Maintaining Fair Competition: A Deep Dive into Map Price Enforcement
Related Articles: Maintaining Fair Competition: A Deep Dive into Map Price Enforcement
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Maintaining Fair Competition: A Deep Dive into Map Price Enforcement. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Maintaining Fair Competition: A Deep Dive into Map Price Enforcement

Introduction
In the intricate world of commerce, the principle of fair competition is paramount. This principle ensures that businesses operate on a level playing field, fostering innovation and protecting consumers from predatory pricing. One crucial mechanism for upholding this principle is map price enforcement, a practice that involves manufacturers setting minimum prices for their products and taking legal action against retailers who undercut those prices. While this practice has been a subject of debate, its significance in maintaining a healthy market ecosystem cannot be understated.
Understanding the Concept
Map price enforcement, or "minimum resale price maintenance" (MSRP), is a strategy employed by manufacturers to control the retail prices of their products. They achieve this by setting a minimum price that retailers are obligated to adhere to. Any retailer selling below this minimum price can face legal consequences, including fines or termination of their distribution agreement.
The Rationale Behind Map Price Enforcement
The implementation of map price enforcement is driven by several key objectives:
- Preserving Brand Image: Manufacturers strive to maintain a consistent brand image across all retail channels. Price disparities can erode brand value and negatively impact consumer perception. Map pricing helps ensure that products are sold at a price commensurate with their perceived quality and prestige.
- Protecting Distribution Channels: Manufacturers invest heavily in building relationships with distributors and retailers. Aggressive price competition can disrupt these relationships, as retailers may prioritize short-term profits over long-term partnerships. Map pricing helps preserve the integrity of these channels.
- Encouraging Product Differentiation: By setting minimum prices, manufacturers can incentivize retailers to focus on providing value-added services, such as knowledgeable sales staff or premium customer experiences. This fosters differentiation and enhances the overall customer journey.
- Promoting Investment in Innovation: Manufacturers rely on consistent pricing to fund research and development, leading to product improvements and innovations. Map pricing ensures that manufacturers can recoup their investments and continue to innovate.
Legal Framework and Regulatory Considerations
The legality of map price enforcement varies significantly across jurisdictions. In some countries, it is strictly prohibited as it is considered anti-competitive. In others, it may be allowed under certain conditions, such as when manufacturers can demonstrate that it is necessary to protect their brand or distribution channels.
The Debate Surrounding Map Price Enforcement
Map price enforcement has been a subject of considerable debate, with proponents and opponents advocating for their respective viewpoints:
Arguments in Favor of Map Price Enforcement:
- Consumer Protection: Map pricing can prevent "predatory pricing," a practice where retailers sell products below cost to drive competitors out of the market. This ultimately protects consumers from potentially higher prices in the long run.
- Brand Integrity: Map pricing helps manufacturers maintain a consistent brand image and prevent "discounting" that can devalue the brand.
- Investment in Innovation: Map pricing allows manufacturers to recoup their investments in research and development, fostering innovation and bringing new products to the market.
Arguments Against Map Price Enforcement:
- Reduced Competition: Map pricing can stifle competition, as retailers are unable to offer lower prices to attract customers. This can lead to higher prices for consumers.
- Limited Consumer Choice: Map pricing can restrict consumer choice, as retailers are limited in their ability to offer competitive pricing.
- Potential for Collusion: Map pricing can create opportunities for manufacturers and retailers to collude and fix prices, harming consumers.
Navigating the Complexity of Map Price Enforcement
The effectiveness of map price enforcement is contingent upon several factors:
- Market Structure: Map pricing is more likely to be effective in markets with a limited number of competitors. In highly competitive markets, it may be difficult to enforce.
- Product Characteristics: Map pricing is more effective for products with strong brand recognition or high perceived value.
- Enforcement Mechanisms: Manufacturers must have effective mechanisms for monitoring and enforcing their map pricing policies.
