The Siege of Alesia: A Turning Point in Roman History
Related Articles: The Siege of Alesia: A Turning Point in Roman History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Siege of Alesia: A Turning Point in Roman History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Siege of Alesia: A Turning Point in Roman History

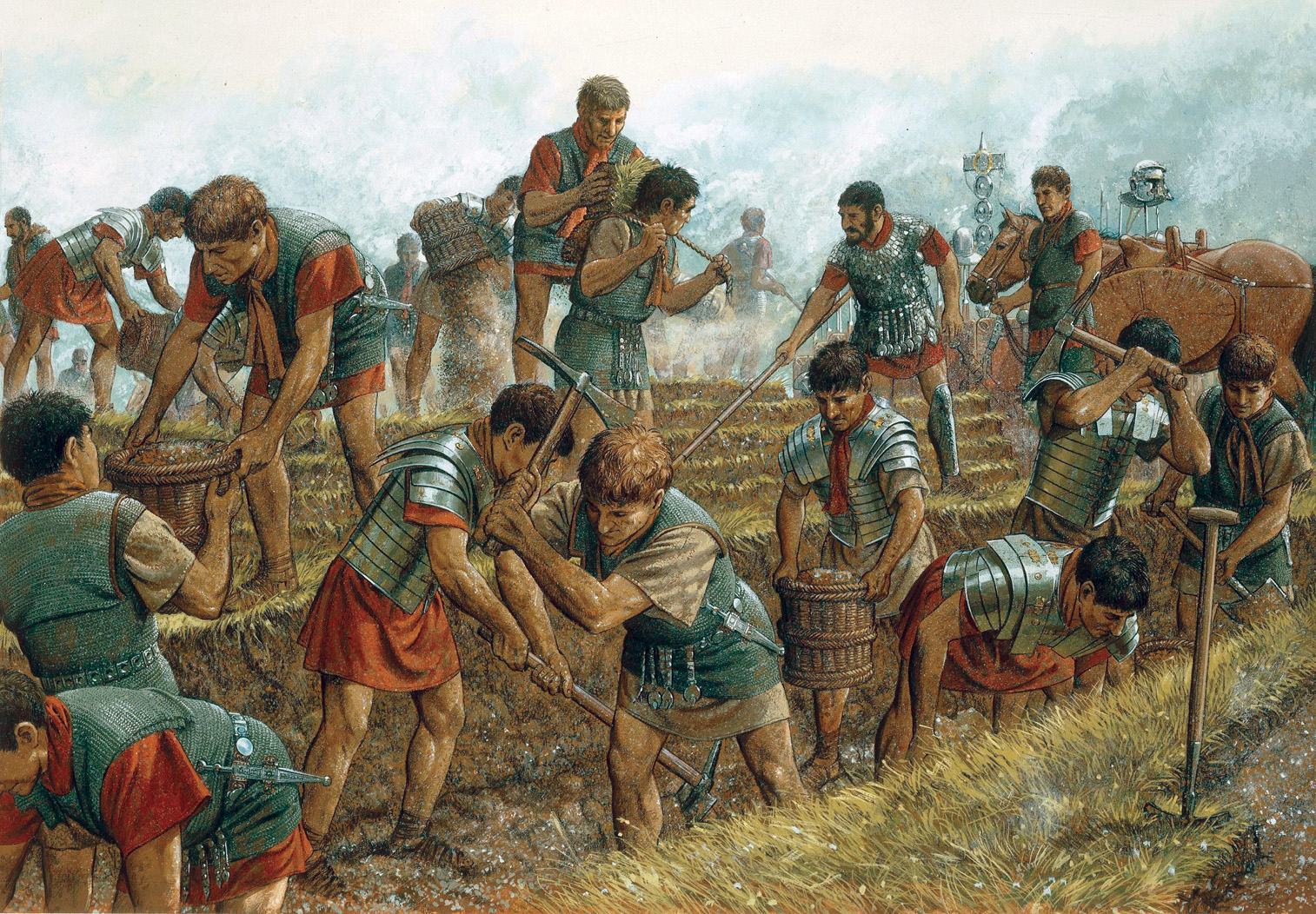
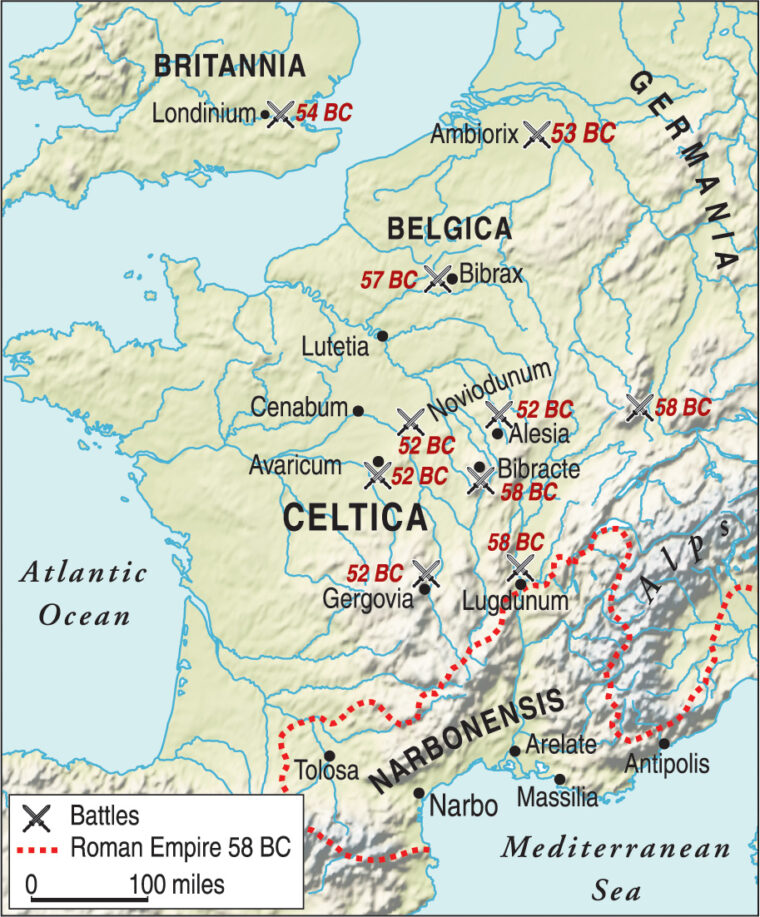
