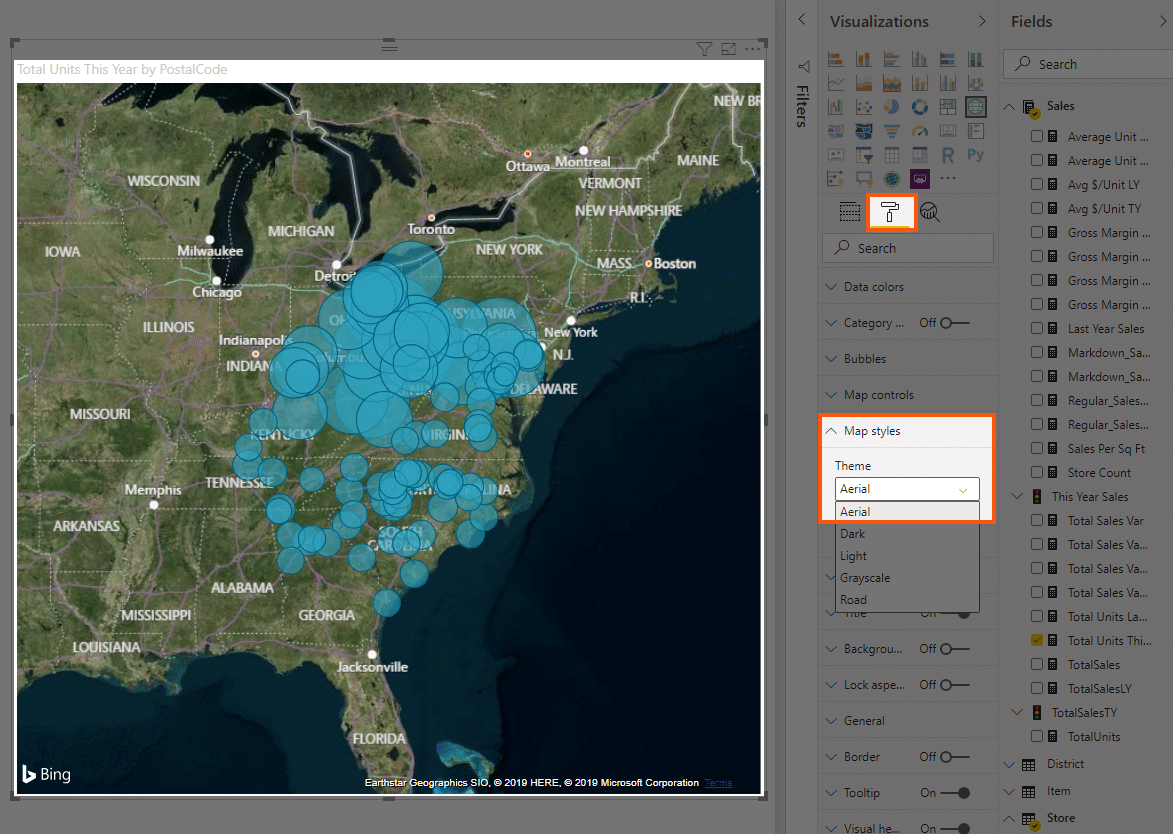
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of Background Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
