A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographical Map of New York State
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographical Map of New York State
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographical Map of New York State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographical Map of New York State

New York State, a tapestry of diverse landscapes and vibrant cities, holds a unique geographical position within the northeastern United States. Understanding its geographical map is essential for appreciating its history, culture, and economic significance. This article delves into the intricate features of New York State’s geography, exploring its physical attributes, regional variations, and the profound influence these elements have on the state’s identity.
The Physical Landscape: A Mosaic of Diverse Terrain
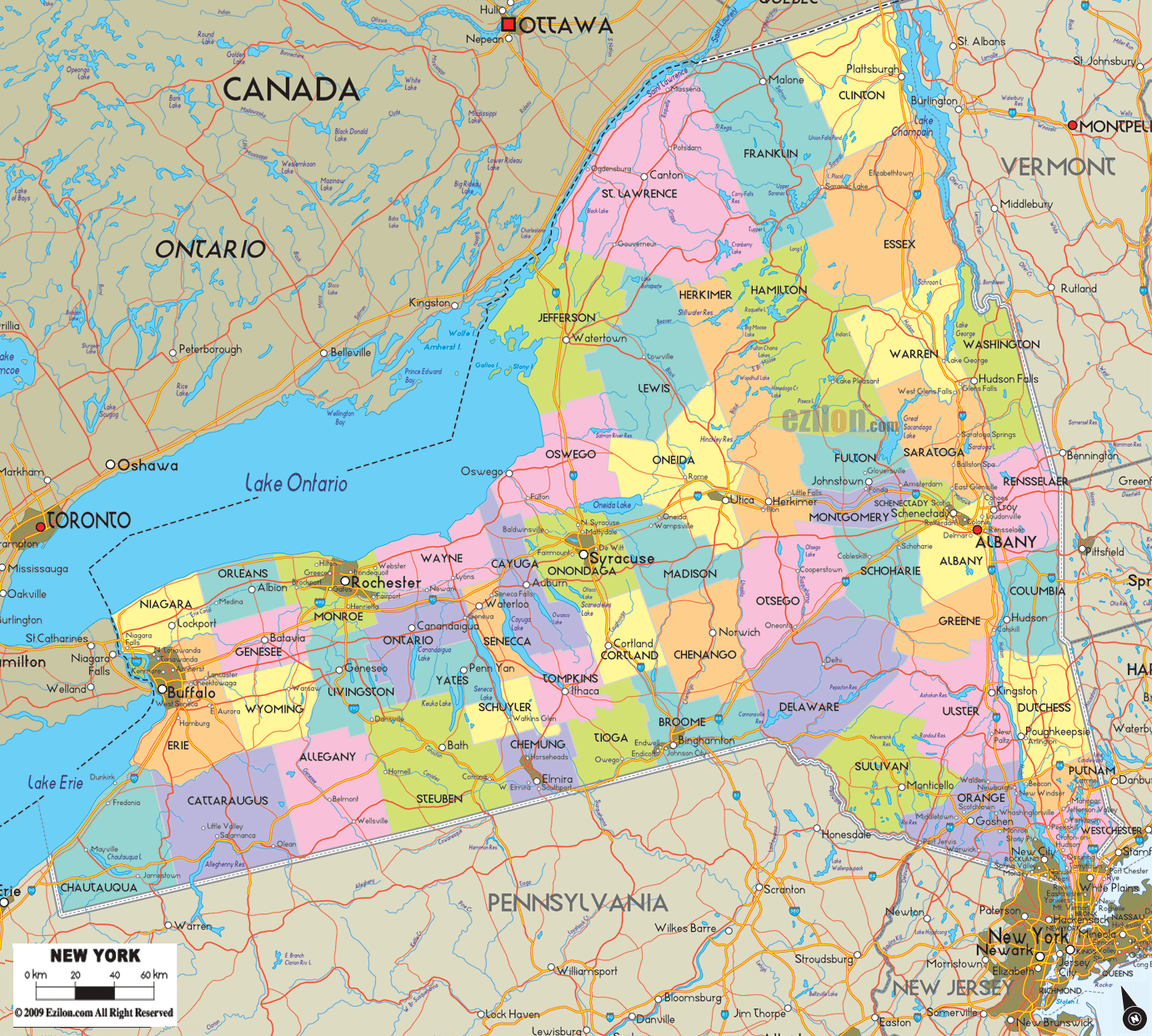
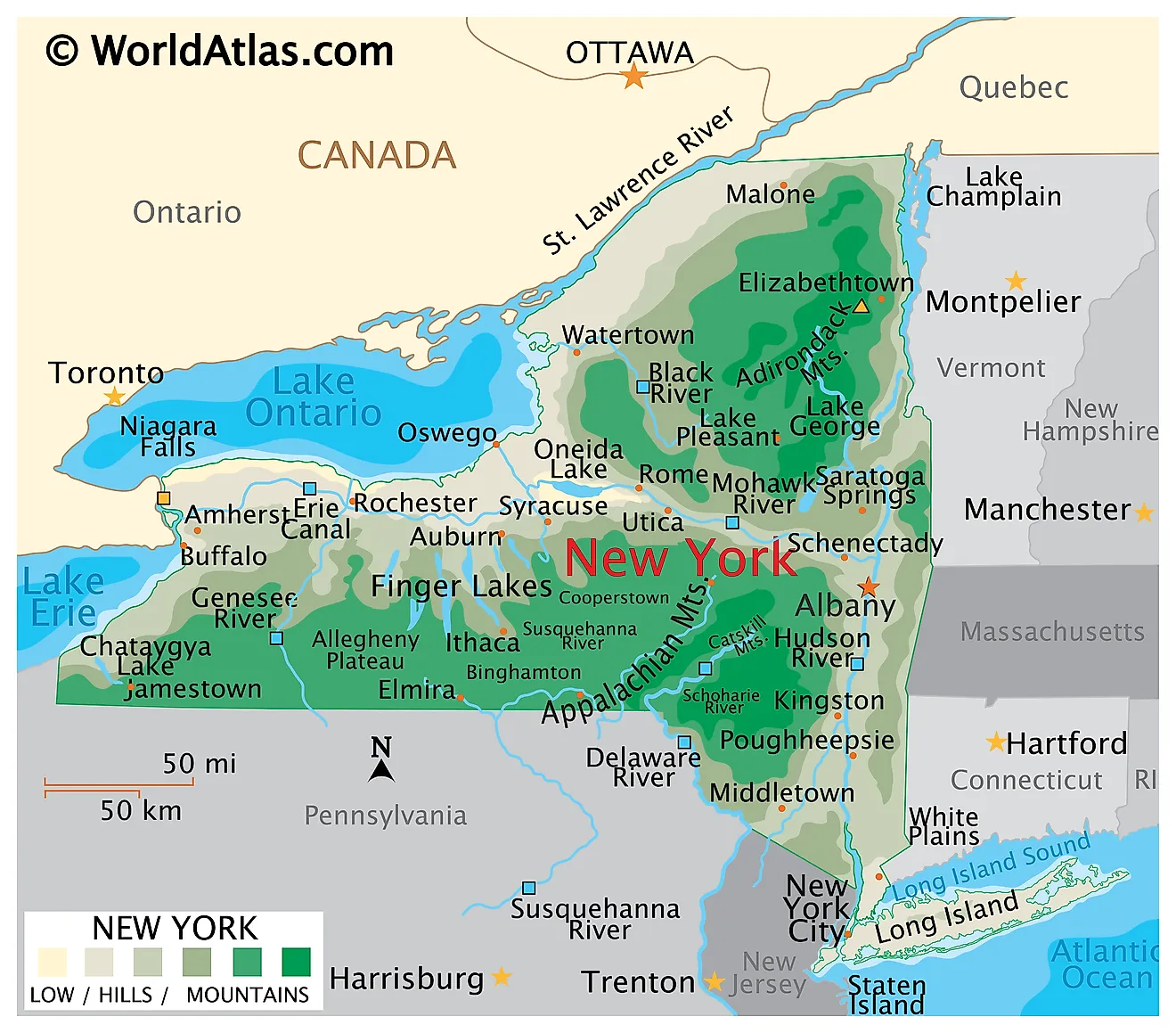
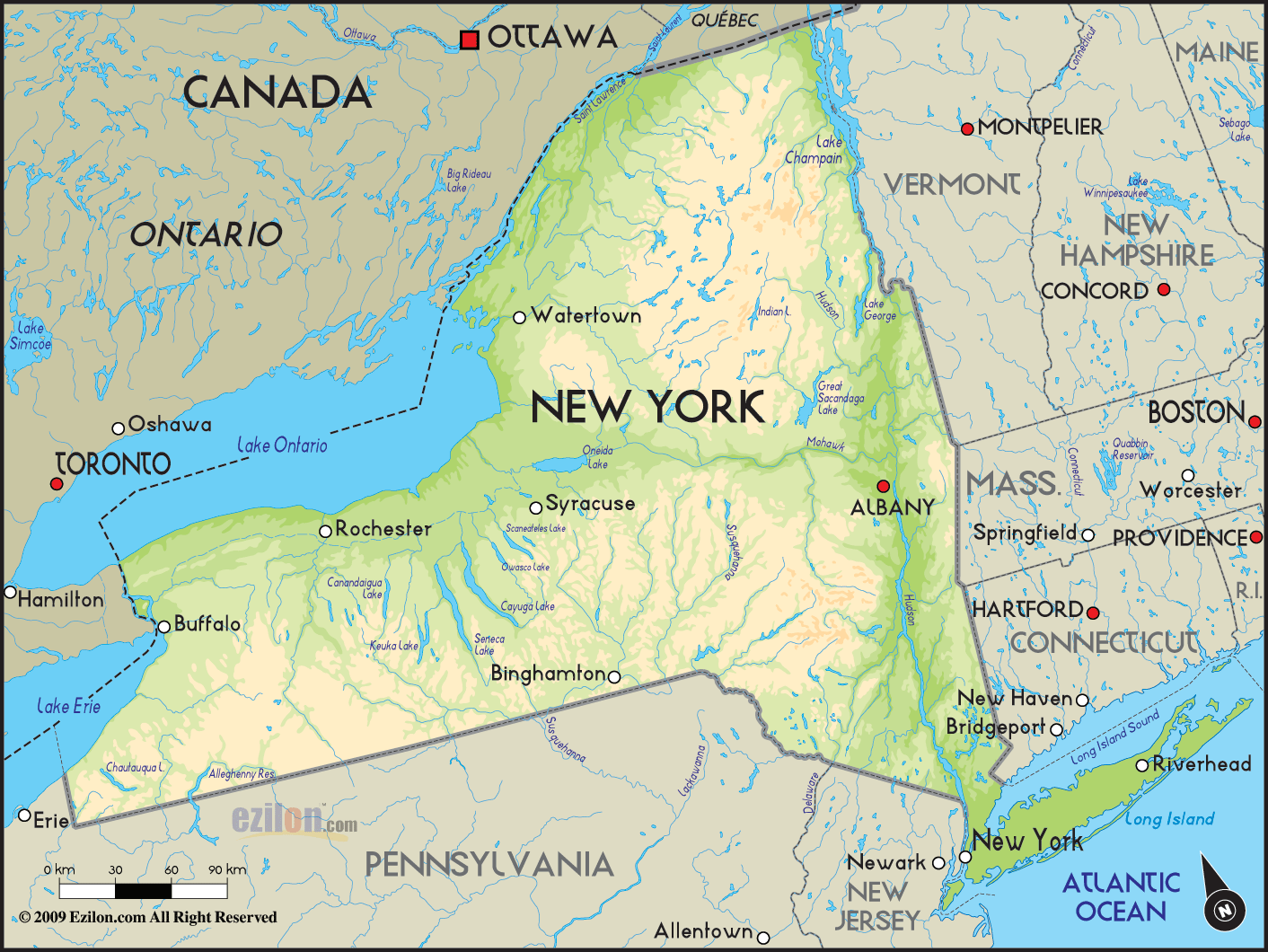
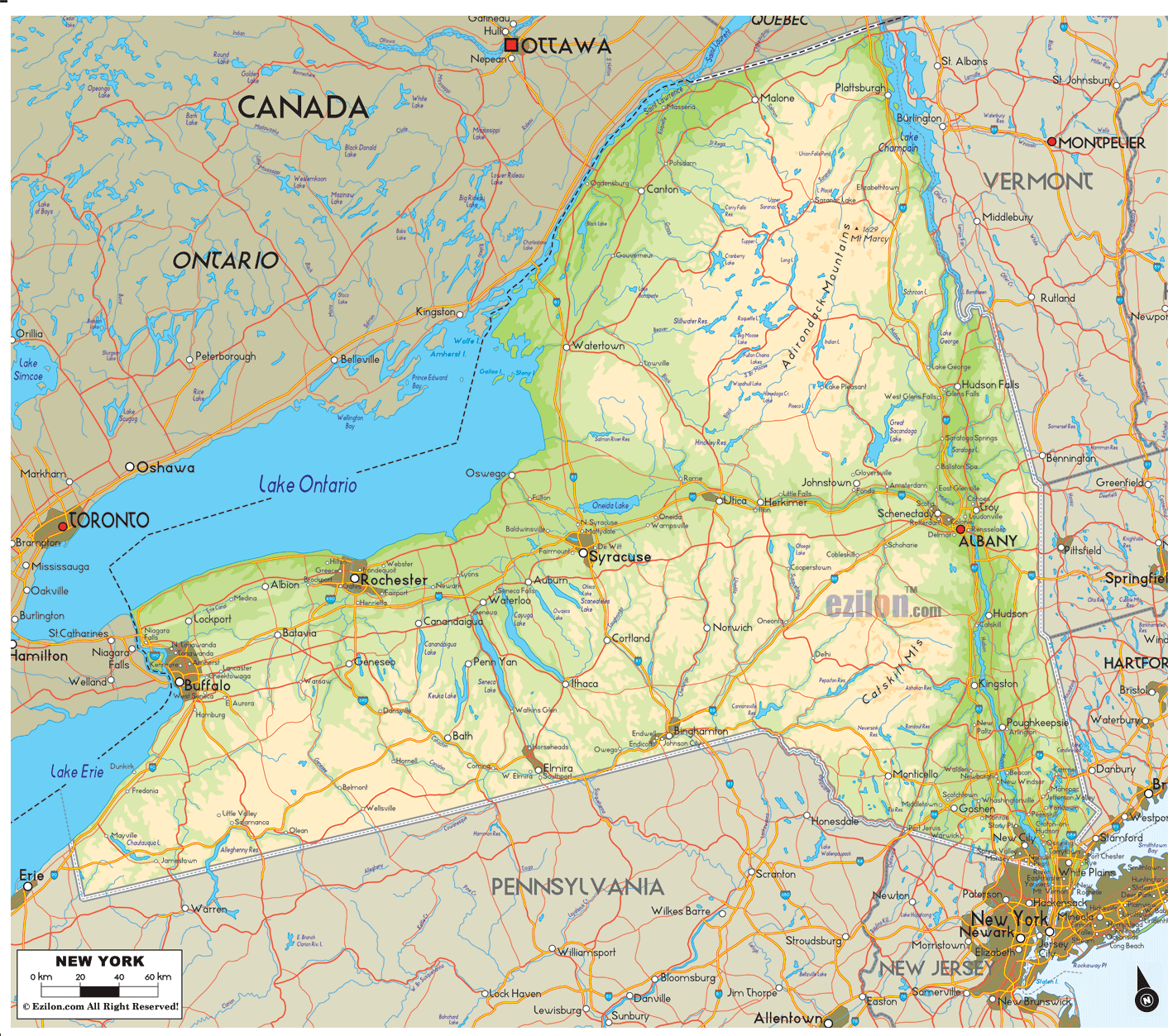
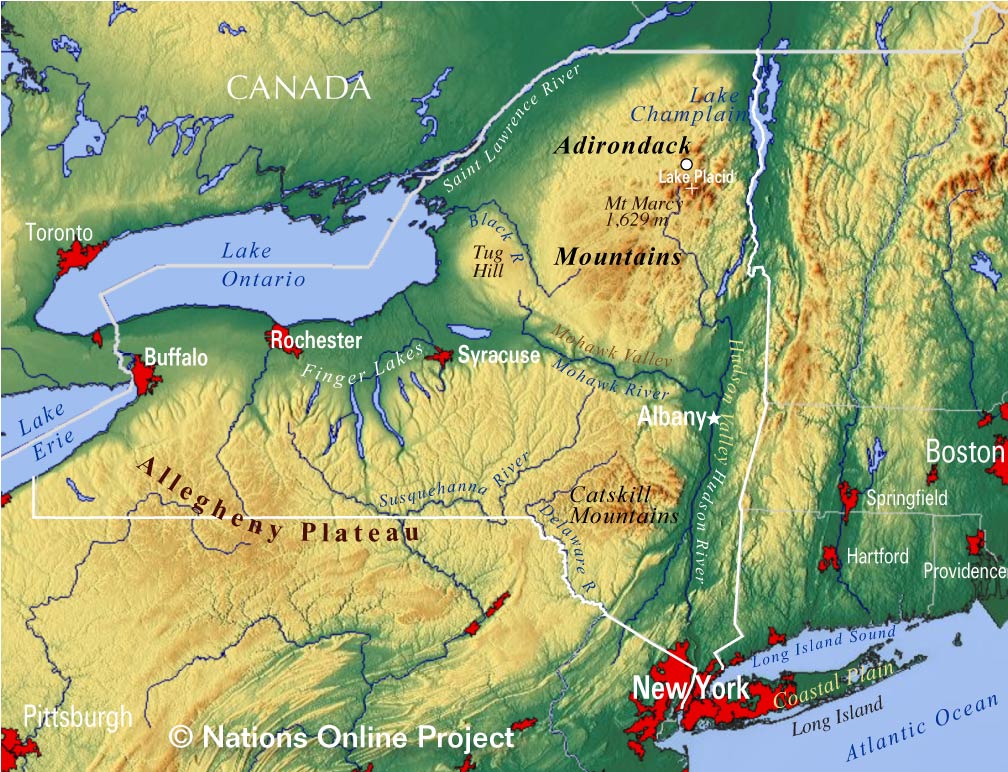
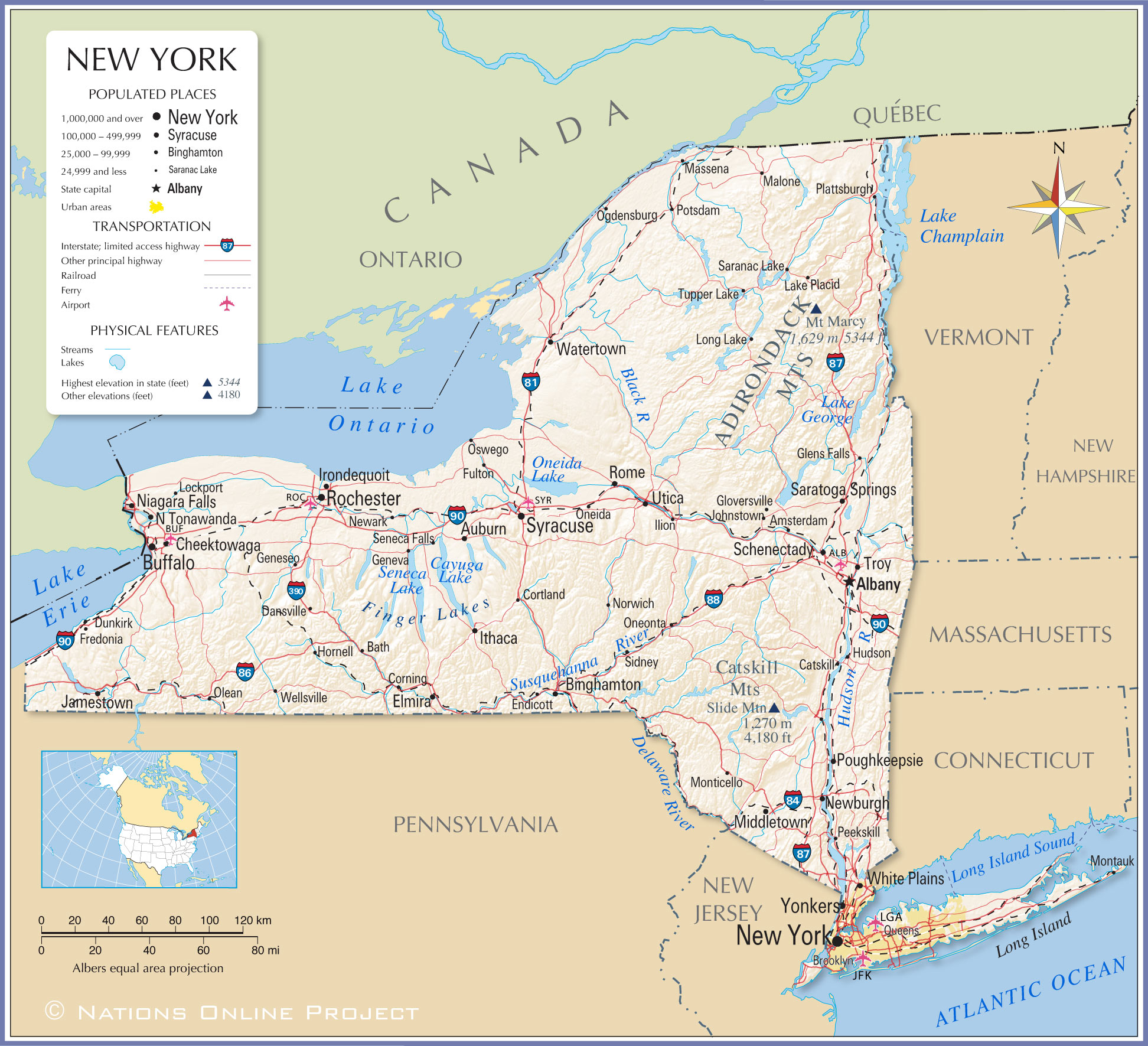
New York State’s geography is a captivating blend of contrasting landscapes, each contributing to its unique character. The state is divided into four physiographic provinces, each possessing distinct geological formations, elevation, and vegetation:
-
The Appalachian Plateau: Occupying the southern tier of the state, this region is characterized by rolling hills, deep valleys, and a rugged terrain sculpted by ancient geological processes. The Appalachian Plateau is renowned for its rich forests, abundant natural resources, and scenic beauty.
-
The Allegheny Plateau: This plateau extends westward from the Appalachian Plateau, encompassing the Finger Lakes region and portions of the Southern Tier. The Allegheny Plateau is known for its fertile soils, abundant water resources, and the distinctive Finger Lakes, a chain of eleven glacial lakes that contribute to the region’s picturesque beauty.
-
The Adirondack Mountains: Located in the northeastern part of the state, the Adirondack Mountains are a vast wilderness area, encompassing the highest peaks in New York State. The region is characterized by rugged mountains, deep forests, and pristine lakes, making it a popular destination for outdoor recreation and nature enthusiasts.
