Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats
- 3.1 Understanding the Importance of Sitemaps
- 3.2 Delving into the Different Sitemap Formats
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Sitemap Format: A Practical Guide
- 3.4 Creating and Submitting Your Sitemap: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Sitemaps
- 3.6 Tips for Optimizing Your Sitemap for Better Search Engine Visibility
- 3.7 Conclusion: Empowering Your Website with Sitemaps
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats

In the vast and ever-expanding digital landscape, where information flows freely and search engines tirelessly crawl the web, maintaining a clear and organized structure for your website is paramount. This is where sitemaps come into play, serving as crucial roadmaps for search engines to effectively navigate and index your website’s content.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various sitemap formats, exploring their purpose, benefits, and implementation strategies. It aims to provide a clear understanding of how these essential tools contribute to enhanced website visibility and improved search engine performance.
Understanding the Importance of Sitemaps
A sitemap, in essence, is a file that lists the URLs of a website, providing search engines with a structured overview of its content. These files are not directly visible to users but act as behind-the-scenes guides for search engine crawlers. By presenting a clear and organized structure, sitemaps help search engines:
- Discover and index all website pages: They ensure that even the most obscure or deeply nested pages are accessible to crawlers, preventing them from being overlooked.
- Prioritize important pages: By specifying the importance of specific pages through attributes like priority and change frequency, sitemaps help search engines understand which pages are most valuable and should be crawled more frequently.
- Improve crawling efficiency: Sitemaps streamline the crawling process by providing a structured list of URLs, allowing crawlers to efficiently navigate the website and index its content.
- Enhance discoverability of new content: Sitemaps facilitate the prompt discovery of newly added or updated content, ensuring its inclusion in search results.
Delving into the Different Sitemap Formats
While the fundamental purpose of sitemaps remains consistent, there are two primary formats used for their creation:
1. XML Sitemaps:
- Format: XML (Extensible Markup Language)
- Purpose: The standard format recommended by Google and other major search engines.
- Structure: Utilizes a specific XML schema to define URLs, their last modification date, change frequency, and priority.
- Benefits: Provides a comprehensive and structured representation of website content, enhancing discoverability and crawling efficiency.
2. HTML Sitemaps:
- Format: HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
- Purpose: Designed for user navigation and not specifically for search engine optimization.
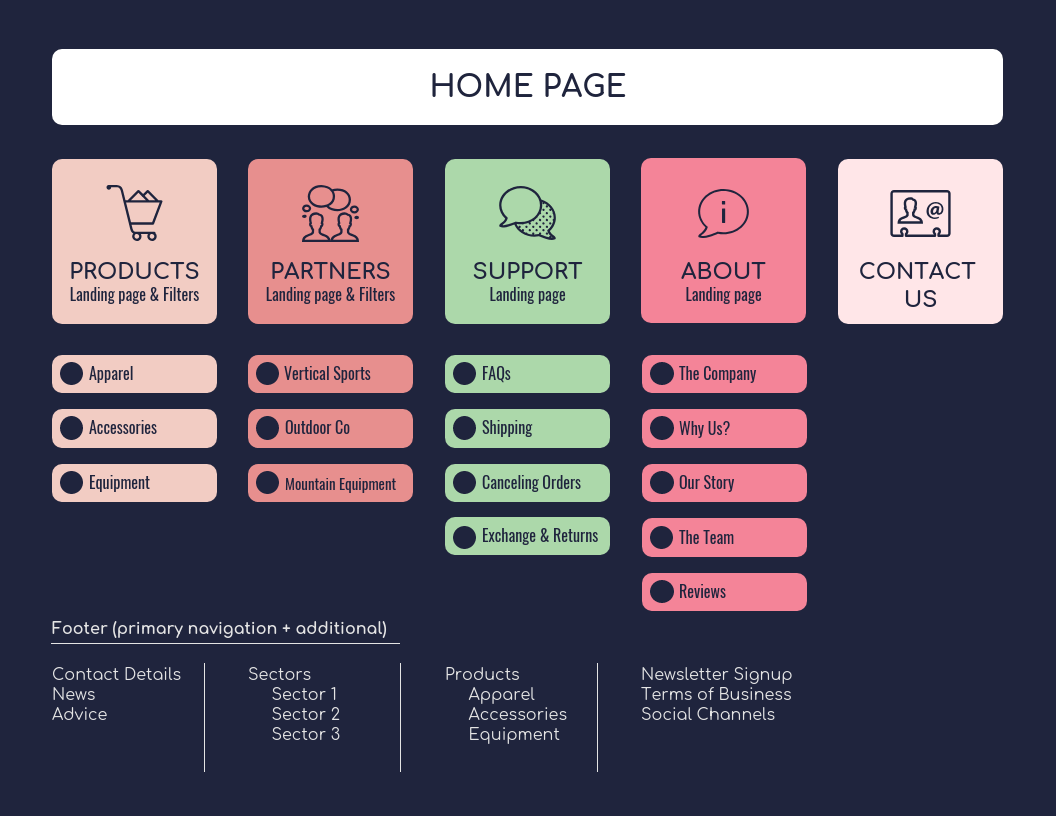
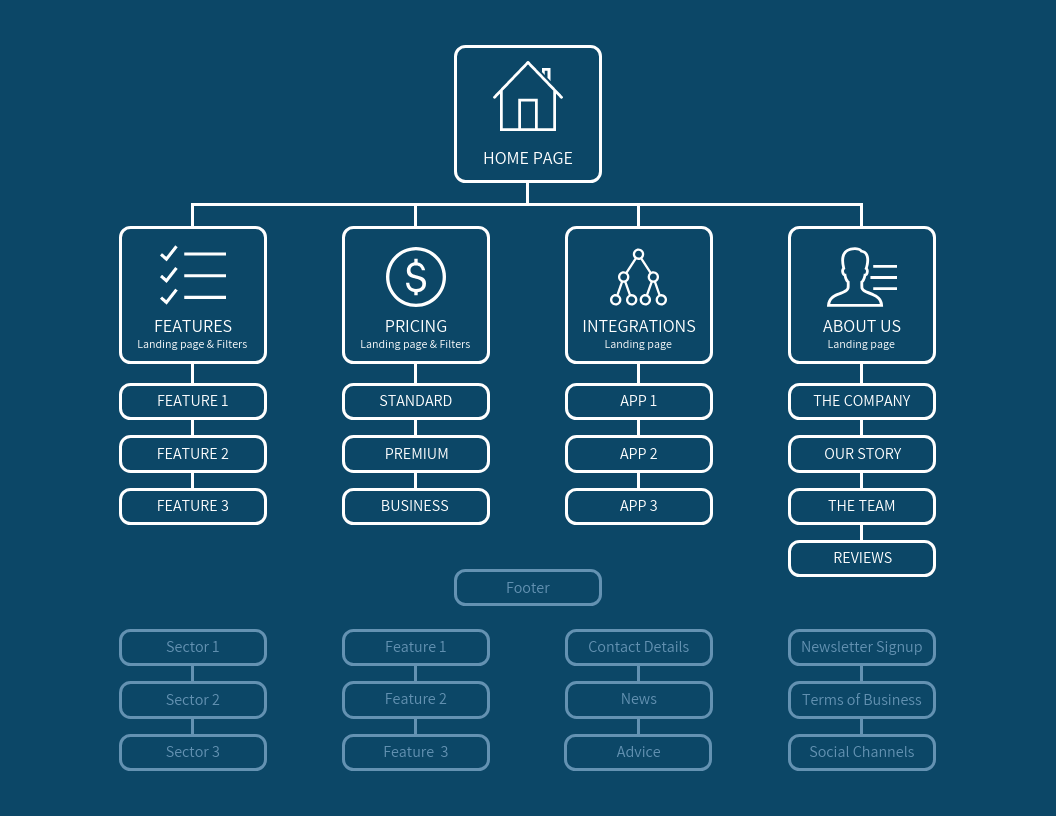
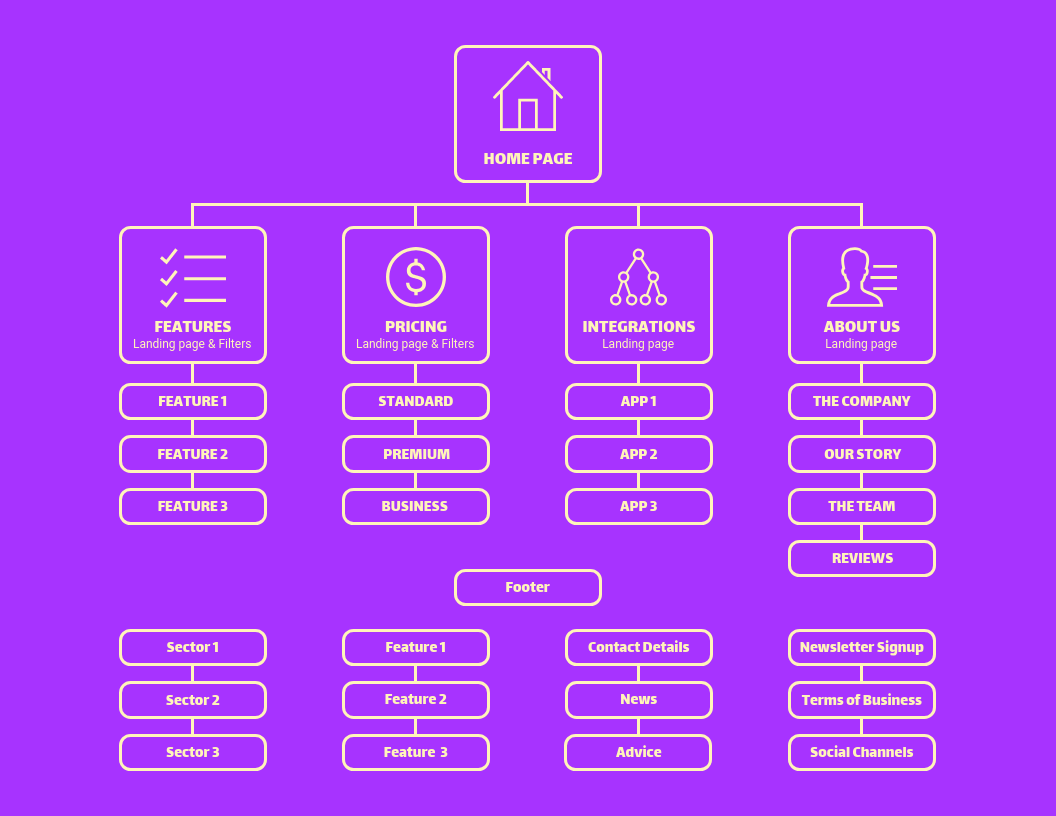
- Structure: Presents a hierarchical view of website pages, similar to a traditional website navigation menu.