The Battle of Alesia, fought in 52 BCE, stands as a pivotal moment in Roman history, marking the culmination of Julius Caesar’s Gallic Wars and the decisive defeat of the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix. This clash, which unfolded near the present-day village of Alise-Sainte-Reine in Burgundy, France, involved a complex series of maneuvers and fortifications, making it one of the most strategically intricate battles in ancient warfare.
Understanding the Battlefield: A Visual Guide
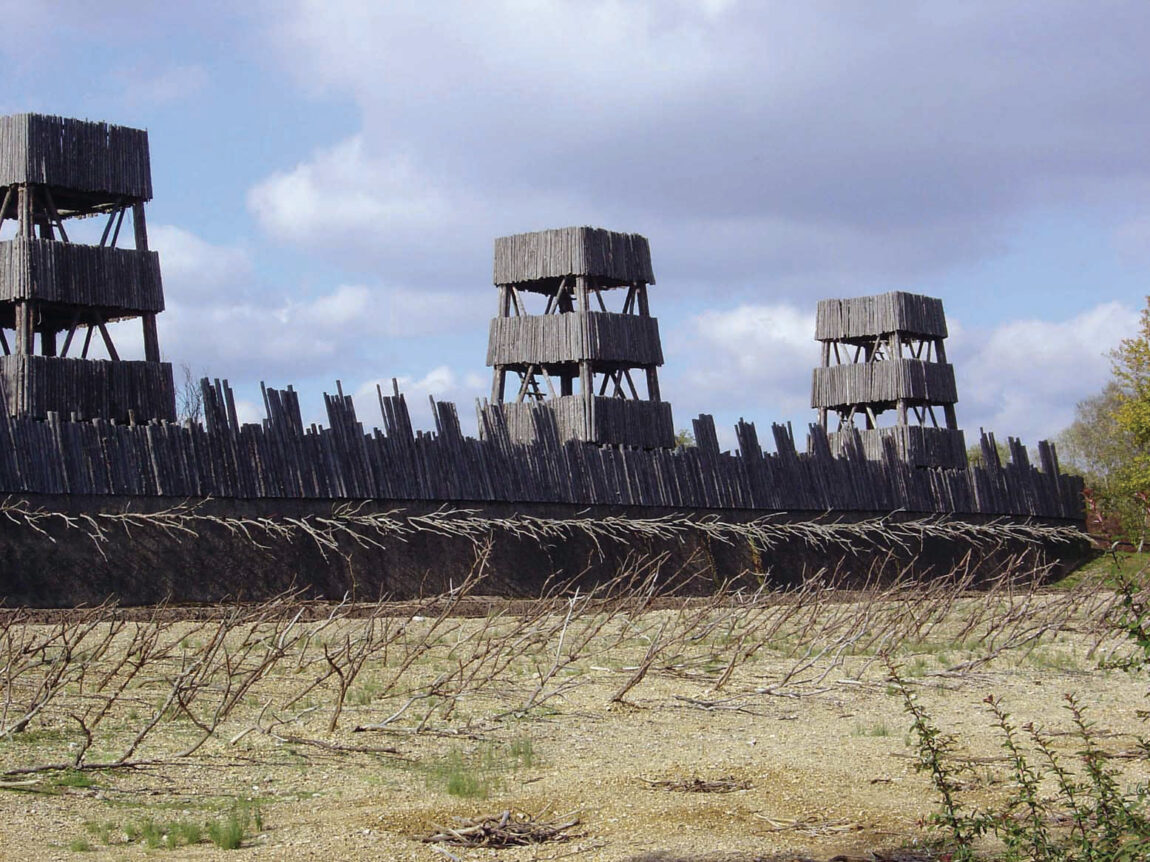