-
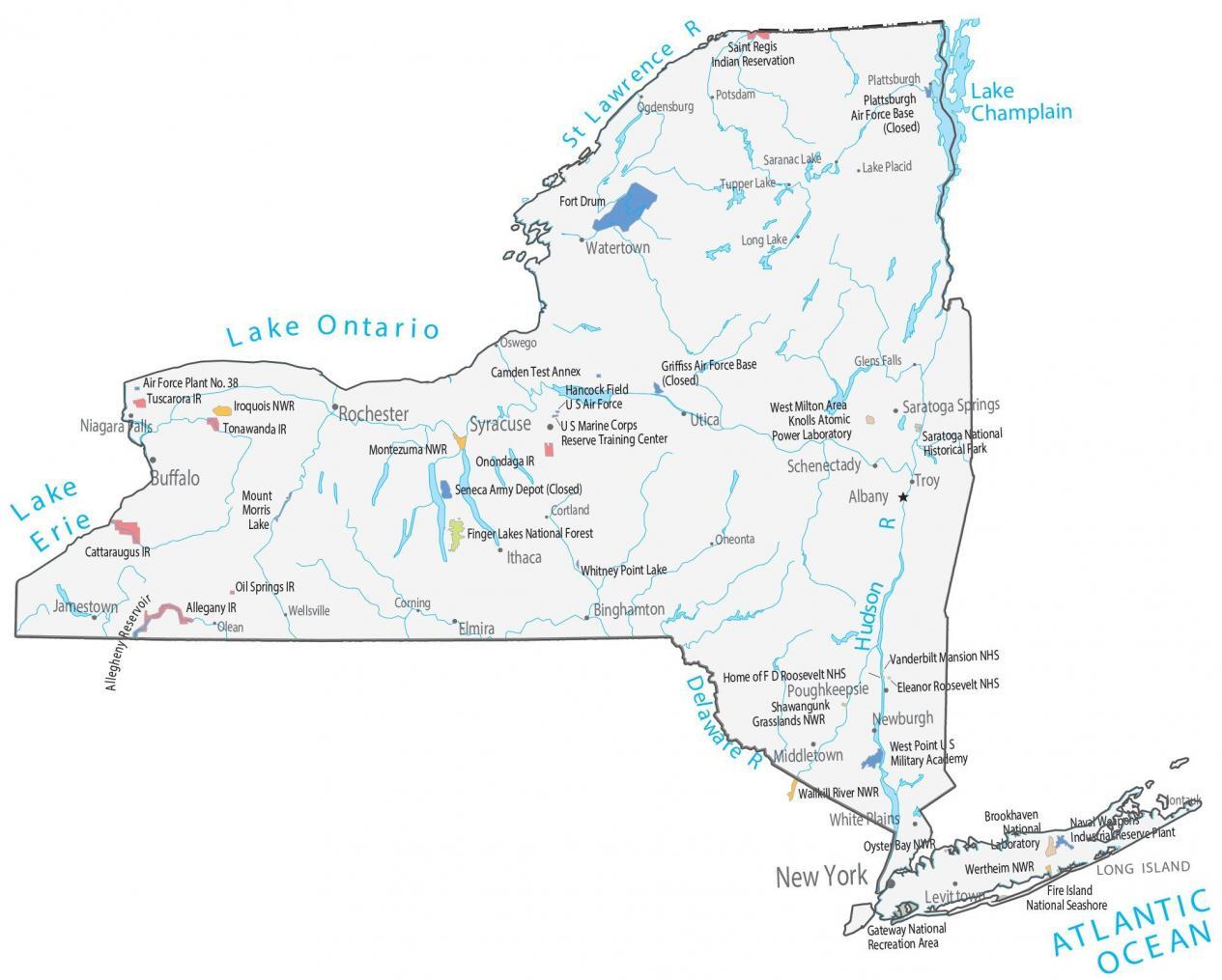
The Erie-Ontario Lowlands: This region encompasses the western and central parts of the state, characterized by flat, fertile plains and gentle slopes. The Erie-Ontario Lowlands are home to the state’s major urban centers, including Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse, and its fertile soils support a thriving agricultural industry.
Regional Variations: A Tapestry of Unique Identities
Within these physiographic provinces, New York State exhibits a fascinating array of regional variations, each with its distinct cultural, economic, and historical nuances:
-
The Hudson Valley: This fertile valley, bordered by the majestic Hudson River, is a historical and cultural landmark. Its rich agricultural lands, charming towns, and historic sites, including the iconic Catskill Mountains, make it a popular destination for tourists and residents alike.
-
The Capital Region: Home to Albany, the state capital, this region boasts a rich history and a vibrant cultural scene. Its proximity to the Adirondack Mountains provides access to outdoor recreation opportunities.
