Jamaica: A Caribbean Jewel on the World Map
Related Articles: Jamaica: A Caribbean Jewel on the World Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Jamaica: A Caribbean Jewel on the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Jamaica: A Caribbean Jewel on the World Map
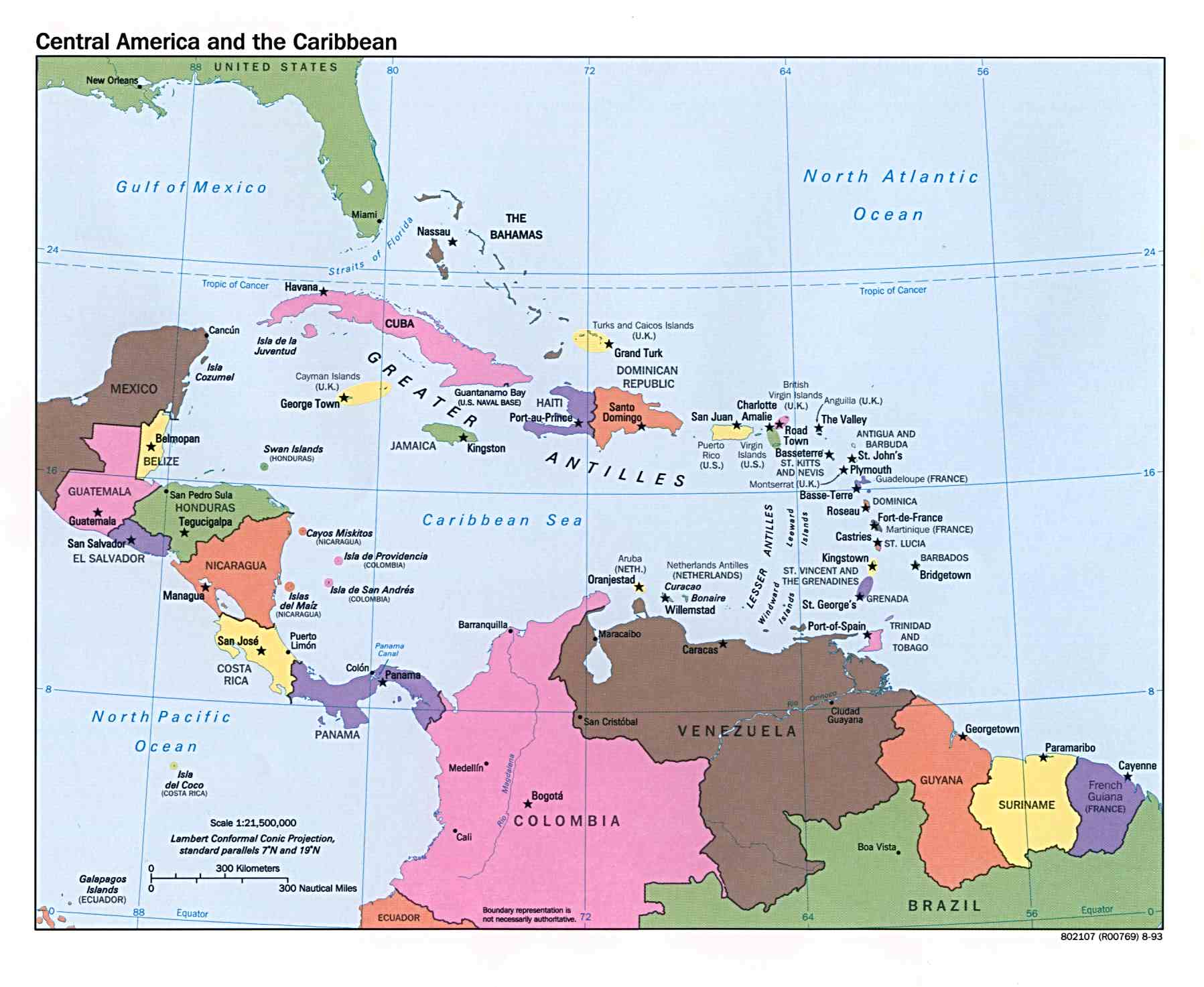
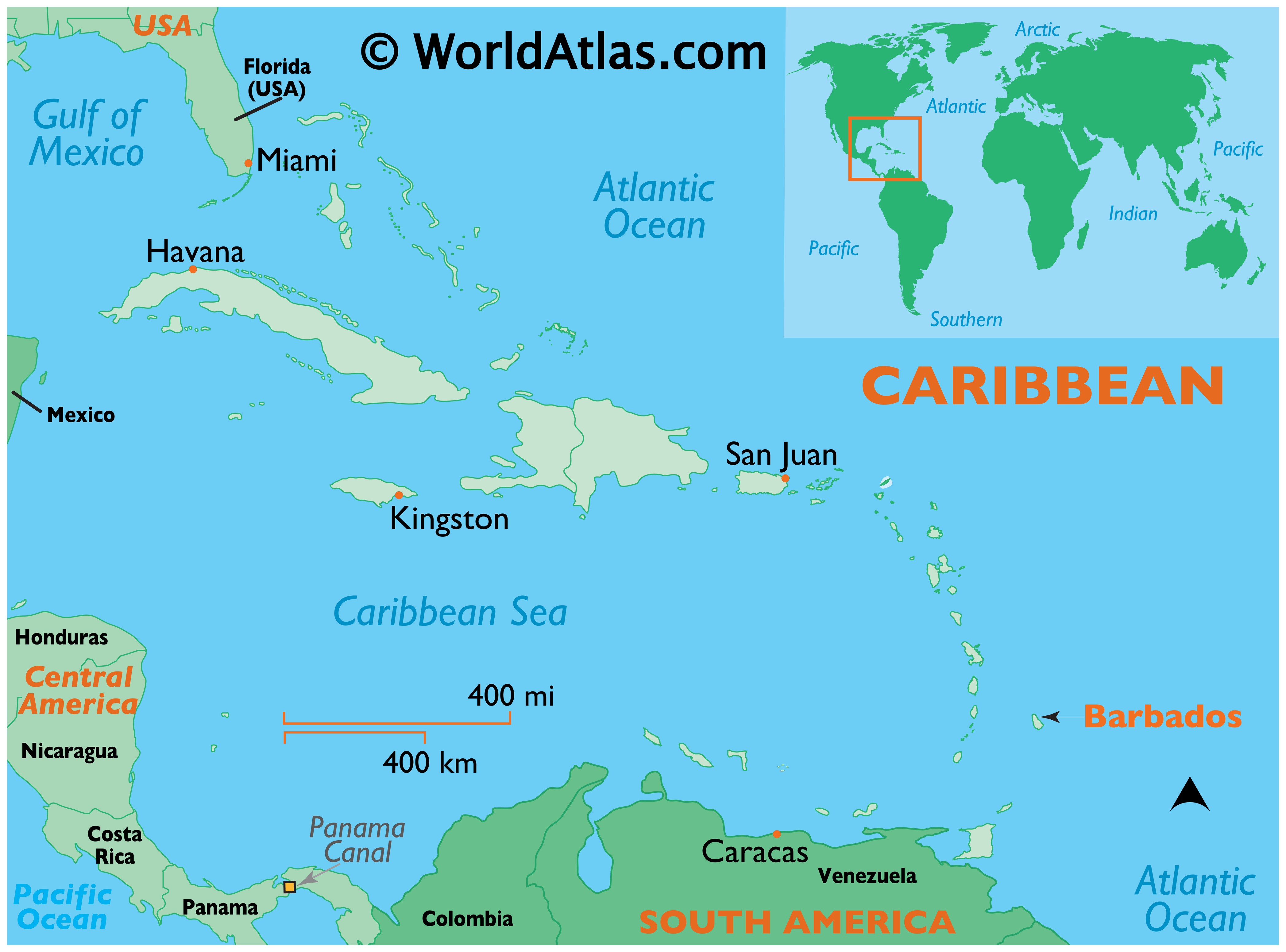
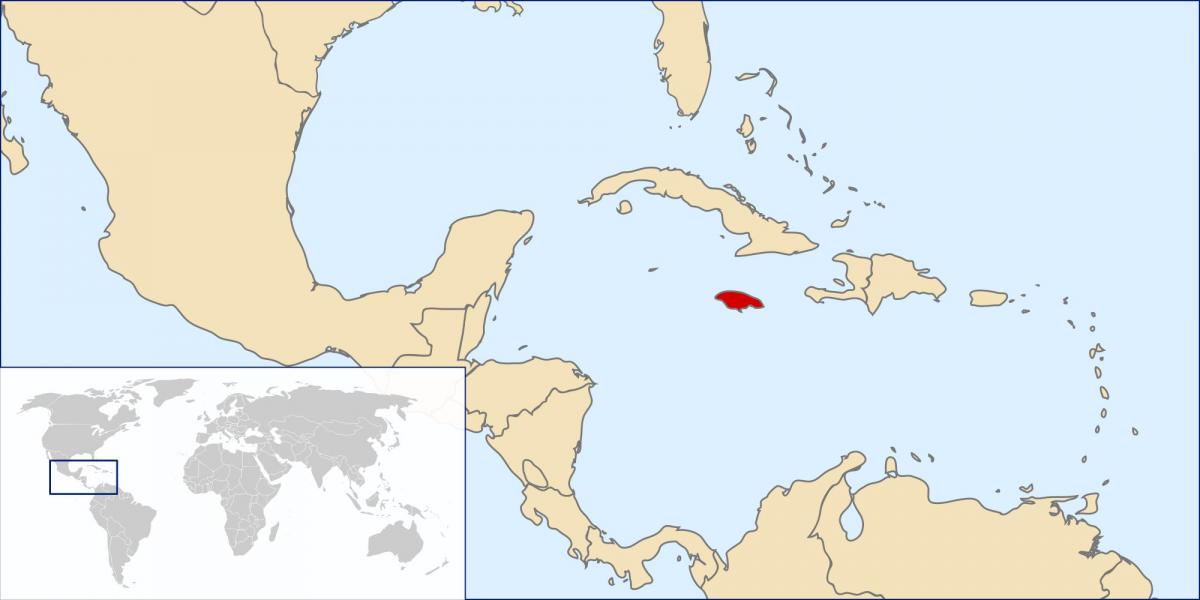
Jamaica, an island nation nestled in the Caribbean Sea, holds a captivating allure for travelers and geographers alike. Its vibrant culture, stunning natural beauty, and rich history make it a standout destination on the world map. Understanding Jamaica’s location is crucial for appreciating its unique characteristics and the factors that have shaped its identity.
Jamaica’s Geographic Positioning:
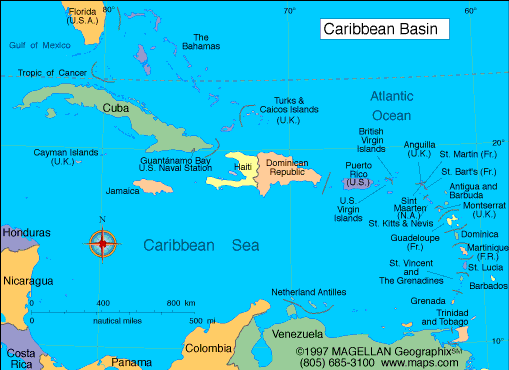
