Mapping Poverty: Understanding the Significance of Low-Income Census Tracts
Related Articles: Mapping Poverty: Understanding the Significance of Low-Income Census Tracts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping Poverty: Understanding the Significance of Low-Income Census Tracts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Poverty: Understanding the Significance of Low-Income Census Tracts
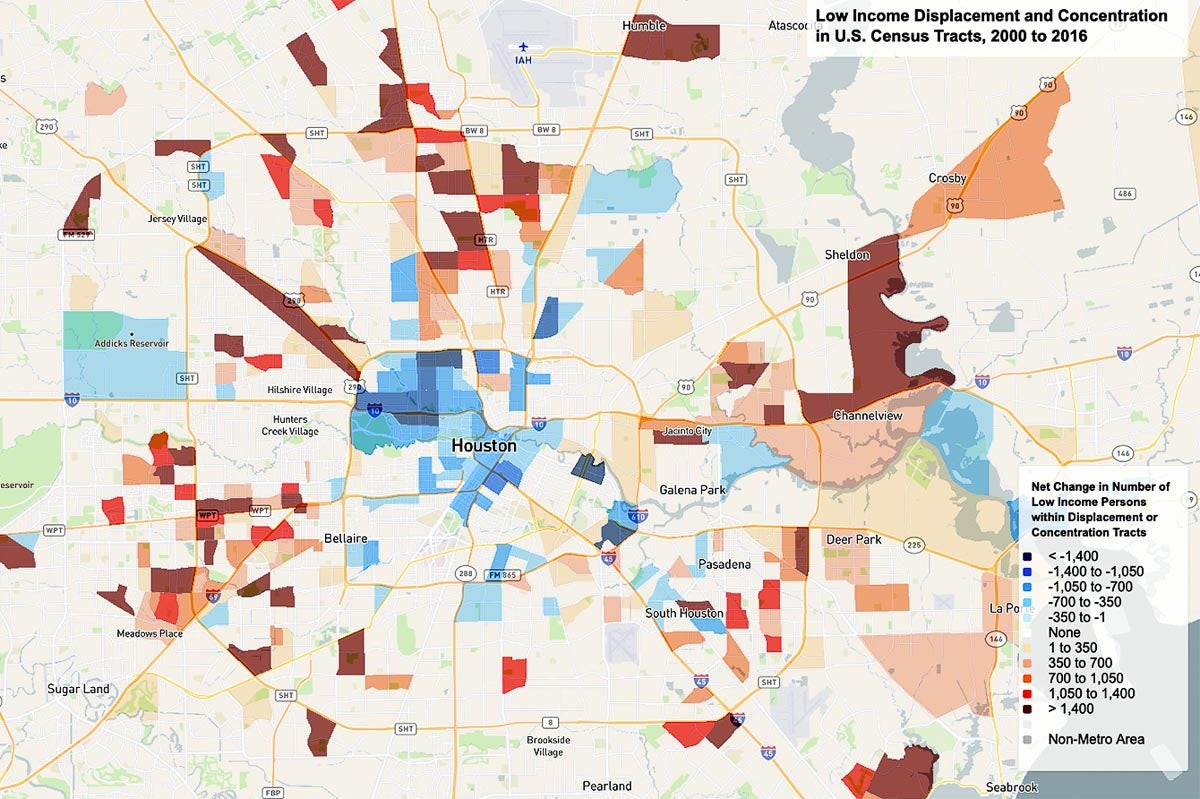
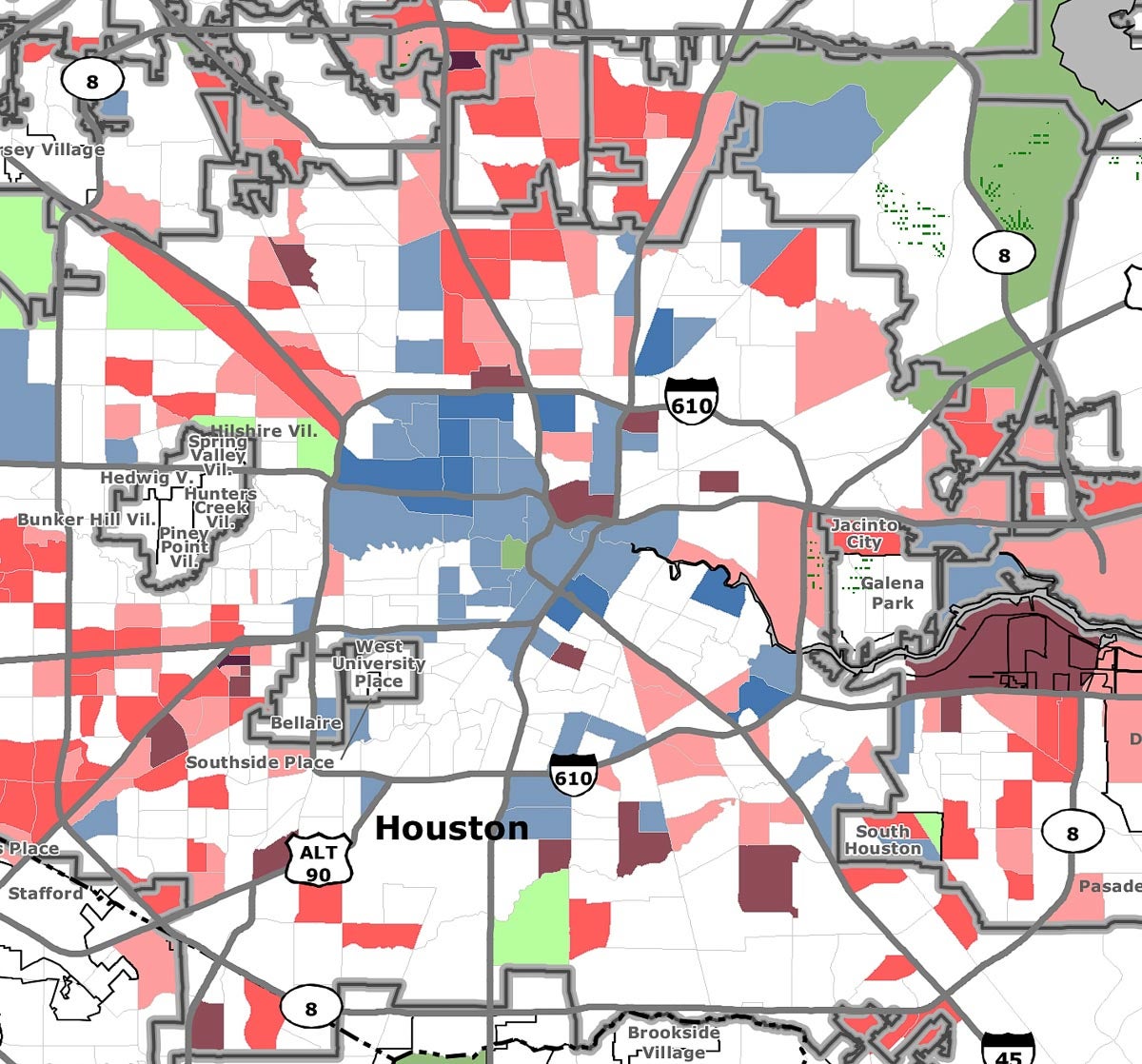
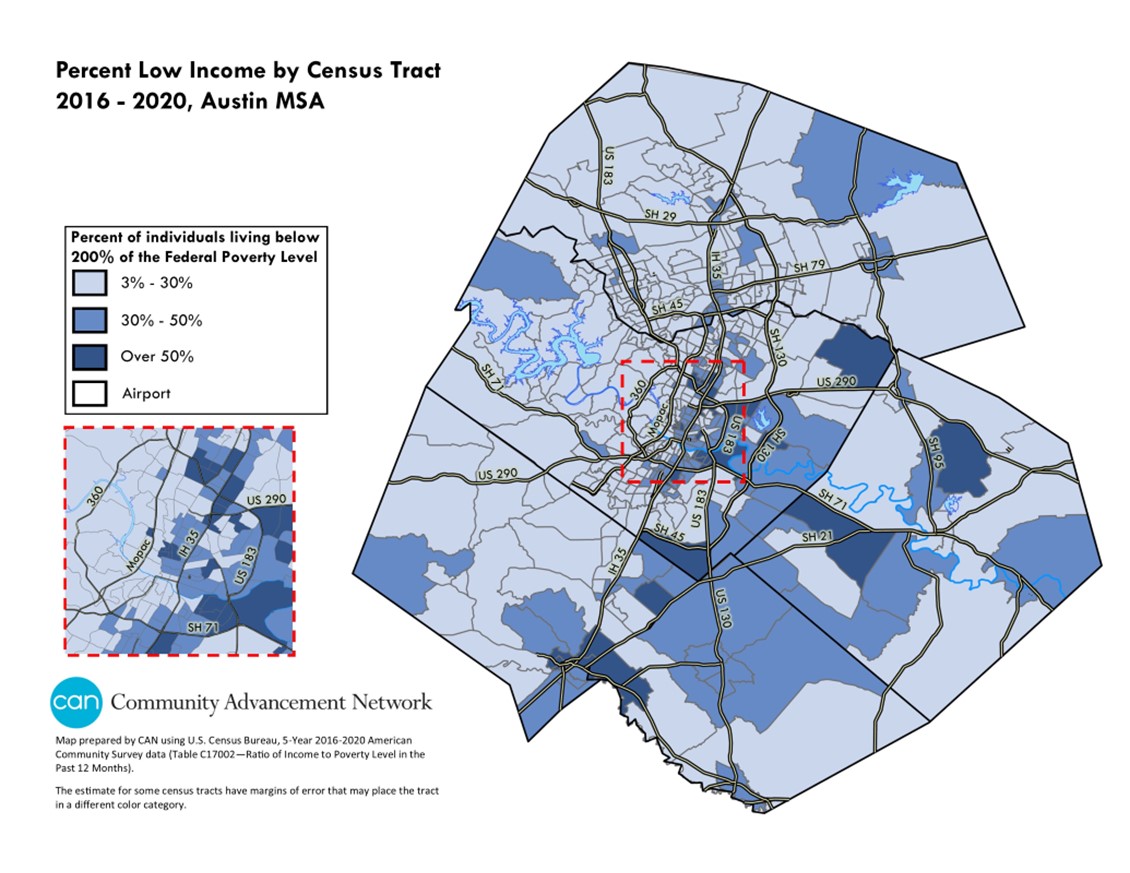
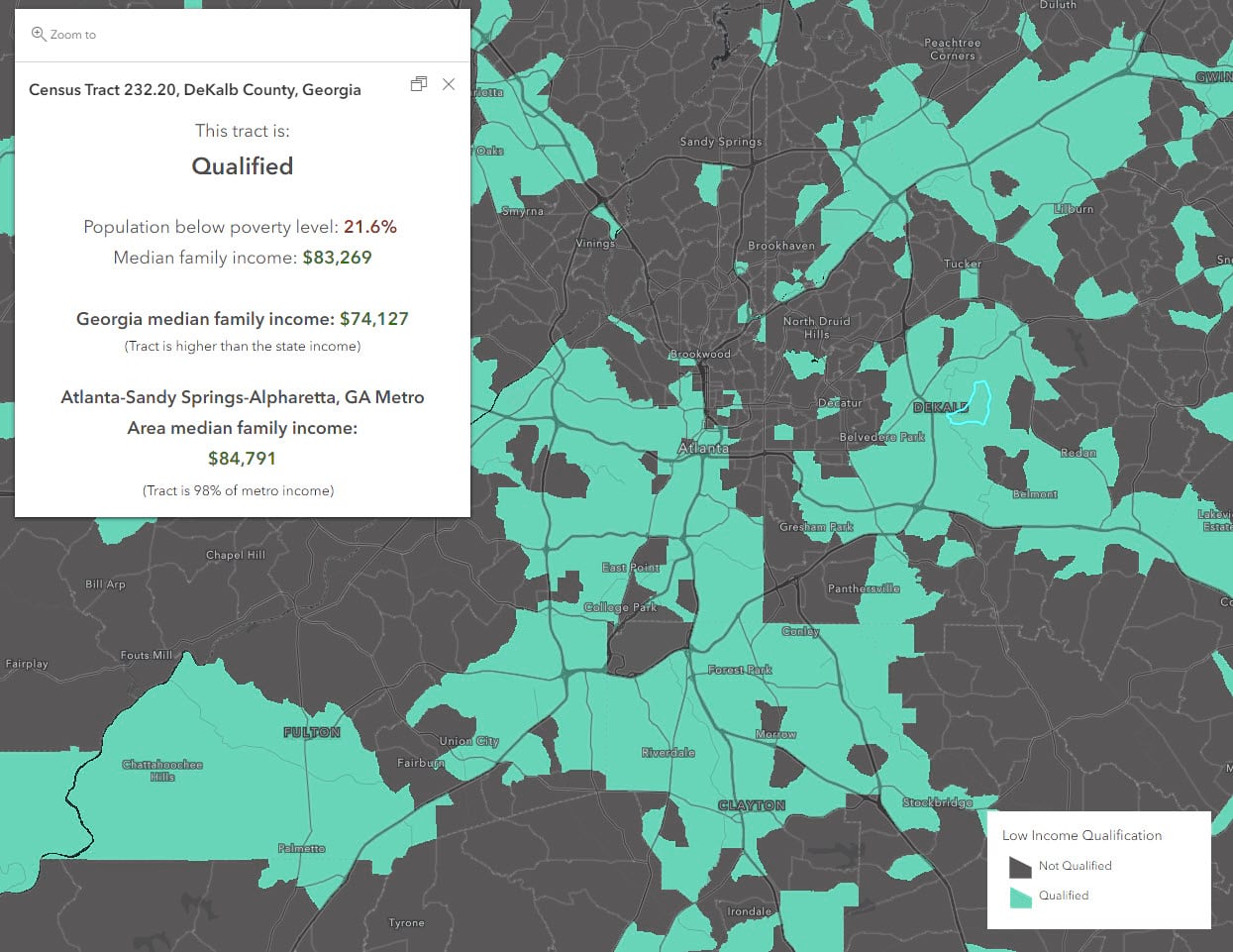
