Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Power of 3D Model Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Power of 3D Model Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Power of 3D Model Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Power of 3D Model Maps

The world around us is inherently three-dimensional, yet our traditional maps have long been confined to a two-dimensional plane. This limitation has hindered our ability to fully grasp the complexities of our environment, especially in areas like urban planning, architectural design, and environmental analysis. Enter 3D model maps, a revolutionary technology that bridges this gap, offering a transformative approach to visualizing and interacting with the world.
A Deeper Dive into 3D Model Maps
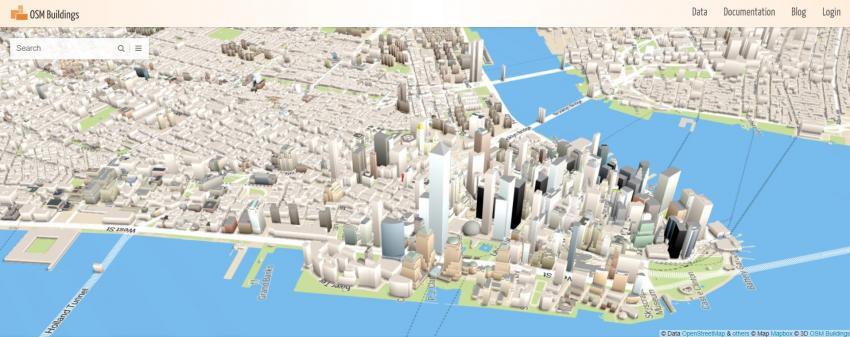
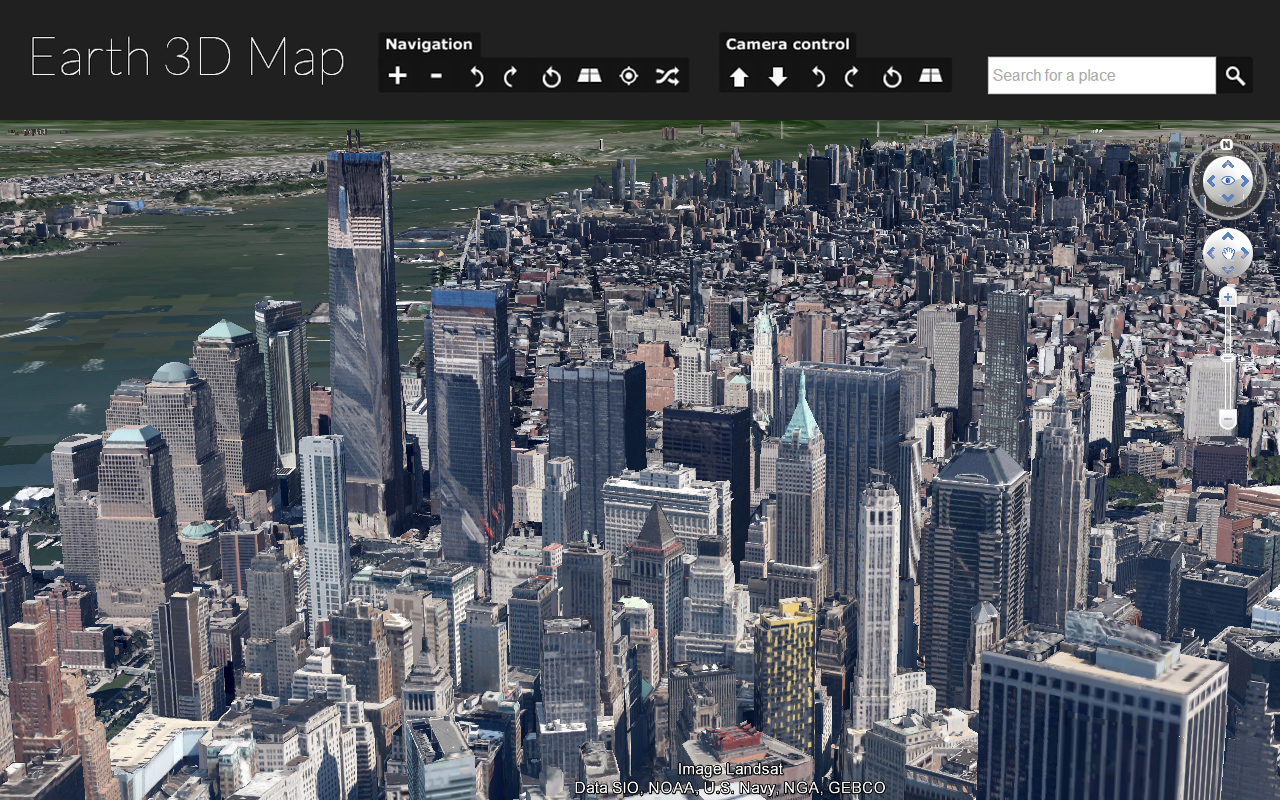
3D model maps are digital representations of real-world environments, built using a combination of data sources such as aerial photography, satellite imagery, laser scanning, and ground surveys. These models are not simply flat images; they are intricate, three-dimensional structures that capture the height, shape, and texture of buildings, terrain, vegetation, and other features.
Understanding the Benefits
The power of 3D model maps lies in their ability to provide a more comprehensive and immersive understanding of the world. Unlike traditional maps, these models offer several key advantages:
- Enhanced Spatial Awareness: By visualizing the environment in three dimensions, users gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships, distances, and the overall layout of a space. This is particularly valuable for urban planners, architects, and engineers who need to assess the impact of new constructions or infrastructure projects.
- Improved Decision-Making: 3D models provide a platform for analyzing data and simulating scenarios, enabling informed decision-making across various sectors. For example, environmental scientists can use 3D models to study the impact of climate change on coastlines, while city planners can evaluate the effectiveness of proposed traffic management strategies.
- Interactive Exploration: Unlike static maps, 3D models allow users to explore the environment interactively, navigating through buildings, streets, and landscapes at their own pace. This immersive experience enhances understanding and fosters a deeper connection with the environment.
