Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness
Related Articles: Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness
- 3.1 The Significance of Flood Risk Zones
- 3.2 Defining Flood Risk Zones: Key Factors
- 3.3 Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Deeper Dive
- 3.4 FAQs: Flood Risk Zones
- 3.5 Tips for Reducing Flood Risk
- 3.6 Conclusion: Flood Risk Zones – A Vital Tool for Resilience
- 4 Closure
Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness

Flooding is a natural phenomenon that can have devastating consequences, causing widespread damage to property, infrastructure, and even loss of life. To mitigate these risks and ensure the safety of communities, flood hazard maps are essential tools used by governments and emergency responders. These maps divide areas into different zones based on their susceptibility to flooding, providing valuable information for planning, development, and emergency response.
This article delves into the significance of flood risk zones, particularly focusing on the factors determining these zones and the implications for residents, businesses, and policymakers. By understanding the nuances of flood risk zones, individuals and communities can make informed decisions to minimize their vulnerability to flooding and enhance their preparedness for such events.
The Significance of Flood Risk Zones
Flood risk zones are not merely geographical classifications; they serve as a critical framework for understanding and managing flood hazards. They provide a visual representation of areas that are at risk from various types of flooding, including:
- Riverine Flooding: Caused by the overflow of rivers and streams due to excessive rainfall or snowmelt.
- Coastal Flooding: Resulting from storm surges, high tides, and tsunamis.
- Urban Flooding: Occurring in urban areas due to inadequate drainage systems, impervious surfaces, and rapid runoff.
- Flash Flooding: Sudden and intense flooding that occurs in a short period, often triggered by heavy rainfall.
By identifying areas susceptible to these types of flooding, flood risk zones enable:
- Effective Floodplain Management: Governments and planning authorities can implement regulations to restrict development in high-risk areas, thereby minimizing potential damage and loss of life.
- Targeted Flood Mitigation Measures: Resources can be allocated to implement measures like floodwalls, levees, and drainage improvements in high-risk zones, enhancing flood protection.
- Informed Community Planning: Residents and businesses can make informed decisions about building and development, choosing locations with lower flood risk.
- Efficient Emergency Response: Emergency responders can prioritize resources and evacuation plans based on the severity of flood risk in different zones, ensuring swift and effective assistance.
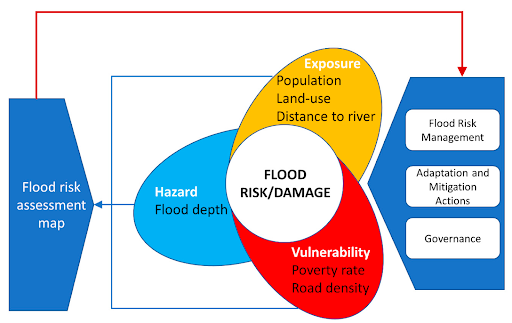
Defining Flood Risk Zones: Key Factors
The delineation of flood risk zones is a complex process involving multiple factors, including:
- Topography: The elevation and slope of the land play a crucial role in determining the flow of water and the likelihood of flooding. Lower-lying areas are more susceptible to flooding, while higher elevations offer greater protection.
- Hydrology: The flow patterns of rivers, streams, and coastal areas influence the extent and intensity of flooding. Factors like river discharge, tidal patterns, and rainfall intensity are considered.
- Land Use: Urban development, deforestation, and agricultural practices can alter the natural drainage patterns, increasing flood risk. Impervious surfaces like roads and parking lots reduce infiltration and increase runoff, exacerbating flooding.
- Historical Flood Data: Analysis of past flood events provides crucial information about flood frequency, duration, and extent, helping to determine flood risk zones.
- Climate Change: Climate change is predicted to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including heavy rainfall and storm surges, leading to greater flood risk in many areas.
Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Deeper Dive
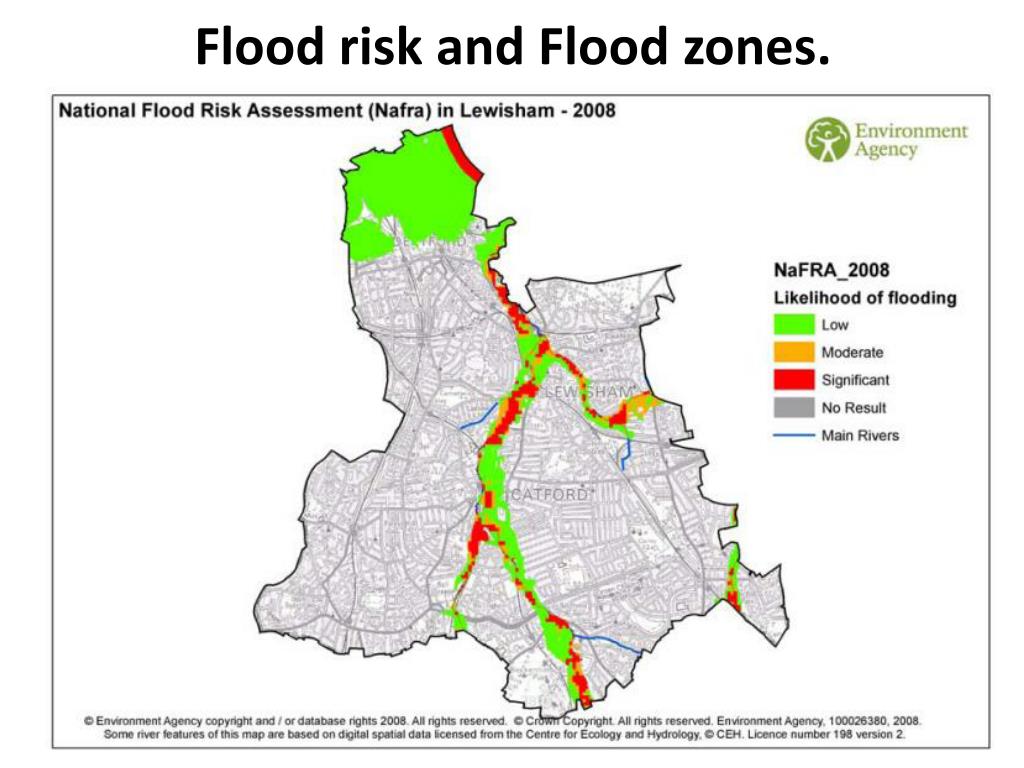
Flood risk zones are often categorized into different levels, typically using letters or numbers to indicate the severity of flood risk. While the specific classification system may vary depending on the region and jurisdiction, the general principle remains the same:
- High-Risk Zones: These areas are most susceptible to flooding and often experience frequent or severe flood events. Development in these zones is typically restricted, and flood mitigation measures are prioritized.
- Moderate-Risk Zones: Areas with a moderate risk of flooding, potentially experiencing occasional flood events. Development in these zones may be permitted with specific flood-resistant design requirements.
- Low-Risk Zones: Areas with a low risk of flooding, potentially experiencing infrequent or minor flood events. Development in these zones is generally less restricted, but flood-resistant design considerations are still recommended.
FAQs: Flood Risk Zones
Q: How can I find out my flood risk zone?
A: Flood risk maps are typically available online through government websites, local planning departments, and insurance providers. You can search for "flood risk map" along with your city or county name to locate the relevant resources.
Q: What are the implications of living in a high-risk flood zone?
A: Living in a high-risk flood zone means you are more vulnerable to flooding and its potential consequences. This may include:
- Increased insurance premiums: Homeowners in high-risk zones often face higher insurance premiums due to the increased risk of damage.
- Stricter building regulations: Development in high-risk zones is often subject to stricter building codes and regulations to ensure flood resistance.
- Potential evacuation requirements: During flood events, residents in high-risk zones may be required to evacuate to safer areas.
Q: Can I purchase flood insurance if I live in a low-risk flood zone?
A: While you may not be required to purchase flood insurance in a low-risk zone, it is still highly recommended. Even areas classified as low-risk can experience unexpected flooding events, and flood insurance can provide financial protection against such occurrences.
Q: What are the responsibilities of homeowners in flood risk zones?
A: Homeowners in flood risk zones have a responsibility to take steps to mitigate their vulnerability to flooding. This includes:
- Elevating structures: Elevating homes above the predicted flood level can significantly reduce damage during flood events.
- Installing flood barriers: Flood barriers such as sandbags and flood-resistant doors can help prevent water from entering the home.
- Maintaining drainage systems: Regularly cleaning gutters and downspouts can prevent water from pooling around the foundation.
- Developing a flood preparedness plan: Having a plan in place for evacuating, securing belongings, and contacting emergency services can ensure a smooth response during a flood event.
Tips for Reducing Flood Risk
- Consider the impact of climate change: As climate change intensifies, flood risk is likely to increase. Be prepared for potential changes in flood patterns and consider incorporating climate change adaptation measures into your planning.
- Engage with your community: Participate in local flood mitigation projects and advocate for policies that address flood risk.
- Stay informed about flood warnings: Monitor weather forecasts and be aware of flood warnings issued by local authorities.
- Be proactive in your flood preparedness: Develop a comprehensive flood preparedness plan that includes evacuation routes, emergency supplies, and contact information for emergency services.
Conclusion: Flood Risk Zones – A Vital Tool for Resilience
Flood risk zones are a critical tool for understanding and managing flood hazards. By providing a clear visual representation of flood vulnerability, these maps empower communities, businesses, and policymakers to take proactive steps to reduce flood risk and enhance resilience. Understanding your flood risk zone is essential for making informed decisions about building, development, and emergency preparedness. By taking steps to mitigate flood risk and preparing for potential events, we can create safer and more resilient communities for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Flood Risk Zones: A Guide to Safety and Preparedness. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