FAQs About Map Price Enforcement
1. How does map price enforcement work in practice?
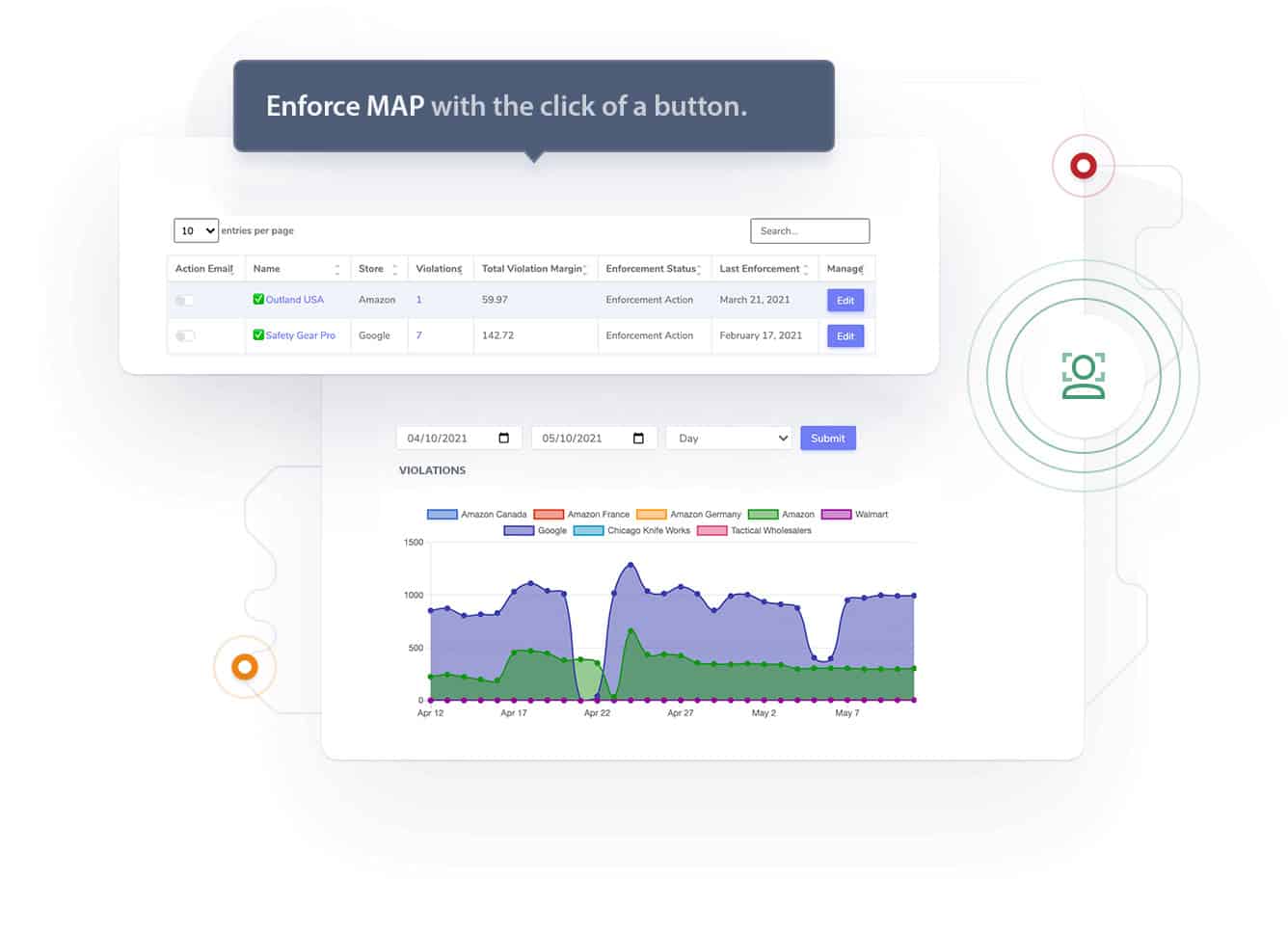
Manufacturers typically include map pricing provisions in their distribution agreements with retailers. These agreements specify the minimum prices that retailers are obligated to charge for the products. Manufacturers may also employ monitoring systems to track retail prices and take action against retailers who violate the agreement.
2. What are the potential legal consequences of violating map price enforcement agreements?
Violating a map price enforcement agreement can result in a range of legal consequences, including:
- Termination of the distribution agreement: Manufacturers can terminate their agreements with retailers who violate map pricing policies.
- Fines and penalties: Manufacturers may impose fines or penalties on retailers who violate map pricing agreements.
- Injunctive relief: Manufacturers can seek court orders to prevent retailers from selling products below the minimum price.
3. Is map price enforcement always legal?
The legality of map price enforcement varies significantly across jurisdictions. In some countries, it is strictly prohibited, while in others it may be allowed under certain conditions. It is essential for businesses to consult with legal counsel to determine the legality of map price enforcement in their specific jurisdiction.
Tips for Implementing Map Price Enforcement
- Clear and Comprehensive Agreements: Ensure that distribution agreements clearly define the minimum prices and the consequences of violating the agreement.
- Effective Monitoring Systems: Implement robust systems for monitoring retail prices and identifying violations.
- Consistent Enforcement: Apply enforcement actions consistently to ensure fairness and deter future violations.
- Transparency and Communication: Communicate map pricing policies clearly to retailers and provide them with adequate training and support.
Conclusion
Map price enforcement remains a complex and controversial topic in the world of commerce. While it can provide benefits such as brand protection and investment in innovation, it also carries the potential for stifling competition and limiting consumer choice. The effectiveness of map price enforcement is contingent upon several factors, including market structure, product characteristics, and enforcement mechanisms. Businesses seeking to implement map price enforcement strategies should carefully consider the legal and ethical implications, as well as the potential impact on consumers and competitors.
Ultimately, the success of map price enforcement hinges on its ability to strike a balance between protecting manufacturers’ interests and promoting a fair and competitive market environment. As the landscape of commerce continues to evolve, the debate surrounding map price enforcement is likely to persist, demanding careful consideration and nuanced solutions.

.jpg?width=343u0026height=200u0026ext=.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Maintaining Fair Competition: A Deep Dive into Map Price Enforcement. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