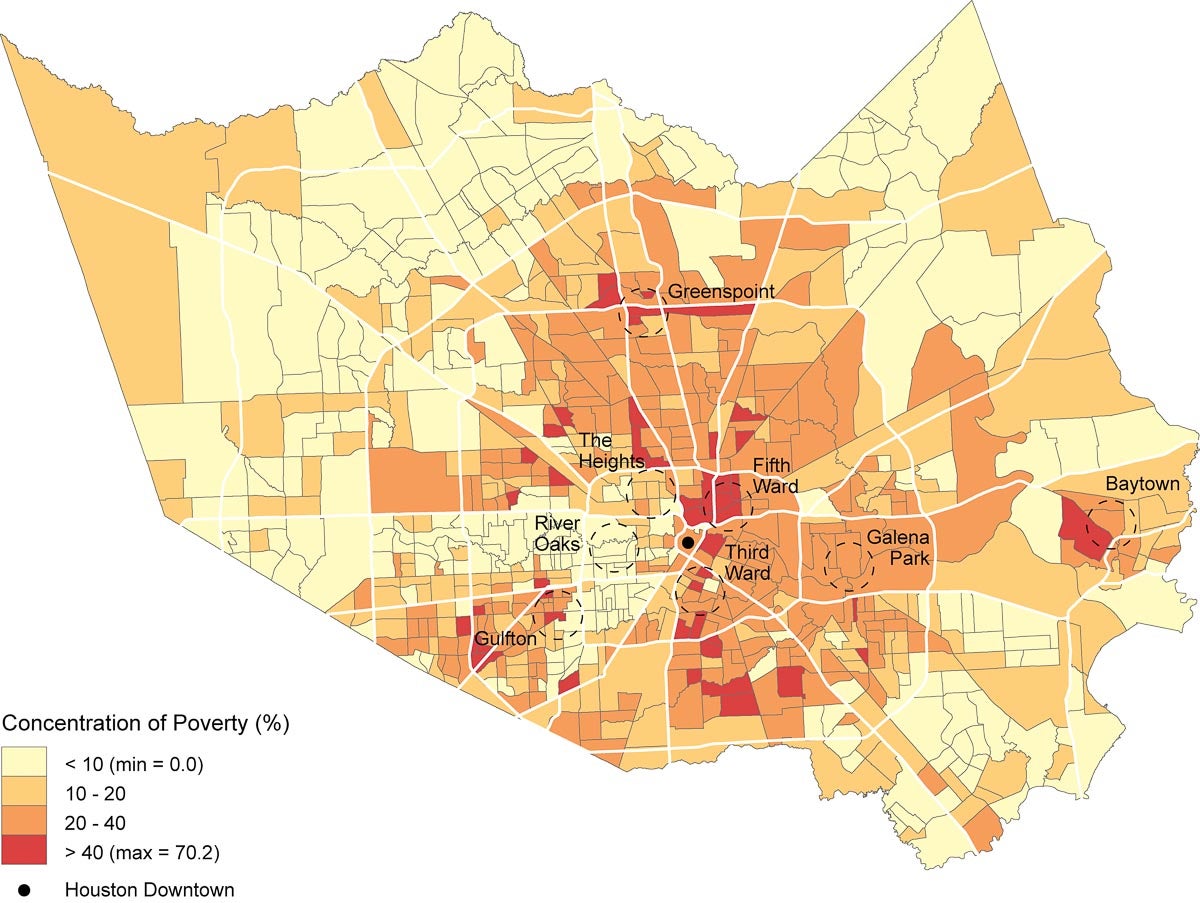
The United States Census Bureau, through its meticulous data collection efforts, provides a detailed snapshot of the nation’s demographics and socioeconomic landscape. Among its many valuable resources is the low-income census tract map, a powerful tool for understanding the distribution of poverty across the country. This map visualizes areas where a significant proportion of the population experiences economic hardship, offering invaluable insights for policymakers, researchers, and community organizations.