- Benefits: Offers a user-friendly way to explore the website’s content, improving navigation and overall user experience.
Choosing the Right Sitemap Format: A Practical Guide
The choice between XML and HTML sitemaps depends on the specific needs and goals of your website.
- For SEO purposes: XML sitemaps are the preferred choice, providing a structured and comprehensive representation of your website’s content for search engines.
- For user navigation: HTML sitemaps serve as a valuable tool for users, offering a clear and hierarchical view of website content.
- Combining both: Many websites utilize both formats, employing an XML sitemap for search engine optimization and an HTML sitemap for user navigation.
Creating and Submitting Your Sitemap: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Generate your sitemap:
- Manual creation: For smaller websites, you can manually create an XML sitemap using a text editor and adhering to the XML schema specifications.
- Sitemap generators: Various online tools and plugins are available to automate sitemap creation, simplifying the process.
- Website CMS features: Popular Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress often offer built-in sitemap generation capabilities.
2. Verify the sitemap:
- Sitemap validator tools: Use online validators to ensure your sitemap adheres to the correct XML schema and is free of errors.
3. Submit your sitemap to search engines:
- Google Search Console: Log in to your Google Search Console account and navigate to the "Sitemaps" section. Submit your XML sitemap URL to Google.
- Bing Webmaster Tools: Follow a similar process in Bing Webmaster Tools to submit your sitemap.
4. Monitor and update your sitemap:
- Regular updates: Ensure your sitemap is updated regularly, reflecting any changes to your website content.
- Error reporting: Monitor for any errors reported by search engine tools, indicating issues with your sitemap.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Sitemaps
1. How often should I update my sitemap?
It is generally recommended to update your sitemap whenever significant changes occur to your website’s content, such as adding new pages, removing outdated content, or modifying existing pages. Aim for a minimum update frequency of monthly, or more frequently if your website experiences frequent content changes.
2. How many URLs can I include in a sitemap?
There is no strict limit on the number of URLs you can include in a sitemap. However, it is advisable to keep the file size under 50MB and the number of URLs below 50,000. For larger websites, consider splitting your sitemap into multiple files and submitting them individually to search engines.
3. Should I submit my sitemap to all search engines?
While submitting your sitemap to major search engines like Google and Bing is crucial, it’s also advisable to submit it to other relevant search engines, particularly if your target audience uses those search engines.
4. Can I use a sitemap for my mobile website?
Yes, you can create separate sitemaps for your desktop and mobile versions of your website. This helps search engines understand the structure of both versions and index them accordingly.
5. How do I know if my sitemap has been submitted successfully?
Search engine tools like Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools will provide feedback on the status of your sitemap submission, indicating whether it has been successfully processed and indexed.
Tips for Optimizing Your Sitemap for Better Search Engine Visibility
- Use descriptive file names: Choose file names that clearly indicate the content of your sitemap, such as "sitemap.xml" or "sitemap-products.xml."
- Specify change frequency and priority: Use the "changefreq" and "priority" attributes in your XML sitemap to indicate the frequency of content updates and the importance of specific pages.
- Include all relevant URLs: Ensure your sitemap includes all important pages on your website, including those that are not directly linked from your navigation menu.
- Use a sitemap index file: For large websites with multiple sitemaps, create a sitemap index file that lists all the individual sitemap files.
- Regularly monitor and update: Keep your sitemap up-to-date, reflecting any changes to your website content.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Website with Sitemaps
Sitemaps play a vital role in website optimization, serving as essential guides for search engine crawlers to efficiently navigate and index your website’s content. By leveraging the appropriate sitemap formats and implementing best practices, you can enhance your website’s discoverability, improve crawling efficiency, and ultimately boost your search engine performance.
By understanding the nuances of sitemap formats and their implementation, you equip your website with the tools necessary to thrive in the competitive digital landscape, ensuring that your valuable content reaches its intended audience. Remember, a well-structured and regularly updated sitemap is a cornerstone of a successful online presence.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Sitemap Formats. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