-
Long Island: This long, narrow island, separated from mainland New York by Long Island Sound, is known for its beaches, diverse communities, and vibrant cultural scene. Its diverse landscape includes sandy beaches, rolling hills, and dense forests.
-
New York City: The most populous city in the United States, New York City is a global center of commerce, finance, culture, and entertainment. Its unique geography, encompassing five boroughs, each with its distinct character, contributes to its diverse and dynamic urban landscape.
-
Upstate New York: This broad term encompasses all of New York State outside of New York City, encompassing diverse regions, from the rolling hills of the Southern Tier to the rugged peaks of the Adirondacks. Upstate New York is known for its natural beauty, charming towns, and vibrant cultural scene.
The Impact of Geography: Shaping the State’s Identity
The geographical map of New York State has played a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. Its diverse landscape has attracted settlers, fostered agricultural development, and influenced its economic and social development.
-
Transportation and Trade: The Hudson River, a natural waterway that flows through the state, has historically served as a vital transportation route, facilitating trade and connecting communities. The Erie Canal, a man-made waterway, further enhanced transportation and economic growth.
-
Agriculture and Industry: The fertile soils of the Erie-Ontario Lowlands and the Hudson Valley have fostered a thriving agricultural industry, contributing to the state’s economy. The abundance of natural resources, including timber, minerals, and hydroelectric power, has supported a diverse industrial base.
-
Tourism and Recreation: New York State’s diverse landscape, from the rugged mountains of the Adirondacks to the sandy beaches of Long Island, attracts millions of visitors each year. Its natural beauty, historical sites, and vibrant cultural scene make it a popular destination for tourism and recreation.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Understanding the State
The geographical map of New York State is a powerful tool for understanding its history, culture, and economy. By studying its physical features, regional variations, and the impact of geography on the state’s development, we gain a deeper appreciation for its unique character and the factors that have shaped its identity.
FAQs about the Geographical Map of New York State
Q: What are the major geographical features of New York State?
A: New York State’s major geographical features include the Appalachian Plateau, the Allegheny Plateau, the Adirondack Mountains, and the Erie-Ontario Lowlands.
Q: What are the major regions of New York State?
A: The major regions of New York State include the Hudson Valley, the Capital Region, Long Island, New York City, and Upstate New York.
Q: How has geography influenced the development of New York State?
A: Geography has influenced New York State’s development in numerous ways, including transportation, agriculture, industry, tourism, and recreation.
Q: What are some of the key historical events that have shaped the geography of New York State?
A: Key historical events that have shaped the geography of New York State include the construction of the Erie Canal, the development of the Hudson River as a transportation route, and the growth of major urban centers.
Q: What are some of the challenges and opportunities presented by New York State’s geography?
A: New York State’s geography presents both challenges and opportunities. Challenges include managing natural resources, responding to climate change, and ensuring equitable access to transportation and infrastructure. Opportunities include leveraging its natural beauty for tourism, promoting sustainable development, and fostering innovation in industries related to its unique geographical features.
Tips for Exploring the Geographical Map of New York State
- Use online resources: Websites like Google Maps, ArcGIS, and the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation provide interactive maps and detailed information about the state’s geography.
- Visit different regions: Traveling to different regions of New York State allows you to experience its diverse landscapes firsthand.
- Explore historical sites: Visiting historical sites, such as Fort Ticonderoga, the Erie Canal, and the Hudson River Valley, provides insights into the state’s past and how geography has shaped its history.
- Engage with local communities: Talking to residents and learning about their experiences can provide valuable insights into the unique character of different regions.
- Consider environmental issues: Being aware of the environmental challenges and opportunities presented by New York State’s geography can contribute to its sustainable development.
Conclusion: A Rich Tapestry of Geography and Identity
The geographical map of New York State is more than just a collection of lines and markers; it is a reflection of the state’s rich history, diverse culture, and dynamic economy. By understanding its physical features, regional variations, and the impact of geography on its development, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique character of this vibrant state. As we navigate the challenges and embrace the opportunities presented by its geography, we contribute to the ongoing evolution of New York State’s identity.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Geographical Map of New York State. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