Delving Deeper into the Data:
Low-income census tracts are defined as areas where at least 20% of the population lives below the poverty line. This threshold, established by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, reflects a minimum income required to meet basic needs, including food, housing, clothing, and transportation. The census tracts themselves are small, geographically defined areas with an average population of 4,000 people, allowing for a granular understanding of poverty within communities.
The Importance of Geographic Visualization:
The power of the low-income census tract map lies in its ability to visually represent the spatial distribution of poverty. This visualization reveals patterns that might not be evident from raw data alone. For instance, the map might highlight:
- Concentrations of poverty: Areas with high densities of low-income census tracts indicate communities facing systemic economic challenges.
- Spatial disparities: Comparing maps across different time periods can reveal shifts in poverty levels and geographic patterns over time.
- Neighborhood-level insights: The map allows for a detailed examination of poverty within specific neighborhoods, enabling targeted interventions and resource allocation.
Applications and Benefits:
The low-income census tract map serves as a critical resource for various stakeholders:
- Policymakers: The map informs the development of targeted policies and programs aimed at alleviating poverty, including housing assistance, job training, and educational support.
- Researchers: Social scientists use the map to study the root causes of poverty, analyze the effectiveness of anti-poverty programs, and explore the social and economic consequences of poverty.
- Community organizations: Non-profit organizations rely on the map to identify areas with high poverty rates and focus their resources on providing essential services, such as food banks, healthcare clinics, and educational programs.
- Businesses: The map can help businesses make informed decisions about location, target marketing strategies, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Context:
While the low-income census tract map offers valuable insights, it is essential to consider the broader context surrounding poverty. Factors such as racial and ethnic disparities, lack of access to quality education and healthcare, and systemic barriers to economic mobility can significantly contribute to poverty levels in specific communities.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How is the poverty line determined?
The poverty line is calculated annually by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services based on a family’s size, age, and location. It is based on the cost of a minimally nutritious food plan, multiplied by three to account for other necessary expenses.
2. What are the limitations of using the low-income census tract map?
The map provides a snapshot of poverty at a specific point in time and may not capture the full complexity of economic hardship. It does not account for factors such as temporary income fluctuations, access to social safety nets, and the availability of affordable housing.
3. How can the low-income census tract map be used to promote social equity?
By identifying areas with high concentrations of poverty, the map can help policymakers and community organizations develop targeted programs that address the specific needs of marginalized communities. This can include initiatives aimed at improving access to education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and affordable housing.
Tips for Utilizing the Low-Income Census Tract Map:
- Combine data: Integrate the map with other socioeconomic indicators to gain a more comprehensive understanding of poverty and its underlying causes.
- Focus on specific needs: Tailor interventions to the unique challenges faced by communities with high poverty rates.
- Engage with residents: Involve community members in developing and implementing solutions that address their specific needs and priorities.
Conclusion:
The low-income census tract map is a powerful tool for understanding the distribution of poverty in the United States. By visualizing areas with high concentrations of low-income households, the map provides valuable insights for policymakers, researchers, and community organizations. However, it is crucial to recognize that poverty is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. Effective solutions require a multi-faceted approach that addresses systemic barriers to economic mobility and promotes social equity. By leveraging the information provided by the low-income census tract map, we can work towards creating a more just and equitable society for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Poverty: Understanding the Significance of Low-Income Census Tracts. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