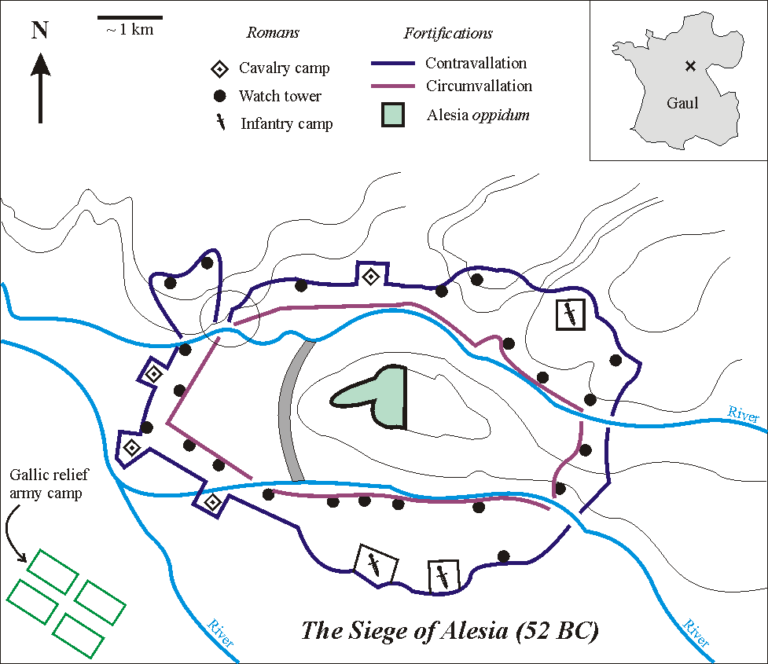
To grasp the significance of Alesia, it’s crucial to visualize the battleground. The site, nestled within a ring of hills, offered both strategic advantages and challenges. The Gauls, under Vercingetorix, chose this location for its natural defenses, establishing a fortified camp on the plateau atop the hill. This camp, boasting formidable ramparts and a large garrison, served as the heart of their resistance.
