The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Related Articles: The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
- 3.1 Tracing the Course of the Tigris
- 3.2 Geographic Significance: A Lifeline for Life and Civilization
- 3.3 Navigating the Tigris: A Journey Through Time
- 3.4 The Tigris River: A Source of Inspiration and Hope
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions about the Tigris River
- 5 Tips for Understanding the Tigris River’s Significance
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Closure
The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography

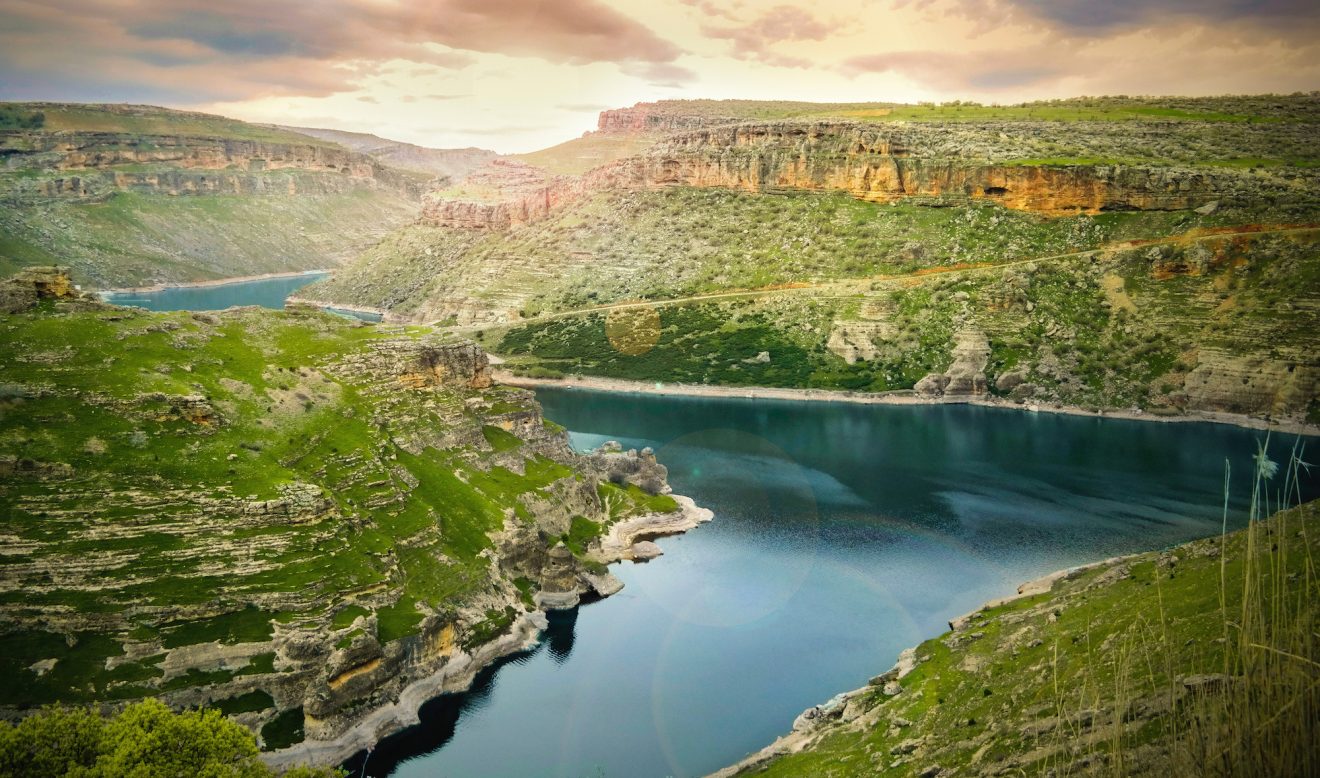
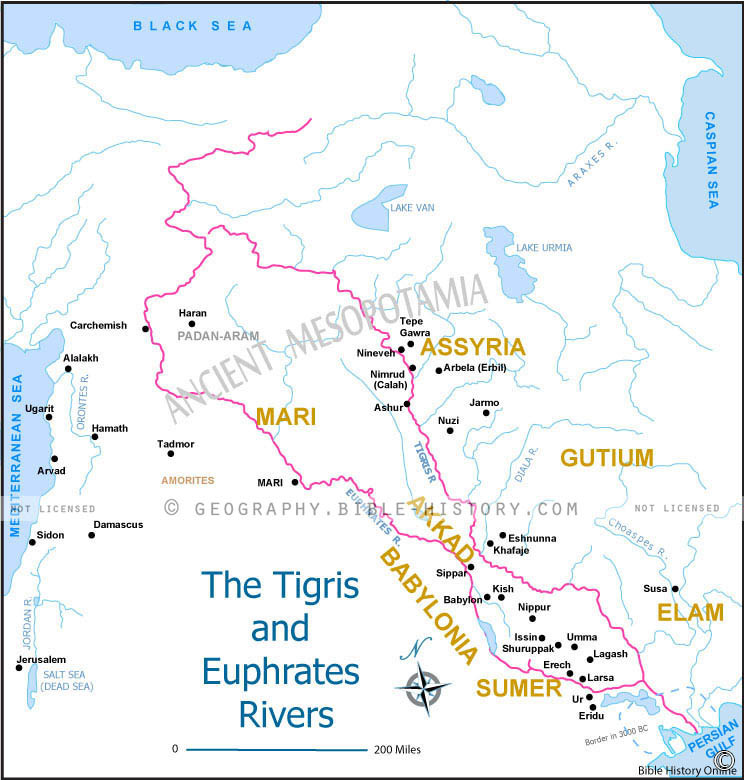
The Tigris River, a vital artery of the Middle East, has played a pivotal role in shaping the history, culture, and landscape of the region for millennia. Its journey, winding through mountains, plains, and deserts, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the development of civilizations, and the evolution of diverse ecosystems. Understanding the Tigris River’s location on a map is crucial for comprehending its profound impact on the region’s past, present, and future.
