Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing
Related Articles: Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing
- 3.1 What is the KP Index?
- 3.2 How is the KP Index Measured?
- 3.3 Understanding the KP Index and Aurora Visibility
- 3.4 Utilizing the KP Index for Aurora Viewing
- 3.5 FAQs about the KP Index and Aurora Viewing
- 3.6 Tips for Aurora Viewing
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing
The aurora borealis, commonly known as the Northern Lights, is a captivating celestial spectacle that draws tourists and scientists alike. However, witnessing this natural light show is not a guaranteed experience. Predicting the intensity and location of auroral displays requires understanding the KP index, a vital tool for aurora enthusiasts.
What is the KP Index?
The KP index, short for "planetary K-index," is a numerical scale that measures the intensity of geomagnetic storms. These storms are caused by disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field, primarily due to solar activity. The sun constantly emits a stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. When these particles interact with Earth’s magnetic field, they can trigger auroras.
The KP index ranges from 0 to 9, with higher values indicating stronger geomagnetic storms and therefore a higher likelihood of auroral activity. Each number corresponds to a specific level of geomagnetic disturbance, with each level associated with a different intensity of auroral activity.
How is the KP Index Measured?
The KP index is determined by a network of ground-based magnetometers strategically placed around the world. These instruments measure the strength and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field. The data collected from these magnetometers is then analyzed to calculate the KP index, which is updated every three hours.
Understanding the KP Index and Aurora Visibility
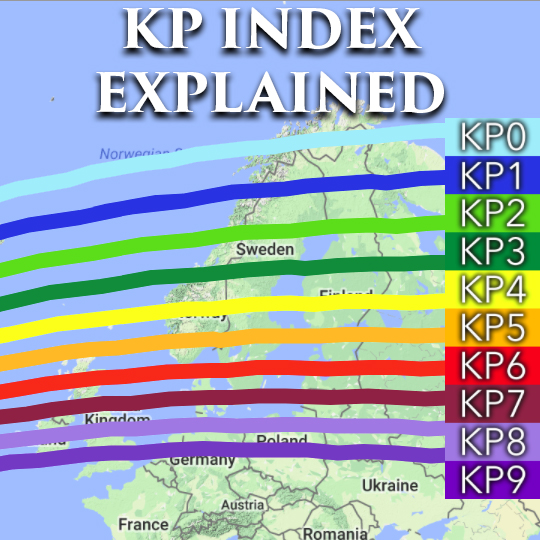
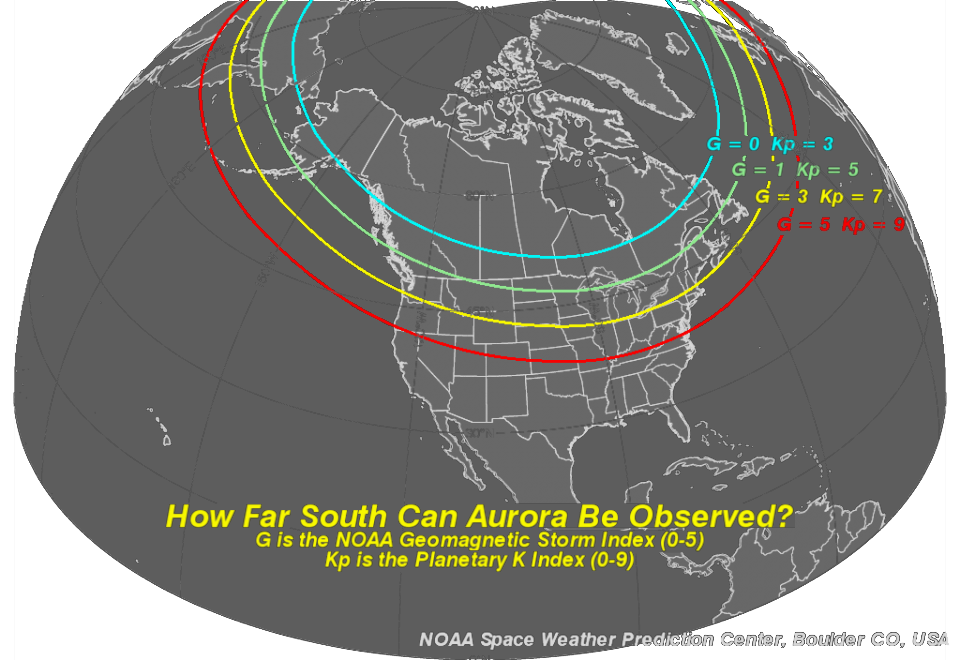
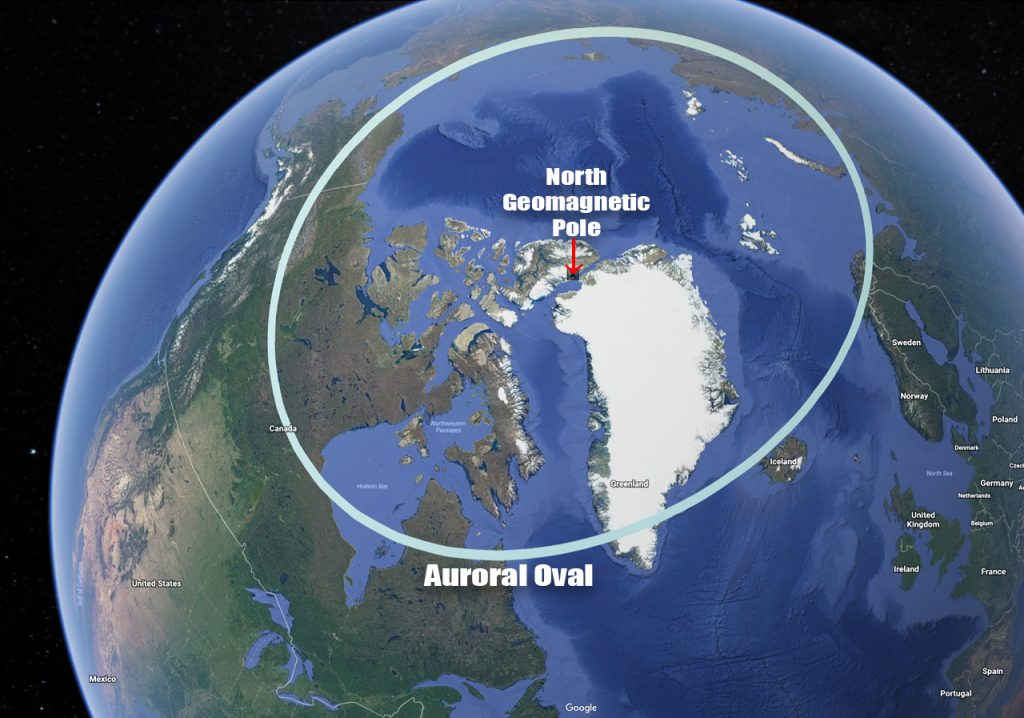
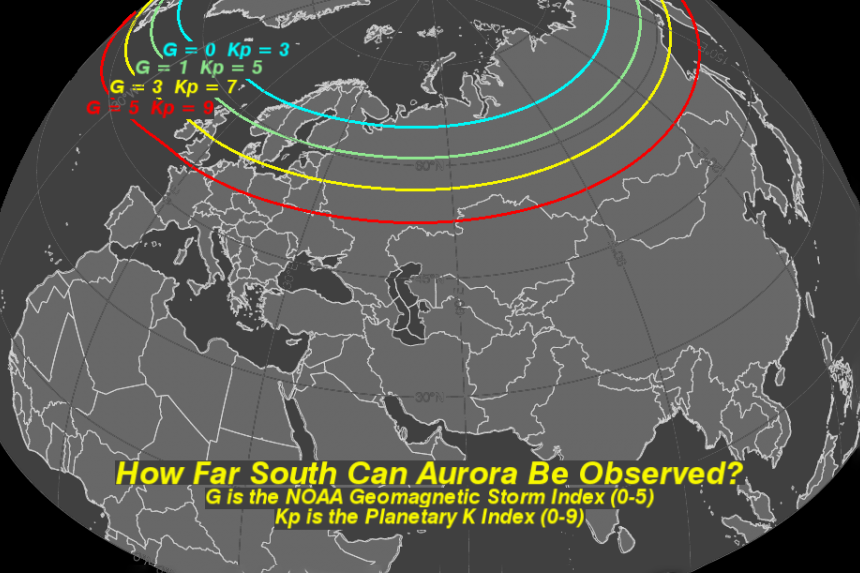
The KP index is a crucial tool for predicting aurora visibility, as it provides an indication of the strength of the geomagnetic storm. The higher the KP index, the further south the auroral oval extends, making it visible from lower latitudes.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the KP index and its corresponding aurora visibility:
- KP 0-2: Weak auroral activity, generally only visible at high latitudes near the Arctic Circle.