Caesar, understanding the strength of the Gallic position, responded with a masterful display of military engineering. He established his own camp, a massive fortified enclosure, at the base of the hill, surrounding the entire Gallic camp. This strategic maneuver effectively cut off Vercingetorix’s army from any potential reinforcements or supplies.
A Map Unveils the Tactics
The Battle of Alesia map, a visual representation of the battlefield, reveals the intricate web of fortifications and siege lines that shaped the battle. It highlights:
- Gallic Camp: The fortified plateau, with its ramparts and garrison, serving as Vercingetorix’s stronghold.
- Roman Camp: Caesar’s massive fortified enclosure at the base of the hill, encircling the Gallic camp.
- Siege Lines: The network of trenches, ditches, and fortifications built by the Romans to isolate and attack the Gallic camp.
- Relief Force: The Gallic reinforcements, led by Vercingetorix’s allies, attempting to break through the Roman lines.
Beyond the Map: The Battle’s Dynamics
The Battle of Alesia was not a single, decisive clash but a series of strategic maneuvers and skirmishes. Caesar’s strategy focused on isolating the Gallic camp and preventing any reinforcements from reaching Vercingetorix. He employed a combination of siege warfare, utilizing siege engines and battering rams to weaken the Gallic defenses, and strategic maneuvers to block any potential relief forces.
The Gauls, under Vercingetorix, fought valiantly, launching sorties from their camp and attempting to break through the Roman lines. However, they were ultimately outmatched by the Romans’ superior military organization and engineering prowess.
The Significance of the Battle
The Battle of Alesia holds immense significance for several reasons:
- End of Gallic Resistance: The battle marked the end of organized Gallic resistance against Roman rule. Vercingetorix’s capture and subsequent execution symbolized the crushing defeat of the Gallic tribes.
- Expansion of Roman Power: The victory at Alesia solidified Roman control over Gaul, expanding the Roman Empire’s territory and resources.
- Military Innovation: Caesar’s innovative use of siege warfare and strategic maneuvers at Alesia became a model for future Roman military campaigns.
- Historical Legacy: The Battle of Alesia remains a testament to Roman military genius and a pivotal moment in the shaping of Western civilization.
FAQs about the Battle of Alesia
Q: How long did the Battle of Alesia last?
A: The siege of Alesia lasted for approximately two months, from late June to late August of 52 BCE.
Q: What was the size of the opposing armies?
A: Estimates vary, but the Gallic force is believed to have numbered around 80,000, while the Roman army is estimated to have been around 60,000.
Q: How did Caesar defeat the Gauls at Alesia?
A: Caesar’s victory was a result of his strategic genius, utilizing a combination of siege warfare, strategic maneuvers, and superior military organization to isolate and defeat the Gallic forces.
Q: What happened to Vercingetorix after the battle?
A: Vercingetorix was captured by the Romans and brought to Rome, where he was paraded in Caesar’s triumphal procession and later executed.
Tips for Studying the Battle of Alesia
- Visualize the Battlefield: Use maps and 3D models to understand the terrain and layout of the battleground.
- Study Primary Sources: Examine Caesar’s own account of the battle in his "Commentaries on the Gallic War" for a firsthand perspective.
- Explore Secondary Sources: Consult scholarly works on the Gallic Wars and the Battle of Alesia for deeper analysis and interpretation.
- Compare and Contrast: Analyze the strategies and tactics employed by both the Romans and the Gauls to understand the factors that led to the Roman victory.
Conclusion
The Battle of Alesia stands as a pivotal event in Roman history, marking the end of organized Gallic resistance and solidifying Roman control over Gaul. The battle’s legacy extends beyond military victory, highlighting Roman military innovation, strategic genius, and the impact of warfare on the shaping of Western civilization. By studying the battle and its complexities, we gain a deeper understanding of the Roman Republic’s rise to power and the dynamics of ancient warfare. The Battle of Alesia, through its map, its strategies, and its consequences, remains a captivating testament to the power of human ingenuity and the enduring impact of historical events.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Siege of Alesia: A Turning Point in Roman History. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