Tracing the Course of the Tigris
The Tigris River originates in the Taurus Mountains of southeastern Turkey, where it springs from the confluence of two tributaries: the Eastern and Western Tigris. From its source, it flows southeastward through Turkey, forming a natural boundary between the Anatolian Plateau and the Mesopotamian Plain.
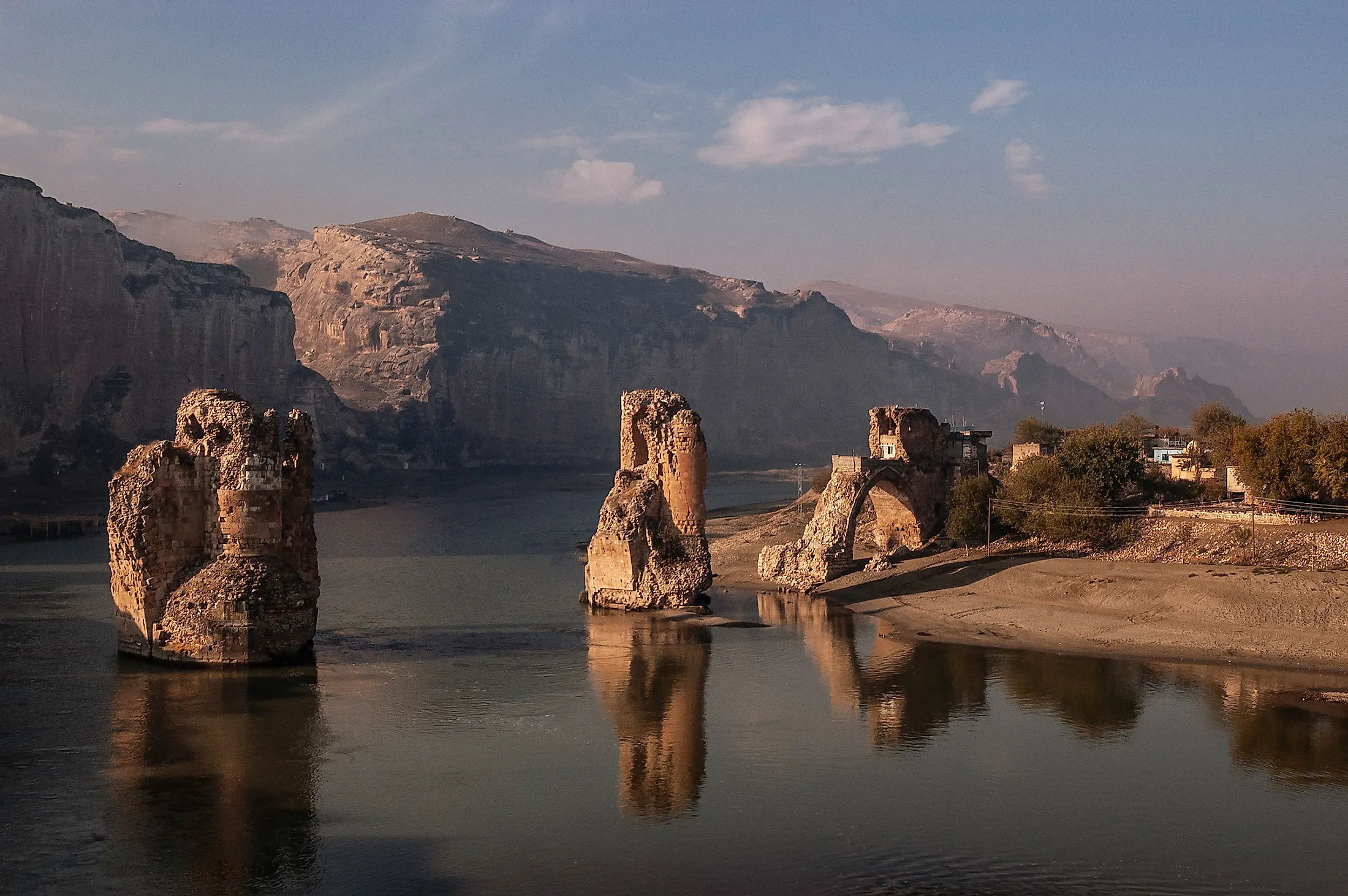
Upon entering Iraq, the Tigris River traverses a fertile valley, providing water for agriculture and supporting a dense population. Its path then winds through the ancient city of Baghdad, the capital of Iraq, before merging with the Euphrates River near the Persian Gulf. This confluence creates the Shatt al-Arab waterway, a critical route for maritime trade and a vital source of freshwater for the surrounding region.