- Data Integration and Visualization: 3D models serve as a powerful platform for integrating and visualizing diverse data sets. This allows users to overlay environmental data, traffic information, demographic statistics, and other relevant information directly onto the 3D model, creating a rich and informative context for analysis.
- Communication and Collaboration: 3D models provide a shared platform for communication and collaboration, facilitating the exchange of ideas and information among stakeholders. Architects can present their designs in a visually compelling way, while urban planners can engage the public in discussions about future development plans.
Applications Across Diverse Fields
The applications of 3D model maps extend across various fields, revolutionizing the way we understand, analyze, and interact with our world:
- Urban Planning and Development: 3D models help planners visualize the impact of new buildings, infrastructure projects, and urban renewal initiatives. They can simulate traffic flow, assess accessibility, and evaluate the environmental impact of proposed developments.
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and engineers use 3D models to design buildings, create virtual walkthroughs, and coordinate construction activities. They can also use these models to assess structural integrity, optimize building materials, and improve energy efficiency.
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: Environmental scientists use 3D models to monitor changes in vegetation, track deforestation, assess the impact of climate change, and manage natural resources.
- Disaster Management and Emergency Response: 3D models can be used to simulate natural disasters like floods and earthquakes, helping emergency responders plan evacuation routes, assess damage, and allocate resources effectively.
- Tourism and Cultural Heritage: 3D models allow tourists to virtually explore historical sites and landmarks, providing an immersive and informative experience. Museums and cultural institutions can use these models to showcase exhibits and artifacts in a new and engaging way.
- Military and Defense: 3D models are used for training simulations, mission planning, and intelligence gathering, providing a realistic and interactive environment for military operations.
- Education and Research: 3D model maps are valuable tools for education and research, providing students and researchers with a visual and interactive platform for learning about geography, history, and environmental science.
Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Model Maps
Q: What are the different types of 3D model maps?
A: There are various types of 3D model maps, categorized based on their purpose, data source, and level of detail. Some common types include:
- City Models: These models focus on urban areas, capturing buildings, streets, parks, and other infrastructure.
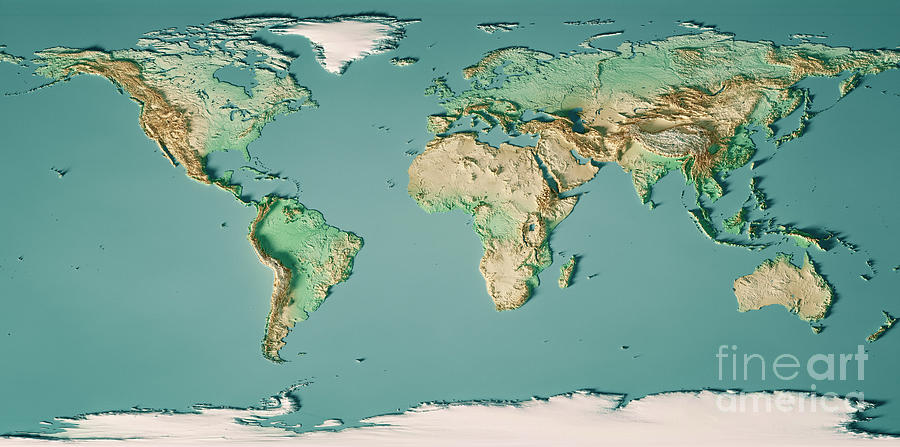
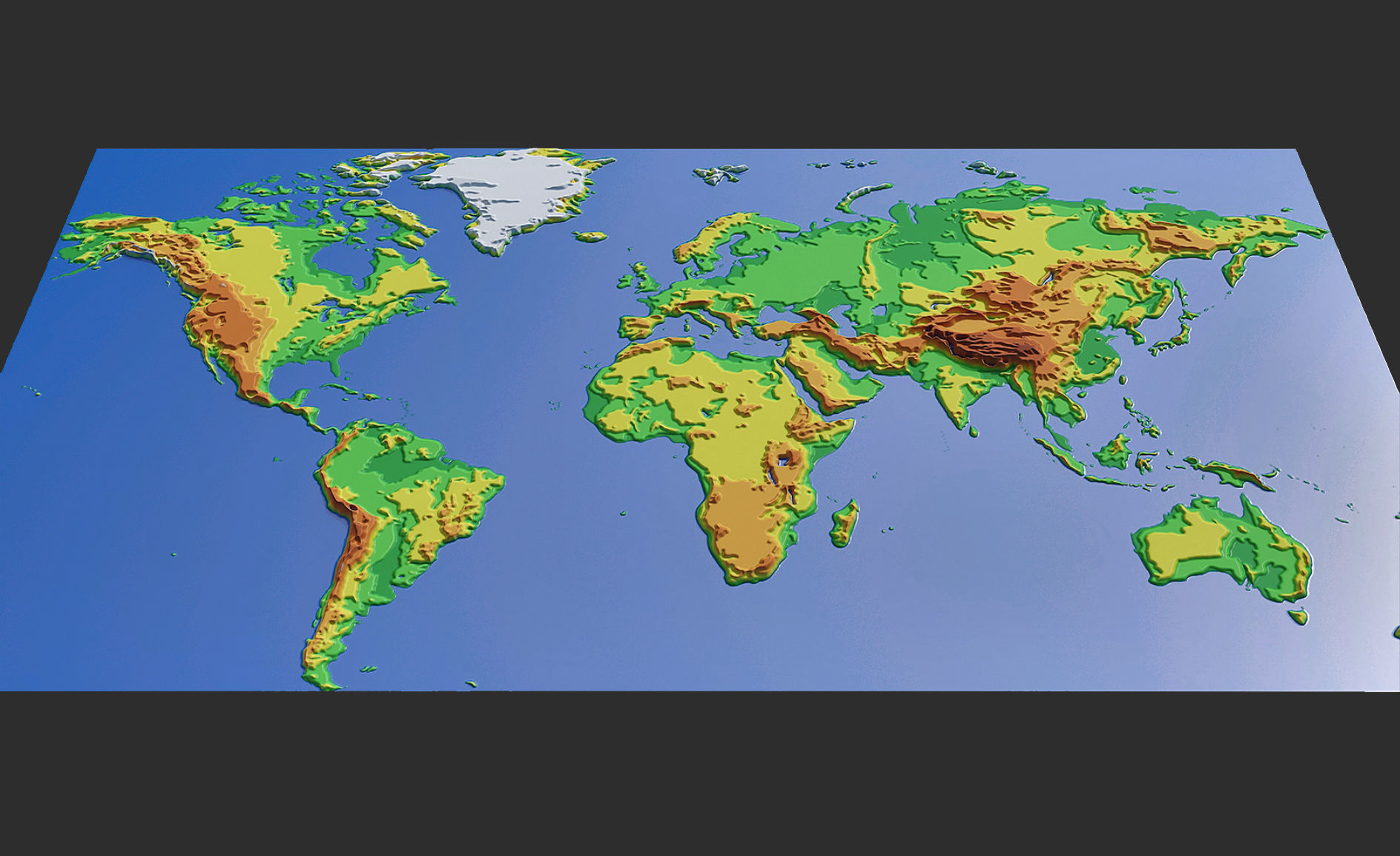
- Terrain Models: These models represent the topography of a region, including mountains, valleys, and rivers.
- Building Information Models (BIM): These models are used in the construction industry, providing detailed information about the design, construction, and operation of buildings.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Models: These models are designed for immersive experiences, allowing users to interact with the environment in a virtual reality setting.
Q: How are 3D model maps created?
A: 3D model maps are created using a combination of data sources and specialized software. The process typically involves:
- Data Acquisition: This involves collecting data from aerial photography, satellite imagery, laser scanning, ground surveys, and other sources.
- Data Processing: The collected data is then processed and cleaned to remove errors and inconsistencies.
- Model Building: Using specialized software, the processed data is used to build the 3D model, creating a digital representation of the environment.
- Texturing and Detailing: The model is then textured and detailed to enhance its realism and visual appeal.
Q: What are the challenges associated with 3D model maps?
A: While 3D model maps offer significant advantages, they also face certain challenges:
- Data Acquisition and Processing: Acquiring and processing large amounts of data can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency across different data sources is crucial for creating reliable 3D models.
- Computational Resources: Creating and manipulating large 3D models requires significant computational resources.
- Accessibility and Usability: Making 3D models accessible and usable for a wide range of users can be challenging.
Tips for Using 3D Model Maps Effectively
- Clearly Define Your Goals: Before creating or using a 3D model map, clearly define your objectives and the specific information you want to extract from the model.
- Choose the Right Data Sources: Select data sources that are relevant to your goals and offer the necessary level of detail and accuracy.
- Utilize Appropriate Software: Use specialized software designed for 3D model creation, visualization, and analysis.
- Collaborate with Experts: Consider working with experts in 3D modeling, data visualization, and the specific field of application.
- Ensure Accessibility: Make sure the 3D model is accessible to all users, regardless of their technical expertise.
Conclusion: A Future Shaped by Three Dimensions
3D model maps represent a significant advancement in our ability to understand and interact with the world. By offering a more immersive and interactive experience, these models empower us to make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and shape a better future. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of 3D model maps, transforming the way we navigate, analyze, and manage our world. The future of mapping is undoubtedly three-dimensional, and the possibilities are limitless.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World in Three Dimensions: Exploring the Power of 3D Model Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