Jamaica is situated in the northwestern Caribbean Sea, approximately 90 miles south of Cuba and 100 miles west of Haiti. Its coordinates are 18.1096° N, 77.2975° W. The island is roughly rectangular in shape, spanning about 146 miles in length and 51 miles in width.
Island Formation and Topography:
Jamaica’s formation is a testament to the dynamic forces of plate tectonics. It was formed millions of years ago as a result of volcanic activity and the collision of tectonic plates. The island boasts a diverse topography, featuring lush green mountains, fertile valleys, and a coastline adorned with pristine beaches. The Blue Mountains, rising to a height of 7,402 feet, dominate the eastern part of the island, while the Cockpit Country, a rugged and karst-ridden region, occupies the central portion.
Climate and Weather Patterns:
Jamaica enjoys a tropical climate, characterized by warm temperatures and high humidity year-round. The island experiences two distinct seasons: the wet season, which runs from May to November, and the dry season, from December to April. The average temperature hovers around 80°F (27°C), with slight variations depending on elevation and location. Rainfall is heaviest during the wet season, while the dry season provides ideal conditions for outdoor activities.
Political and Administrative Structure:
Jamaica is an independent parliamentary democracy, with a governor-general as head of state and a prime minister as head of government. The island is divided into 14 parishes, each with its own local government. Kingston, the capital city, serves as the administrative center and is located on the southeastern coast.