- KP 3-4: Moderate auroral activity, visible at higher latitudes and potentially visible from lower latitudes during periods of intense activity.
- KP 5-6: Strong auroral activity, visible from lower latitudes, potentially reaching as far south as the northern United States and southern Canada.
- KP 7-9: Very strong auroral activity, visible from even lower latitudes, potentially reaching as far south as the mid-latitudes.
It’s important to note that the KP index is just one factor influencing aurora visibility. Other factors, such as cloud cover, light pollution, and the time of year, can also play a role.
Utilizing the KP Index for Aurora Viewing
The KP index is a valuable tool for aurora enthusiasts, providing a reliable way to track geomagnetic activity and predict the likelihood of auroral displays. Here are some ways to utilize the KP index for optimal aurora viewing:
- Check the KP index forecast: Several websites and apps provide real-time and forecasted KP index values.
- Plan your trip accordingly: Based on the forecasted KP index, you can choose a location with a higher chance of auroral activity.
- Be patient: Even with a high KP index, auroras can be unpredictable. It’s important to be patient and observe the sky for extended periods.
- Consider using an aurora app: Many apps utilize the KP index, weather data, and other factors to provide personalized aurora forecasts.
FAQs about the KP Index and Aurora Viewing
Q: What is the best time of year to see the aurora borealis?
A: The best time to see the aurora borealis is during the winter months, from September to April. During this time, the nights are longer and darker, providing optimal viewing conditions.
Q: How can I find the best location to see the aurora borealis?
A: The best locations for aurora viewing are typically in the high latitudes near the Arctic Circle. Popular destinations include Alaska, Canada, Norway, Iceland, Greenland, and Finland.
Q: What is the difference between the KP index and the Kp index?
A: There is no difference between the KP index and the Kp index. Both are the same scale, with "Kp" being the official abbreviation.
Q: Is the KP index a perfect predictor of auroral activity?
A: The KP index is a reliable indicator of geomagnetic activity, but it’s not a perfect predictor of auroral activity. Other factors, such as cloud cover and light pollution, can also influence visibility.
Q: What happens during a geomagnetic storm?
A: Geomagnetic storms are caused by disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field, primarily due to solar activity. These storms can disrupt satellite communications, power grids, and even cause auroras to be visible from lower latitudes.
Tips for Aurora Viewing
- Get away from light pollution: Find a location with minimal light pollution, such as a remote area or a national park.
- Dress warmly: Even on a clear night, the temperature can drop significantly, so dress in layers and be prepared for cold conditions.
- Be patient: Auroras can be unpredictable, so be patient and observe the sky for extended periods.
- Use a camera: Capture the beauty of the auroras with a camera equipped with a wide-angle lens and a long exposure setting.
- Learn about the local aurora forecast: Check online resources and apps for local aurora forecasts and predictions.
Conclusion
The KP index is a valuable tool for understanding and predicting auroral activity. By understanding the KP index and its relationship to geomagnetic storms, aurora enthusiasts can plan their trips and maximize their chances of witnessing this breathtaking natural phenomenon. The aurora borealis is a testament to the dynamic nature of our solar system and a reminder of the awe-inspiring beauty of the cosmos.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the KP Index: A Guide to Aurora Viewing. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!