Geographic Significance: A Lifeline for Life and Civilization
The Tigris River’s geographic location is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Water Source: The Tigris River is a primary source of water for a vast region encompassing parts of Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. Its waters sustain agricultural production, provide drinking water for millions, and support a diverse ecosystem.
- Transportation Route: Historically, the Tigris River served as a vital transportation route, connecting cities and facilitating trade within the region. While its use for commercial navigation has declined in modern times, it remains a significant waterway for internal transportation.
- Historical Significance: The Tigris River played a pivotal role in the development of ancient Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization. The fertile land along its banks provided the foundation for early agricultural societies, which led to the rise of city-states, empires, and cultural advancements.
- Ecological Importance: The Tigris River is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including fish, birds, and mammals. Its wetlands and riparian ecosystems provide critical habitat for a variety of species and contribute to the region’s biodiversity.
Navigating the Tigris: A Journey Through Time
Examining the Tigris River on a map reveals its significance as a historical and geographical landmark.
- Ancient Mesopotamia: The Tigris River, along with the Euphrates, formed the heart of ancient Mesopotamia, a region renowned for its early civilizations, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. The fertile plains along the riverbanks witnessed the birth of agriculture, the development of writing, and the establishment of city-states.
- Modern Iraq: The Tigris River continues to be a vital resource for modern Iraq, providing water for irrigation, power generation, and drinking water. Its presence has shaped the country’s urban development, with major cities like Baghdad and Mosul located along its banks.
- Regional Challenges: The Tigris River faces challenges due to water scarcity, pollution, and dam construction. The increasing demand for water resources, coupled with climate change, has put pressure on the river’s flow and its ability to sustain ecosystems.
The Tigris River: A Source of Inspiration and Hope
The Tigris River’s journey through history and geography is a testament to its enduring significance. Its waters have nurtured civilizations, shaped landscapes, and provided a lifeline for millions. Understanding its location on a map is essential for appreciating its impact on the region and its role in shaping the lives of countless people.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Tigris River
Q: What is the length of the Tigris River?
A: The Tigris River is approximately 1,850 kilometers (1,150 miles) long.
Q: Where does the Tigris River flow?
A: The Tigris River flows through Turkey, Syria, and Iraq, ultimately merging with the Euphrates River to form the Shatt al-Arab waterway.
Q: What are the major cities located along the Tigris River?
A: Some of the major cities located along the Tigris River include:
- Turkey: Diyarbakır, Batman, and Silvan.
- Iraq: Baghdad, Mosul, Kirkuk, and Samarra.
Q: What are the main tributaries of the Tigris River?
A: The Tigris River has several major tributaries, including:
- Turkey: The Eastern and Western Tigris, the Murat River, and the Garzan River.
- Iraq: The Great Zab, the Little Zab, the Diyala River, and the Adhaim River.
Q: What are the ecological challenges facing the Tigris River?
A: The Tigris River faces several ecological challenges, including:
- Water Scarcity: Increasing demand for water resources, coupled with climate change, has led to water scarcity in the Tigris River basin.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities have contributed to pollution in the river, threatening its water quality and biodiversity.
- Dam Construction: The construction of dams along the Tigris River has disrupted natural flow patterns and impacted downstream ecosystems.
Q: What are the cultural and historical significance of the Tigris River?
A: The Tigris River has played a vital role in shaping the history, culture, and civilizations of the region. It was a key factor in the development of ancient Mesopotamia, the birthplace of agriculture, writing, and urban life. The river has also been a source of inspiration for art, literature, and folklore throughout the centuries.
Tips for Understanding the Tigris River’s Significance
- Study a map: Use a physical or online map to visualize the Tigris River’s course and its relationship to surrounding regions.
- Explore historical resources: Read books, articles, and online materials about the history of ancient Mesopotamia and the role of the Tigris River in its development.
- Visit the Tigris River basin: If possible, travel to the Tigris River basin and experience its beauty and significance firsthand.
- Engage with local communities: Talk to people living near the Tigris River to understand its importance in their lives and the challenges they face.
- Support conservation efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect the Tigris River and its ecosystems.
Conclusion
The Tigris River, a testament to the power and resilience of nature, has played a pivotal role in shaping the history, culture, and landscape of the Middle East. Its location on a map is a reminder of its enduring importance as a source of life, a symbol of civilization, and a vital resource for the region’s future. Understanding its geographical significance, historical legacy, and present-day challenges is crucial for ensuring its continued relevance and protecting its vital role in sustaining the region’s ecosystems and communities.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Tigris River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