Economic Significance and Industries:
Jamaica’s economy is primarily driven by tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing. The island’s stunning natural beauty, vibrant culture, and warm hospitality make it a popular destination for visitors worldwide. The agricultural sector plays a significant role, producing a variety of crops, including sugar cane, coffee, bananas, and citrus fruits. Manufacturing industries focus on areas like aluminum, textiles, and food processing.
Cultural Significance and Heritage:
Jamaica’s cultural heritage is a rich tapestry woven from African, European, and indigenous influences. The island is renowned for its vibrant music, particularly reggae and dancehall, which have gained global recognition. Jamaican cuisine is a delightful blend of flavors, incorporating ingredients like spices, seafood, and local fruits and vegetables. The island’s vibrant arts scene, including painting, sculpture, and crafts, reflects its unique cultural identity.
Ecological Importance and Biodiversity:
Jamaica is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, making it an important ecological hotspot. The island’s diverse habitats, ranging from rainforests to coastal wetlands, support a wide range of species. The Blue Mountains, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, are home to a remarkable variety of endemic plants and animals. Jamaica’s rich biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and providing valuable resources.
Strategic Location and Global Connections:
Jamaica’s location in the Caribbean Sea makes it a strategically important location for trade, transportation, and international relations. The island serves as a hub for regional trade and a gateway to the wider Caribbean. Its proximity to major shipping routes and its deep-water harbors make it a significant maritime center. Jamaica also plays an active role in international organizations, fostering cooperation and collaboration on regional and global issues.
Tourism and Hospitality:
Tourism is a cornerstone of Jamaica’s economy, contributing significantly to its GDP and providing employment opportunities for many Jamaicans. The island’s pristine beaches, stunning natural landscapes, and vibrant culture attract millions of visitors each year. Tourists can enjoy a wide range of activities, from relaxing on the beach to exploring historical sites, engaging in water sports, and experiencing the island’s lively nightlife. Jamaica’s hospitality industry is known for its warmth and friendliness, providing a memorable experience for visitors.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Jamaica boasts numerous advantages, it also faces challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental issues. The island is susceptible to natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes, which can have a significant impact on its economy and infrastructure. However, Jamaica is actively addressing these challenges through sustainable development initiatives, investments in education and healthcare, and efforts to promote environmental conservation.
FAQs about Jamaica’s Location:
- What is the closest mainland country to Jamaica? The closest mainland country to Jamaica is Haiti, located approximately 100 miles to the east.
- What is the time difference between Jamaica and the United States? Jamaica is five hours behind Eastern Standard Time (EST) and four hours behind Eastern Daylight Time (EDT).
- What are the major cities in Jamaica? The major cities in Jamaica include Kingston (the capital), Montego Bay, Ocho Rios, and Negril.
- Is Jamaica a safe place to visit? Jamaica is generally a safe place to visit, but it is important to exercise caution and be aware of your surroundings, particularly in urban areas.
- What are the best times to visit Jamaica? The best times to visit Jamaica are during the dry season, from December to April, when the weather is sunny and dry.
Tips for Visiting Jamaica:
- Research your destination: Before you travel, familiarize yourself with Jamaica’s different regions and attractions to plan your itinerary effectively.
- Pack appropriately: Pack light clothing, swimwear, comfortable shoes, and sunscreen, as the weather is typically warm and sunny.
- Respect local customs: Be respectful of Jamaican culture and traditions, including their dress code, social norms, and religious practices.
- Learn a few basic phrases: Learning a few basic Jamaican phrases can enhance your interactions with locals and make your trip more enjoyable.
- Enjoy the local cuisine: Sample the diverse flavors of Jamaican cuisine, from jerk chicken to ackee and saltfish.
Conclusion:
Jamaica’s location on the world map is a testament to its unique blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and strategic importance. The island’s stunning landscapes, vibrant culture, and friendly people have made it a beloved destination for travelers worldwide. Understanding Jamaica’s geographic positioning, its diverse topography, and its rich history allows us to appreciate the factors that have shaped its identity and the opportunities it presents for the future. As a Caribbean jewel, Jamaica continues to captivate the world with its allure and its promise of a memorable experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Jamaica: A Caribbean Jewel on the World Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
